Devising the technology for thickening and dehydration of activated sludge from municipal treatment plants in sedimentation centrifuges
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.337917Keywords:
activated sludge, activated sludge dewatering, centrifugal units, thickening of excess sludge, environmental safety, fermented sludge, stabilized sludgeAbstract
The object of this study is the process of thickening and dewatering excess activated sludge from municipal wastewater treatment plants in sedimentation centrifuges. The subject of the study is the conditions and factors that affect the efficiency of sludge dewatering, taking into account environmental safety, energy efficiency, and the possibility of reusing resources. The study is aimed at solving the problem of the efficiency and environmental safety of dewatering excess activated sludge.
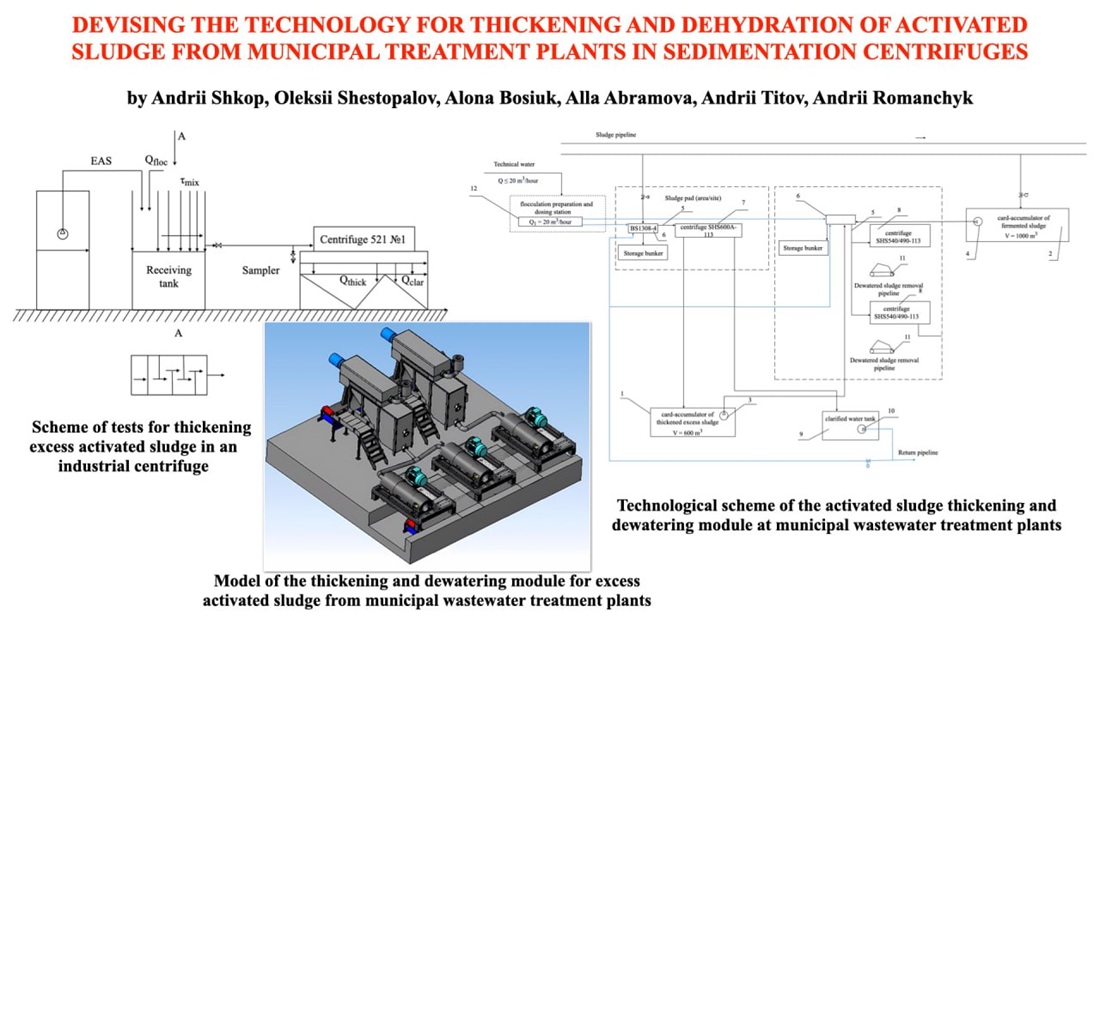
The results of studies on the centrifugation of samples of excess and stabilized activated sludge in a laboratory centrifuge showed that effective separation into sediment and clarified liquid is achieved at a separation factor of 200–600 with the use of a flocculant. In an industrial centrifuge under a flow mode, the best results were obtained at a separation factor of 450 and a flow rate of 9.4 m3/h: the solid phase content in the thickened product was 12.8 g/l, at an input concentration of 4.2 g/l and the residual in the clarified liquid – 0.3 g/l.
The proposed scheme for thickening and dewatering sludge stabilizes the process and improves the quality of the product for further use or disposal. For effective dewatering, mixing the thickened sludge with thickened activated sludge is recommended due to the need for a mineral component. It has been established that thickening of activated sludge is possible using centrifuges in a weak centrifugal field (Fr = 200–600), with a cationic flocculant consumption of 5 kg/t. The second stage – dehydration – is implemented using sedimentation centrifuges.
