An interpretable ECG-based approach for detecting hemodynamically significant arrhythmias using lightweight machine learning models
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.340493Keywords:
ECG-based EF estimation, ejection fraction, machine learning, ECG classification, tQRS/tRR ratioAbstract
The object of this study is the diagnostic process of patients with suspected hemodynamically significant arrhythmia in emergency and telemedicine settings, where rapid and interpretable decision support is required. The problem addressed is the limited access to echocardiographic assessment in emergency and resource-constrained environments, where interpretable and computationally efficient alternatives are urgently needed, particularly for mobile and field-deployed applications.
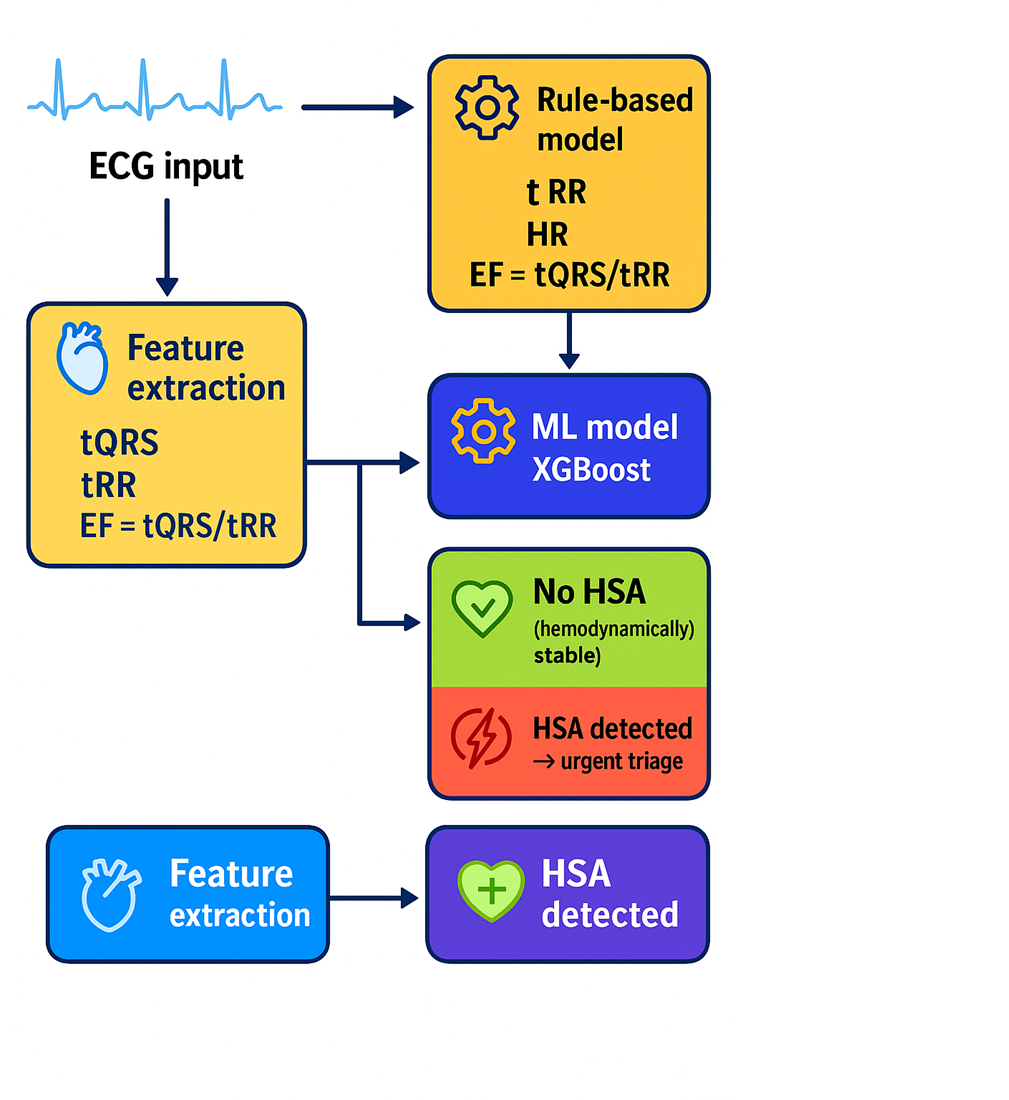
The main results show that machine learning models, such as XGBoost, achieved strong diagnostic performance (F1-score = 0.84, AUC = 0.91), while rule-based classifiers provided clinically interpretable accuracy. These results enabled partial compensation for the absence of echocardiography and contributed to reliable triage in acute and time-sensitive settings.
