Development of polyadsorbents based on polyethylenimine and low molecular weight ligands for the extraction of group II metal ions from wastewater
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.337919Keywords:
metal, ion, complexation, polyethyleneimine, ligand, wastewater, titration, thermodynamics, adsorptionAbstract
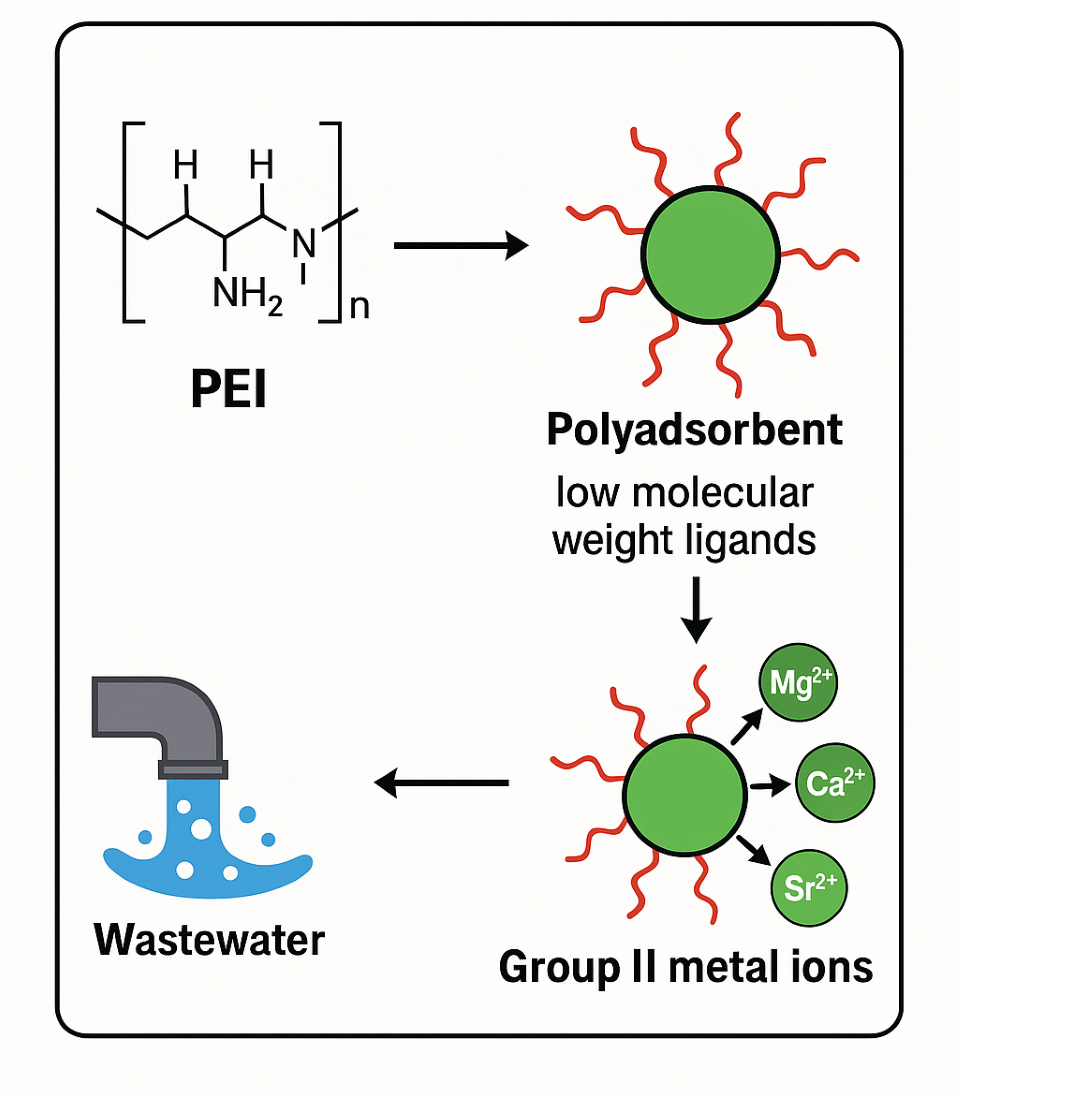
The object of this study is the physicochemical processes of interaction between Group II metal ions and polyethyleneimine (PEI) and low-molecular-weight ligands (salicylic acid, sulfosalicylic acid, EDTA) with the aim of developing polyadsorbents for the selective extraction of toxic ions from aqueous media. The problem to be solved is the development of effective and selective polyadsorbents for removing toxic metal ions from wastewater.
