Розробка технології згущення і зневоднення активного мулу міських очисних споруд в осаджувальних центрифугаг
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.337917Ключові слова:
активний мул, зневоднення активного мулу, центрифугальні установки, згущення надлишкового мулу, екологічна безпека, зброджений осад, стабілізований мулАнотація
Об’єктом дослідження є процес згущення та зневоднення надлишкового активного мулу міських очисних споруд в осаджувальних центрифугах.. Предмет дослідження – умови та фактори, що впливають на ефективність зневоднення мулу, з урахуванням екологічної безпеки, енергоефективності та можливостей повторного використання ресурсів. Дослідження спрямоване на вирішення проблеми ефективності та екологічної безпеки зневоднення надлишкового активного мулу.
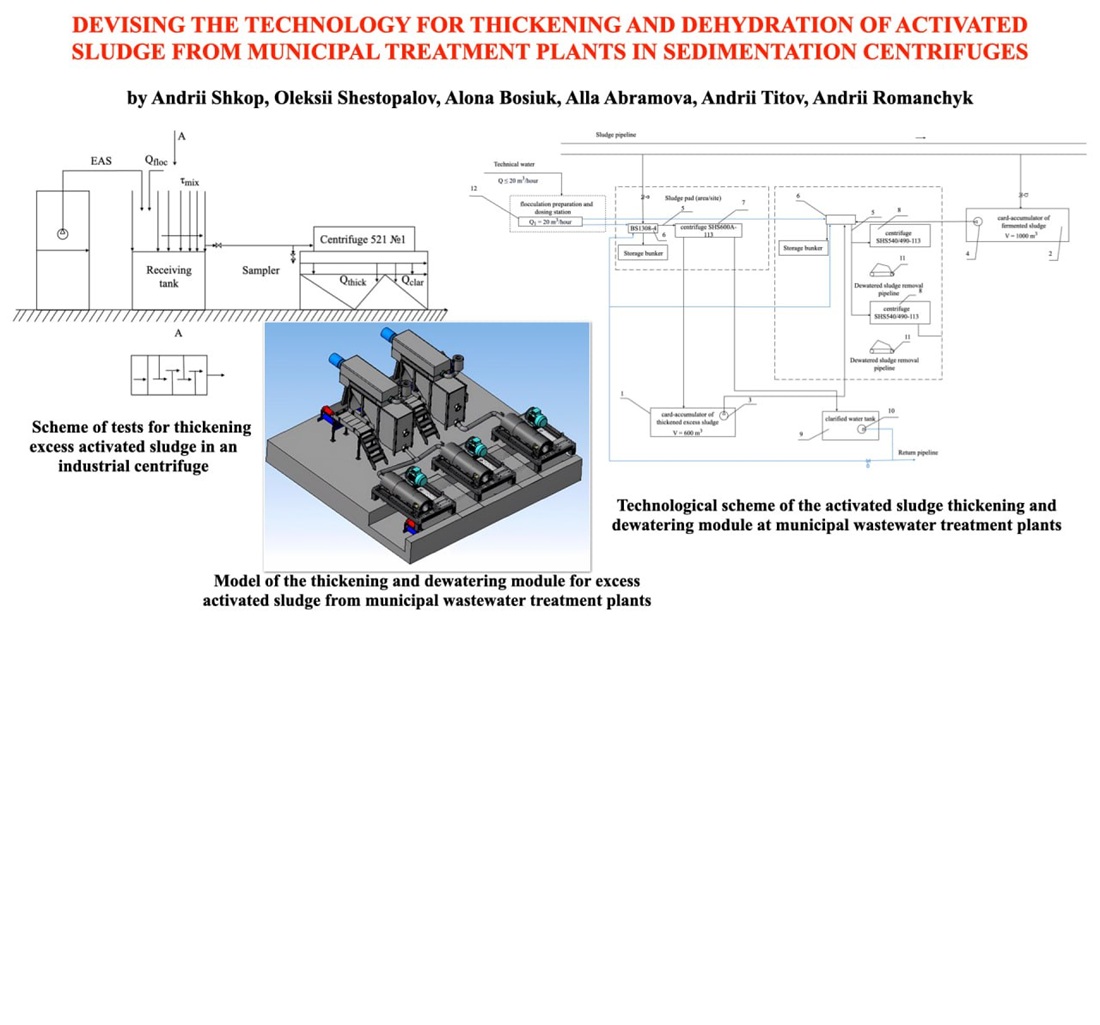
Результати досліджень центрифугування зразків надлишкового та стабілізованого активного мулу у лабораторній центрифузі показали, що ефективне розділення на осад і освітлену рідину досягається при факторі розділення 200–600 із застосуванням флокулянту. У промисловій центрифузі в проточному режимі найкращі результати отримано при факторі розділення 450 та витраті 9,4 м³/год: вміст твердої фази в згущеному продукті становив 12,8 г/л, при вхідній концентрації 4,2 г/л та залишковій у освітленій рідині – 0,3 г/л.