This effectiveness stems from key features of the method: reliance on interpretable ECG features (tQRS, tRR, HR, and EF derived from tQRS/tRR) and low computational complexity, setting it apart from more opaque deep learning methods. The results are explained by the strong correlation between these features and both electrical and mechanical heart function, enabling hemodynamic assessment without imaging. This supports clinical trust in the algorithm’s outputs.
The proposed approach is applicable in primary screening, emergency triage, telemedicine, and remote monitoring, combining accuracy with explainability and autonomy from imaging tools. Therefore, research on interpretable ECG-based detection of hemodynamically significant arrhythmias remains highly relevant, especially in settings lacking access to specialized diagnostics
References
- Hannun, A. Y., Rajpurkar, P., Haghpanahi, M., Tison, G. H., Bourn, C., Turakhia, M. P., Ng, A. Y. (2019). Cardiologist-level arrhythmia detection and classification in ambulatory electrocardiograms using a deep neural network. Nature Medicine, 25 (1), 65–69. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0268-3
- Ribeiro, A. H., Ribeiro, M. H., Paixão, G. M. M., Oliveira, D. M., Gomes, P. R., Canazart, J. A. et al. (2020). Automatic diagnosis of the 12-lead ECG using a deep neural network. Nature Communications, 11 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15432-4
- Attia, Z. I., Kapa, S., Lopez-Jimenez, F., McKie, P. M., Ladewig, D. J., Satam, G. et al. (2019). Screening for cardiac contractile dysfunction using an artificial intelligence–enabled electrocardiogram. Nature Medicine, 25 (1), 70–74. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0240-2
- Eleyan, A., Alboghbaish, E. (2024). Electrocardiogram Signals Classification Using Deep-Learning-Based Incorporated Convolutional Neural Network and Long Short-Term Memory Framework. Computers, 13 (2), 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers13020055
- Goto, S., Kimura, M., Katsumata, Y., Goto, S., Kamatani, T., Ichihara, G. et al. (2019). Artificial intelligence to predict needs for urgent revascularization from 12-leads electrocardiography in emergency patients. PLOS ONE, 14 (1), e0210103. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0210103
- Alamatsaz, N., Tabatabaei, L. S., Yazdchi, M., Payan, H., Alamatsaz, N., Nasimi, F. (2022). A lightweight hybrid CNN-LSTM model for ECG-based arrhythmia detection. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2209.00988
- Li, Q., Rajagopalan, C., Clifford, G. D. (2014). A machine learning approach to multi-level ECG signal quality classification. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 117 (3), 435–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2014.09.002
- Acharya, U. R., Fujita, H., Lih, O. S., Hagiwara, Y., Tan, J. H., Adam, M. (2017). Automated detection of arrhythmias using different intervals of tachycardia ECG segments with convolutional neural network. Information Sciences, 405, 81–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2017.04.012
- Samet, P. (1973). Hemodynamic Sequelae of Cardiac Arrhythmias. Circulation, 47 (2), 399–407. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.47.2.399
- Acharya, U. R., Fujita, H., Oh, S. L., Hagiwara, Y., Tan, J. H., Adam, M. (2017). Application of deep convolutional neural network for automated detection of myocardial infarction using ECG signals. Information Sciences, 415-416, 190–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2017.06.027
- Mailybayev, Y., Muratbekova, G., Altayeva, Z., Zhatkanbayev, O. (2022). Development of models and improvement of methods for formalization of design problems and automating technical and operational works of railway stations. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (3 (118)), 6–16. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.263167
- Annam, J. R., Surampudi, B. R. (2016). Inter-patient heart-beat classification using complete ECG beat time series by alignment of R-peaks using SVM and decision rule. 2016 International Conference on Signal and Information Processing (IConSIP), 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/iconsip.2016.7857480
- Smailov, N., Uralova, F., Kadyrova, R., Magazov, R., Sabibolda, A. (2025). Optymalizacja metod uczenia maszynowego do deanonimizacji w sieciach społecznościowych. Informatyka, Automatyka, Pomiary w Gospodarce i Ochronie Środowiska, 15 (1), 101–104. https://doi.org/10.35784/iapgos.7098
- Goettling, M., Hammer, A., Malberg, H., Schmidt, M. (2024). xECGArch: a trustworthy deep learning architecture for interpretable ECG analysis considering short-term and long-term features. Scientific Reports, 14 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-63656-x
- Zilberman, A., Rogel, S. (1990). Hemodynamic evaluation of common cardiac arrhythmias. International Journal of Cardiology, 27 (3), 341–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-5273(90)90291-c