Potentiometric, conductometric, and viscometric analysis methods have established that in binary PEI-M2+ systems, coordination complexes are formed with a molar ratio of PEI:M2+ = 2:1. For systems with Sr2+ and Ba2+ ions, stepwise complexation was identified, with particles of composition 6:1 and 4:1 being formed at the initial stage, respectively. The stability of the complexes formed was established in the following order: Be2+ > Ca2+ > Sr2+ > Ba2+ > Mg2+.
Thermodynamic parameters showed that the complexation processes are spontaneous and exothermic, with the decrease in entropy being associated with an increase in order within the system. Stability constants (lgβ0) range from 5.4 (Mg2+) to 10.16 (Be2+).
Quantum chemical calculations have shown that the reaction centers in the ligand molecules are: the oxygen atoms of the carbonyl group (H2Sal), the sulfonate group (H3Ssal), and the carboxyl group (H2edta2⁻). It has been established that donor-acceptor interactions predominate in PEI-M2+-H2Sal/H3Ssal ternary systems, while electrostatic interactions dominate in PEI-Zn2+/Cd2+-H2Sal and PEI-Be2+-H2edta2⁻ systems.
In sorption tests in model solutions, the ternary complexes PEI-Be2+-H3Ssal and PEI-Hg2+-H3Ssal demonstrated the highest efficiency: the degree of removal of Be2+ reached 97.1%, Hg2+ – 93.4%, while for Mg2+ and Ba2+ it was less than 70%. Modified PEI with H3sal proved to be the most effective adsorbent among those studied. In industrial trials, the developed adsorbents reduced the concentrations of Be2+ and Hg2+ in wastewater to 0.004 and 0.002 mg/l, respectively, which meets the maximum permissible concentrations for discharge into water bodies
References
- Ayalew, Z. M., Guo, X., Zhang, X. (2022). Synthesis and application of polyethyleneimine (PEI)‐based composite/nanocomposite material for heavy metals removal from wastewater: A critical review. Journal of Hazardous Materials Advances, 8, 100158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hazadv.2022.100158
- Bertagnolli, C., Grishin, A., Vincent, T., Guibal, E. (2016). Recovering Heavy Metal Ions from Complex Solutions Using Polyethylenimine Derivatives Encapsulated in Alginate Matrix. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 55 (8), 2461–2470. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.5b04683
- Semenova, A., Vidallon, M. L. P., Follink, B., Brown, P. L., Tabor, R. F. (2021). Synthesis and Characterization of Polyethylenimine–Silica Nanocomposite Microparticles. Langmuir, 38 (1), 191–202. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.1c02393
- Yoo, S.-H., Lee, S.-C., Ko, M., Yoon, S., Lee, J., Park, J.-A., Kim, S.-B. (2023). Adsorption of Hg(II) on polyethyleneimine-functionalized carboxymethylcellulose beads: Characterization, toxicity tests, and adsorption experiments. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 241, 124516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.124516
- Larsson, M., Nosrati, A., Kaur, S., Wagner, J., Baus, U., Nydén, M. (2018). Copper removal from acid mine drainage-polluted water using glutaraldehyde-polyethyleneimine modified diatomaceous earth particles. Heliyon, 4 (2), e00520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e00520
- Tran, A. T.-K., Hoang, N. T.-T., Nguyen, P. T. (2023). Optimizing sulfonation process of polystyrene waste for hardness and heavy metal removal. Case Studies in Chemical and Environmental Engineering, 8, 100396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscee.2023.100396
- Houari, B., Louhibi, S., Tizaoui, K., Boukli-hacene, L., Benguella, B., Roisnel, T., Dorcet, V. (2019). New synthetic material removing heavy metals from aqueous solutions and wastewater. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 12 (8), 5040–5048. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2016.11.010
- Zhang, D., Wu, B., Wang, T., Yılmaz, M., Sharma, G., Kumar, A., Shi, H. (2025). Multi-mechanism synergistic adsorption of lead and cadmium in water by structure-functionally adapted modified biochar: A review. Desalination and Water Treatment, 322, 101156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dwt.2025.101156