The results could be used at municipal treatment plants to optimize the processes of thickening and dewatering of excess activated sludge, taking into account energy efficiency and environmental safety. The proposed centrifuge operating modes and the technological scheme enable process stability, reduce sludge volumes, and improve the quality of the final product for further use or disposal
References
- Pradel, M. (2019). Survey data of sewage sludge treatment and disposal routes originated from activated sludge water treatment in France. Data in Brief, 26, 104541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2019.104541
- Zhang, Q., Hu, J., Lee, D.-J., Chang, Y., Lee, Y.-J. (2017). Sludge treatment: Current research trends. Bioresource Technology, 243, 1159–1172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.07.070
- Xiao, T., Wang, H., Wang, X., Wu, H., Yuan, S., Dai, X., Dong, B. (2023). New strategy of drinking water sludge as conditioner to enhance waste activated sludge dewaterability: Collaborative disposal. Water Research, 233, 119761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2023.119761
- Czarnota, J., Masłoń, A., Pajura, R. (2023). Wastewater Treatment Plants as a Source of Malodorous Substances Hazardous to Health, Including a Case Study from Poland. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20 (7), 5379. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20075379
- González, D., Colón, J., Sánchez, A., Gabriel, D. (2019). A systematic study on the VOCs characterization and odour emissions in a full-scale sewage sludge composting plant. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 373, 733–740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.03.131
- Li, K., Zhou, F., Fu, S., Zhang, Y., Dai, C., Yuan, H., Yu, S. (2023). Study on the separation performance of a decanter centrifuge used for dewatering coal water slurry. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 195, 711–720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2023.06.013
- Takdastan, A., Talepour, N., Taherian, M. (2024). A review of the oxic-settling-anaerobic (OSA) process for sustainable sludge minimisation from biological treatment of wastewater. Environmental Technology Reviews, 14 (1), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1080/21622515.2024.2439068
- Takabe, Y., Ida, K. (2023). Simultaneous phosphorus precipitation and sludge thickening by electrolysis with an anode covered by bivalve shells. Water Research, 247, 120789. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2023.120789
- Shestopalov, O., Briankin, O., Rykusova, N., Hetta, O., Raiko, V., Tseitlin, M. (2020). Optimization of floccular cleaning and drainage of thin dispersed sludges. EUREKA: Physics and Engineering, 3, 75–86. https://doi.org/10.21303/2461-4262.2020.001239
- Shkop, A., Shestopalov, O., Sakun, A., Tseitlin, M., Ponomarova, N. et al. (2025). Research of efficiency of cleaning and dehydration of coal slims in centrifuges. International Journal of Mechatronics and Applied Mechanics, 19 (1), 112–121. https://doi.org/10.17683/ijomam/issue19.13
- Wu, B., Dai, X., Chai, X. (2020). Critical review on dewatering of sewage sludge: Influential mechanism, conditioning technologies and implications to sludge re-utilizations. Water Research, 180, 115912. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.115912
- Mariñelarena, A. J., Di Giorgi, H., Donadelli, J. (2021). Dewatering, Stabilization, and Final Disposal of Waste Activated Sludge in Constructed Wetlands. Ingenieria y Universidad, 25. https://doi.org/10.11144/javeriana.iued25.dsfd
- Nega, R. (2018). Microbial Environmental Risks Associated Sewage Sludge Disposal. Open Access Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 3 (2). https://doi.org/10.23880/oajmb-16000131
- Shkop, A., Trembitskyi, D., Shestopalov, O., Bosiuk, A., Loboiko, V., Sakun, A. (2025). Study of the process of mechanical dewatering of liquid waste from municipal wastewater treatment plants in sedimentation centrifuges. International Journal of Mechatronics and Applied Mechanics, 1 (20). https://doi.org/10.17683/ijomam/issue20.38
- Karahiaur, A., Airapetian, T., Novokhatniy, V., Matyash, O. (2020). The Influence of Oxygen Regime on Aerotank-Displacer with Fixed Biocenosis Operation. Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Building Innovations, 591–599. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-42939-3_58
- Chub, I., Airapetian, T., Karahiaur, A., Zabara, I. (2023). The use of biological activation of microorganisms of activated sludge to increase the efficiency of wastewater treatment. World Multidisciplinary Civil Engineering-Architecture-Urban Planning Symposium WMCAUS 2022, 2928, 060033. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0123327
- Tang, Q., Xing, J., Sun, Z., Gan, M., Fan, X., Ji, Z. et al. (2022). Enhancing the Dewaterability of Oily Cold Rolling Mill Sludge Using Quicklime as a Conditioning Agent. ACS Omega, 7 (48), 44278–44286. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.2c05771
- Wang, S., Ma, C., Zhu, Y., Yang, Y., Du, G., Li, J. (2018). Deep dewatering process of sludge by chemical conditioning and its potential influence on wastewater treatment plants. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26 (33), 33838–33846. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2351-1
- Hamraoui, L., Bergani, A., Ettoumi, M., Aboulaich, A., Taha, Y., Khalil, A. et al. (2024). Towards a Circular Economy in the Mining Industry: Possible Solutions for Water Recovery through Advanced Mineral Tailings Dewatering. Minerals, 14 (3), 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14030319
- MVV No. 081/12-0785-11. Grunty ta vidkhody. Metodyka vykonannia vymiriuvan volohosti metodom vysushuvannia do postiynoi masy. Available at: https://online.budstandart.com/ua/catalog/doc-page.html?id_doc=76615
- Shkop, A. O., Ponomarova, N. G., Bosiuk, A. S., Shestopalov, O. V. (2025). Study of the process of purifying potassium humate suspension from suspended particles using industrial centrifuges. EAI Endorsed Transactions on Digital Transformation of Industrial Processes, 1 (2). Available at: https://publications.eai.eu/index.php/dtip/article/view/9678/3655
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Andrii Shkop, Oleksіi Shestopalov, Alona Bosiuk, Alla Abramova, Andrii Titov, Andriі Romanchyk

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