- Smailov, N., Orynbet, M., Nazarova, A., Torekhan, Z., Koshkinbayev, S., Yssyraiyl, K. et al. (2025). Optymalizacja pracy światłowodowych czujników w warunkach kosmicznych. Informatyka, Automatyka, Pomiary w Gospodarce i Ochronie Środowiska, 15 (2), 130–134. https://doi.org/10.35784/iapgos.7200
- Hamo, C. E., DeJong, C., Hartshorne-Evans, N., Lund, L. H., Shah, S. J., Solomon, S., Lam, C. S. P. (2024). Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Nature Reviews Disease Primers, 10 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-024-00540-y
- Sabibolda, A., Tsyporenko, V., Smailov, N., Tsyporenko, V., Abdykadyrov, A. (2024). Estimation of the Time Efficiency of a Radio Direction Finder Operating on the Basis of a Searchless Spectral Method of Dispersion-Correlation Radio Direction Finding. Advances in Asian Mechanism and Machine Science, 62–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-67569-0_8
- Braunwald, E., Frahm, C. J., Ross, J. (1961). Studies on starling’s law of the heart. V. Left ventricular function in man. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 40 (10), 1882–1890. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci104412
- Smailov, N., Akmardin, S., Ayapbergenova, A., Ayapbergenova, G., Kadyrova, R., Sabibolda, A. (2025). Analiza wydajności VLC w optycznych systemach komunikacji bezprzewodowej do zastosowań wewnętrznych. Informatyka, Automatyka, Pomiary w Gospodarce i Ochronie Środowiska, 15 (2), 135–138. https://doi.org/10.35784/iapgos.6971
- deChazal, P., O’Dwyer, M., Reilly, R. B. (2004). Automatic Classification of Heartbeats Using ECG Morphology and Heartbeat Interval Features. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 51 (7), 1196–1206. https://doi.org/10.1109/tbme.2004.827359
- Yildirim, O., Baloglu, U. B., Tan, R.-S., Ciaccio, E. J., Acharya, U. R. (2019). A new approach for arrhythmia classification using deep coded features and LSTM networks. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 176, 121–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2019.05.004
- Abdykadyrov, A., Smailov, N., Sabibolda, A., Tolen, G., Dosbayev, Z., Ualiyev, Z., Kadyrova, R. (2024). Optimization of distributed acoustic sensors based on fiber optic technologies. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (5 (131)), 50–59. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.313455
- Acharya, U. R., Oh, S. L., Hagiwara, Y., Tan, J. H., Adam, M., Gertych, A., Tan, R. S. (2017). A deep convolutional neural network model to classify heartbeats. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 89, 389–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2017.08.022
- Bekbay, A., Ozhikenov, K., Ozhikenova, A., Bodin, O., Bezborodova, O., Rakhmatullov, F. (2019). Heart State Monitoring Using Multi-Agent Technology. 2019 8th Mediterranean Conference on Embedded Computing (MECO), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/meco.2019.8760007
- Bekbay, A., Alimbayeva, Z., Alimbayev, C., Bayanbay, N., Ozhikenov, K., Mukazhanov, Y. (2022). Development of an atrioventricular block prediction of method for portable heart monitoring system. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 3 (5 (117)), 15–27. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.258791
- Smailov, N., Tsyporenko, V., Sabibolda, A., Tsyporenko, V., Abdykadyrov, A., Kabdoldina, A. et al. (2024). Usprawnienie cyfrowego korelacyjno-interferometrycznego ustalania kierunku za pomocą przestrzennego sygnału analitycznego. Informatyka, Automatyka, Pomiary w Gospodarce i Ochronie Środowiska, 14 (3), 43–48. https://doi.org/10.35784/iapgos.6177
- Smailov, N., Tsyporenko, V., Ualiyev, Z., Issova, А., Dosbayev, Z., Tashtay, Y. et al. (2025). Improving accuracy of the spectral-correlation direction finding and delay estimation using machine learning. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2 (5 (134)), 15–24. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.327021
- Rahman, H. U., Ahmad, J., Akhmediyarova, A., Oralbekova, D., Mamyrbayev, O. (2024). Deciphering the Role of Circadian Clock in Inflammatory Response and Immune Disorders Using Model Checking and Petri Nets. IEEE Access, 12, 196576–196590. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2024.3521499
- Zilgarayeva, A., Smailov, N., Pavlov, S., Mirzakulova, S., Alimova, M., Kulambayev, B., Nurpeissova, D. (2024). Optical sensor to improve the accuracy of non-invasive blood sugar monitoring. Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, 34 (3), 1489. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijeecs.v34.i3.pp1489-1498
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Ainur Bekbay, Lashin Bazarbay, Zhanar Bigaliyeva, Vinera Baiturganova, Akezhan Sabibolda, Yersaiyn Mailybayev, Nurzhigit Smailov

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