- Verma, M., Ahmad, W., Park, J.-H., Kumar, V., Vlaskin, M. S., Vaya, D., Kim, H. (2022). One-step functionalization of chitosan using EDTA: Kinetics and isotherms modeling for multiple heavy metals adsorption and their mechanism. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 49, 102989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.102989
- Ma, J., Zhou, G., Chu, L., Liu, Y., Liu, C., Luo, S., Wei, Y. (2016). Efficient Removal of Heavy Metal Ions with An EDTA Functionalized Chitosan/Polyacrylamide Double Network Hydrogel. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 5 (1), 843–851. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b02181
- Qasem, N. A. A., Mohammed, R. H., Lawal, D. U. (2021). Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater: a comprehensive and critical review. Npj Clean Water, 4 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-021-00127-0
- Sharma, K., Choudhary, P., Majeed, A., Guleria, S., Kumar, M., Rana, A. K., Rajauria, G. (2025). Cellulose based membranes, hydrogels and aerogels for water treatment application. Industrial Crops and Products, 225, 120474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2025.120474
- López-Maldonado, E. A., Abdellaoui, Y., Abu Elella, M. H., Abdallah, H. M., Pandey, M., Anthony, E. T. et al. (2024). Innovative biopolyelectrolytes-based technologies for wastewater treatment. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 273, 132895. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.132895
- Sheraz, N., Shah, A., Haleem, A., Iftikhar, F. J. (2024). Comprehensive assessment of carbon-, biomaterial- and inorganic-based adsorbents for the removal of the most hazardous heavy metal ions from wastewater. RSC Advances, 14 (16), 11284–11310. https://doi.org/10.1039/d4ra00976b
- Danouche, M., El Ghachtouli, N., El Arroussi, H. (2021). Phycoremediation mechanisms of heavy metals using living green microalgae: physicochemical and molecular approaches for enhancing selectivity and removal capacity. Heliyon, 7 (7), e07609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07609
- Shi, H., He, Y., Pan, Y., Di, H., Zeng, G., Zhang, L., Zhang, C. (2016). A modified mussel-inspired method to fabricate TiO2 decorated superhydrophilic PVDF membrane for oil/water separation. Journal of Membrane Science, 506, 60–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2016.01.053
- Zhu, Y., Xie, W., Li, J., Xing, T., Jin, J. (2015). pH-Induced non-fouling membrane for effective separation of oil-in-water emulsion. Journal of Membrane Science, 477, 131–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2014.12.026
- Yuan, X., Li, W., Liu, H., Han, N., Zhang, X. (2016). A novel PVDF/graphene composite membrane based on electrospun nanofibrous film for oil/water emulsion separation. Composites Communications, 2, 5–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coco.2016.10.001
- Venault, A., Chiang, C.-H., Chang, H.-Y., Hung, W.-S., Chang, Y. (2018). Graphene oxide/PVDF VIPS membranes for switchable, versatile and gravity-driven separation of oil and water. Journal of Membrane Science, 565, 131–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2018.08.018
- Alaba, P. A., Oladoja, N. A., Sani, Y. M., Ayodele, O. B., Mohammed, I. Y., Olupinla, S. F., Daud, W. M. W. (2018). Insight into wastewater decontamination using polymeric adsorbents. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 6 (2), 1651–1672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.02.019
- Liu, C., Zhang, H.-X. (2022). Modified-biochar adsorbents (MBAs) for heavy-metal ions adsorption: A critical review. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 10 (2), 107393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.107393
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Nazgul Ashimkhan, Manshuk Murzagaliyeva, Gulnur Daribayeva, Ardak Sapiyeva

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