Запропонована схема згущення та зневоднення мулів стабілізує процес і покращує якість продукту для подальшого використання або утилізації. Для ефективного зневоднення рекомендовано змішування збрижених осадів із згущеним активним мулом через необхідність мінеральної складової. Встановлено, що згущення активного мулу можливо з використанням центрифуг в слабкому відцентрованому полі (Fr = 200–600), із витратою катіонного флокулянту 5 кг/т. Друга стадія – зневоднення – реалізується за допомогою осаджувальних центрифуг.
Отримані результати можуть бути використані на міських очисних спорудах для оптимізації процесів згущення та зневоднення надлишкового активного мулу з урахуванням енергоефективності та екологічної безпеки. Запропоновані режими роботи центрифуг і технологічна схема забезпечують стабільність процесу, зменшення обсягів осаду та підвищення якості кінцевого продукту для подальшого використання або утилізації
Посилання
- Pradel, M. (2019). Survey data of sewage sludge treatment and disposal routes originated from activated sludge water treatment in France. Data in Brief, 26, 104541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2019.104541
- Zhang, Q., Hu, J., Lee, D.-J., Chang, Y., Lee, Y.-J. (2017). Sludge treatment: Current research trends. Bioresource Technology, 243, 1159–1172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.07.070
- Xiao, T., Wang, H., Wang, X., Wu, H., Yuan, S., Dai, X., Dong, B. (2023). New strategy of drinking water sludge as conditioner to enhance waste activated sludge dewaterability: Collaborative disposal. Water Research, 233, 119761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2023.119761
- Czarnota, J., Masłoń, A., Pajura, R. (2023). Wastewater Treatment Plants as a Source of Malodorous Substances Hazardous to Health, Including a Case Study from Poland. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20 (7), 5379. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20075379
- González, D., Colón, J., Sánchez, A., Gabriel, D. (2019). A systematic study on the VOCs characterization and odour emissions in a full-scale sewage sludge composting plant. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 373, 733–740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.03.131
- Li, K., Zhou, F., Fu, S., Zhang, Y., Dai, C., Yuan, H., Yu, S. (2023). Study on the separation performance of a decanter centrifuge used for dewatering coal water slurry. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 195, 711–720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2023.06.013
- Takdastan, A., Talepour, N., Taherian, M. (2024). A review of the oxic-settling-anaerobic (OSA) process for sustainable sludge minimisation from biological treatment of wastewater. Environmental Technology Reviews, 14 (1), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1080/21622515.2024.2439068
- Takabe, Y., Ida, K. (2023). Simultaneous phosphorus precipitation and sludge thickening by electrolysis with an anode covered by bivalve shells. Water Research, 247, 120789. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2023.120789
- Shestopalov, O., Briankin, O., Rykusova, N., Hetta, O., Raiko, V., Tseitlin, M. (2020). Optimization of floccular cleaning and drainage of thin dispersed sludges. EUREKA: Physics and Engineering, 3, 75–86. https://doi.org/10.21303/2461-4262.2020.001239
- Shkop, A., Shestopalov, O., Sakun, A., Tseitlin, M., Ponomarova, N. et al. (2025). Research of efficiency of cleaning and dehydration of coal slims in centrifuges. International Journal of Mechatronics and Applied Mechanics, 19 (1), 112–121. https://doi.org/10.17683/ijomam/issue19.13
- Wu, B., Dai, X., Chai, X. (2020). Critical review on dewatering of sewage sludge: Influential mechanism, conditioning technologies and implications to sludge re-utilizations. Water Research, 180, 115912. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.115912
- Mariñelarena, A. J., Di Giorgi, H., Donadelli, J. (2021). Dewatering, Stabilization, and Final Disposal of Waste Activated Sludge in Constructed Wetlands. Ingenieria y Universidad, 25. https://doi.org/10.11144/javeriana.iued25.dsfd
