Impact of prebiotic additives composition on technological and sensory properties of dressings in horeca sector
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.339809Keywords:
sauces-dressings, prebiotic additives, inulin, oligofructose, rheological characteristics, sensory profileAbstract
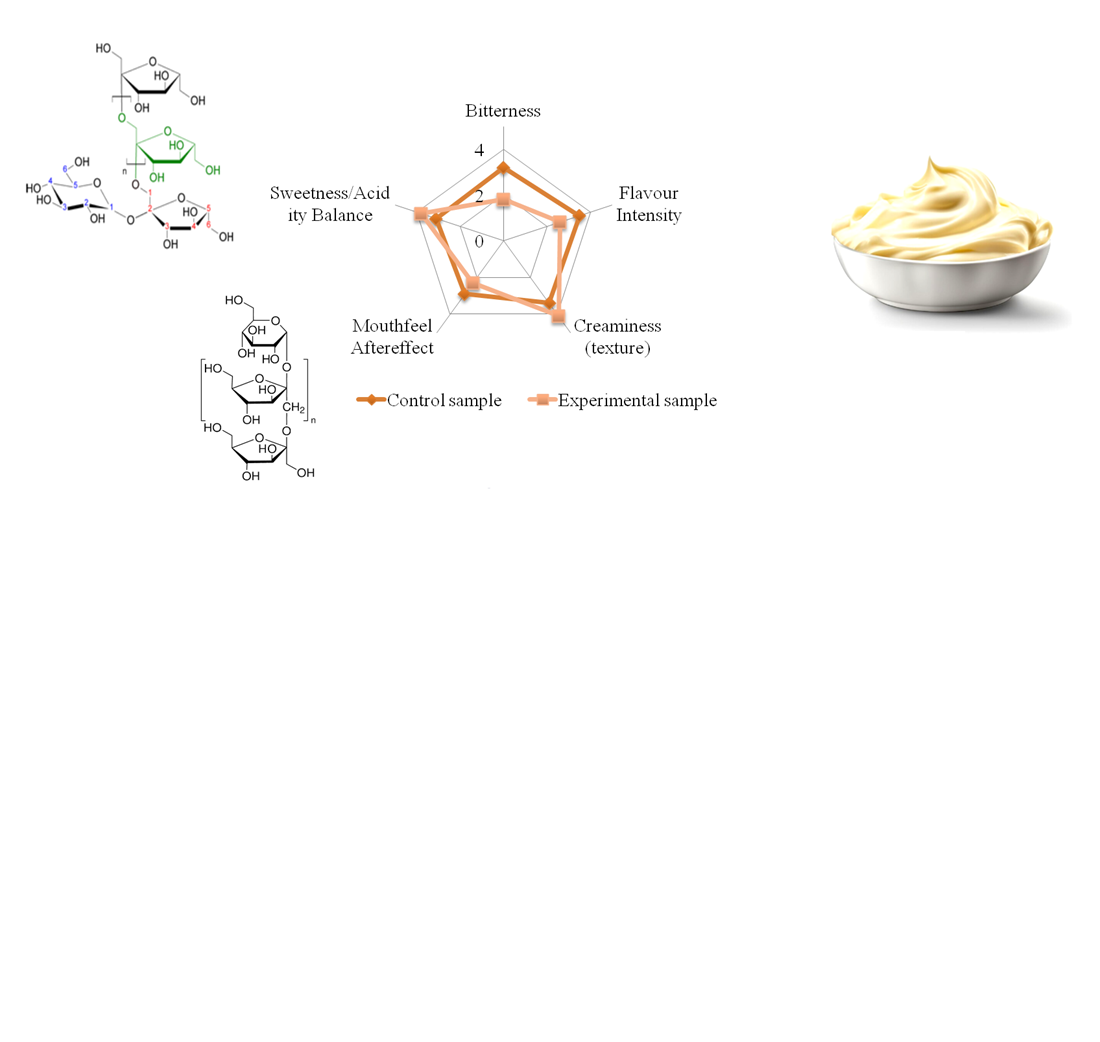
The object of the study is the process of forming the quality characteristics of emulsion sauces-dressings for the HoReCa system, enriched with prebiotic additives. The problem of rationalizing the stability and improving the organoleptic profile of model emulsion systems for sauces-dressings containing valuable hemp oil, prone to oxidation due to the content of ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, is considered. The concentration of prebiotic additives in the model emulsion system of the sauce-dressing is justified (inulin – 3.5%, oligofructose – 4.0%). It was established that the combined use of these additives not only stabilizes the consistency of the product, but also significantly reduces bitterness (by 44%) and increases the creaminess of the texture (by 21%) compared to the control sample. This phenomenon is due to the complex effect of prebiotic additives, which exhibit both stabilizing and antioxidant activity. The mechanism of action consists in modulating the rheological properties of the system by changing the interfacial tension and forming additional water-binding complexes. In parallel, selective binding of free radicals is observed at the interface of the oil and water phases, which inhibits the processes of lipid oxidation. Such structural changes lead to increased stability of the emulsion and improvement of its textural characteristics. A feature of the obtained results is an integrated approach that combines improved sensory qualities with increased stability of the finished product. Economic calculations confirm that the increase in the cost of the sauce-dressing of the proposed composition by 21% is compensated by the possibility of premium pricing and reduced logistics costs for sales. Practical application of the results allows developing health dressings with improved consumer qualities, adapted to the requirements of the modern catering market
References
- Lakshmayya, N. S. V., Mishra, A. K., Mohanta, Y. K., Panda, J., Naik, B., Mishra, B., Varma, R. S. (2023). Essential oils-based nano-emulsion system for food safety and preservation: Current status and future prospects. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 53, 102897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2023.102897
- Ali, S., Hamayun, M., Siraj, M., Khan, S. A., Kim, H.-Y., Lee, B. (2025). Recent advances in prebiotics: Classification, mechanisms, and health applications. Future Foods, 12, 100680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fufo.2025.100680
- Kunitsa, K., Dikhtyar, A., Kotliar, O., Andrieieva, S., Gontar, T., Stankevych, S. et al. (2025). Development of a stabilization system composition for sauces and dressings. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2 (11 (134)), 26–32. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.325772
- Gautam, A. R., Junarto, A. W., Benjakul, S., Mittal, A., Baloch, K. A., Singh, A. (2024). Omega-3 and unsaturated fatty acid enrichment of shrimp oil: Preparation, characterization, and its application in salad dressings. LWT, 212, 116993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2024.116993
- Ge, R., Pu, Y., Long, Y., Xu, D., Zhu, H., Tao, N., Wang, H. (2024). Mechanisms of Pickering emulsion formation and stabilization by composite arabinoxylan–whey protein isolate particles. LWT, 209, 116774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2024.116774