- Nega, R. (2018). Microbial Environmental Risks Associated Sewage Sludge Disposal. Open Access Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 3 (2). https://doi.org/10.23880/oajmb-16000131
- Shkop, A., Trembitskyi, D., Shestopalov, O., Bosiuk, A., Loboiko, V., Sakun, A. (2025). Study of the process of mechanical dewatering of liquid waste from municipal wastewater treatment plants in sedimentation centrifuges. International Journal of Mechatronics and Applied Mechanics, 1 (20). https://doi.org/10.17683/ijomam/issue20.38
- Karahiaur, A., Airapetian, T., Novokhatniy, V., Matyash, O. (2020). The Influence of Oxygen Regime on Aerotank-Displacer with Fixed Biocenosis Operation. Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Building Innovations, 591–599. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-42939-3_58
- Chub, I., Airapetian, T., Karahiaur, A., Zabara, I. (2023). The use of biological activation of microorganisms of activated sludge to increase the efficiency of wastewater treatment. World Multidisciplinary Civil Engineering-Architecture-Urban Planning Symposium WMCAUS 2022, 2928, 060033. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0123327
- Tang, Q., Xing, J., Sun, Z., Gan, M., Fan, X., Ji, Z. et al. (2022). Enhancing the Dewaterability of Oily Cold Rolling Mill Sludge Using Quicklime as a Conditioning Agent. ACS Omega, 7 (48), 44278–44286. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.2c05771
- Wang, S., Ma, C., Zhu, Y., Yang, Y., Du, G., Li, J. (2018). Deep dewatering process of sludge by chemical conditioning and its potential influence on wastewater treatment plants. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26 (33), 33838–33846. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2351-1
- Hamraoui, L., Bergani, A., Ettoumi, M., Aboulaich, A., Taha, Y., Khalil, A. et al. (2024). Towards a Circular Economy in the Mining Industry: Possible Solutions for Water Recovery through Advanced Mineral Tailings Dewatering. Minerals, 14 (3), 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14030319
- MVV No. 081/12-0785-11. Grunty ta vidkhody. Metodyka vykonannia vymiriuvan volohosti metodom vysushuvannia do postiynoi masy. Available at: https://online.budstandart.com/ua/catalog/doc-page.html?id_doc=76615
- Shkop, A. O., Ponomarova, N. G., Bosiuk, A. S., Shestopalov, O. V. (2025). Study of the process of purifying potassium humate suspension from suspended particles using industrial centrifuges. EAI Endorsed Transactions on Digital Transformation of Industrial Processes, 1 (2). Available at: https://publications.eai.eu/index.php/dtip/article/view/9678/3655
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2025 Andrii Shkop, Oleksіi Shestopalov, Alona Bosiuk, Alla Abramova, Andrii Titov, Andriі Romanchyk

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.
Ліцензійний договір – це документ, в якому автор гарантує, що володіє усіма авторськими правами на твір (рукопис, статтю, тощо).
Автори, підписуючи Ліцензійний договір з ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР», мають усі права на подальше використання свого твору за умови посилання на наше видання, в якому твір опублікований. Відповідно до умов Ліцензійного договору, Видавець ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР» не забирає ваші авторські права та отримує від авторів дозвіл на використання та розповсюдження публікації через світові наукові ресурси (власні електронні ресурси, наукометричні бази даних, репозитарії, бібліотеки тощо).
За відсутності підписаного Ліцензійного договору або за відсутністю вказаних в цьому договорі ідентифікаторів, що дають змогу ідентифікувати особу автора, редакція не має права працювати з рукописом.
Важливо пам’ятати, що існує і інший тип угоди між авторами та видавцями – коли авторські права передаються від авторів до видавця. В такому разі автори втрачають права власності на свій твір та не можуть його використовувати в будь-який спосіб.