- Ferreira da Silva, E., Rafaela da Silva Monteiro Wanderley, B., Duarte de Lima, N., Bettim Bianchini, C., Beddin Fritzen-Freire, C., Dias de Mello Castanho Amboni, R. et al. (2025). Vegan salad dressing based on cashew nuts with or without Spirulina platensis: Physicochemical, rheological, and sensory characterization and in vitro digestion of phenolic compounds. International Journal of Gastronomy and Food Science, 41, 101199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgfs.2025.101199
- Joshi, T., Kapoor, S., Rana, S., Bala, M., Singh, A., Mahajan, B. V. C. (2024). Valorization of guava seed oil as a functional ingredient in salad dressing: implications on quality characteristics, rheological behaviour, morphology, oxidative stability and shelf life. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization, 18 (8), 6698–6710. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-024-02683-8
- Mohamad, R., Putri Agus, B. A., Hussain, N. (2019). Changes of Phytosterols, Rheology, Antioxidant Activity and Emulsion Stability of Salad Dressing with Cocoa Butter During Storage. Food Technology and Biotechnology, 57 (1), 59–67. https://doi.org/10.17113/ftb.57.01.19.5692
- Dehghan Manshadi, A., Peighambardoust, S. H., Azadmard-Damirchi, S., Niakosari, M. (2018). Oxidative and physical stability, rheological properties and sensory characteristics of ‘salad dressing’ samples formulated with flaxseed oil and n-OSA starch. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization, 13 (1), 26–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-018-9915-0
- Kunitsia, E., Popov, M., Gontar, T., Stankevych, S., Zabrodina, I., Stepankova, G. et al. (2024). Determination of the influence of hemp oil-based emulsion systems composition on the oxidation products content during storage. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 3 (6 (129)), 6–13. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.304466
- Naknaen, P., Chinnapitiwong, N., Kruayoo, P. (2018). Enhancing the quality attributes of salad dressing by incorporating Gac aril as a biologically active ingredient. Brazilian Journal of Food Technology, 21. https://doi.org/10.1590/1981-6723.12917
- Nasiri, F., Mohtarami, F., Esmaiili, M., Pirsa, S. (2023). Production of gluten-free biscuits with inulin and flaxseed powder: investigation of physicochemical properties and formulation optimization. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, 14 (17), 21443–21459. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-023-04297-4
- Kalyna, V., Stankevych, S., Zabrodina, I., Shubina, L., Chuiko, M., Mikheeva, O. et al. (2024). Development of the composition of anoxidation-stable dressing with high nutritional value. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (11 (127)), 29–37. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.296621
- Stankevych, S., Yakymenko-Tereshchenko, N., Panasenko, V., Gontar, T., Zabrodina, I., Kolontaievskyi, O. et al. (2024). Development of a complex antioxidant for stabilization of dressing enriched with omega-3 fatty acids. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (6 (131)), 6–14. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.311326
- Singh, P., Ban, Y. G., Kashyap, L., Siraree, A., Singh, J. (2020). Sugar and Sugar Substitutes: Recent Developments and Future Prospects. Sugar and Sugar Derivatives: Changing Consumer Preferences, 39–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-6663-9_4
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Katerina Kunitsa, Natalіia Yakymenko-Tereshchenko, Nadiia Lapytska, Tatiana Gontar, Denis Lypovyi, Svitlana Iurchenko, Iryna Balandina, Anton Ryabev, Natalya Kibenko, Larysa Obolentseva

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








