Інтерпретований підхід на основі ЕКГ для виявлення гемодинамічно значущих аритмій з використанням легких моделей машинного навчання
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.340493Ключові слова:
оцінка фракції викиду на основі ЕКГ, фракція викиду, машинне навчання, класифікація ЕКГ, співвідношення tQRS/tRRАнотація
Об'єктом цього дослідження є діагностичний процес пацієнтів з підозрою на гемодинамічно значущу аритмію в умовах невідкладної допомоги та телемедицини, де потрібна швидка та інтерпретована підтримка рішень. Проблема, що розглядається, полягає в обмеженому доступі до ехокардіографічної оцінки в умовах невідкладної допомоги та обмежених ресурсів, де терміново потрібні інтерпретовані та обчислювально ефективні альтернативи, особливо для мобільних та польових застосувань.ff
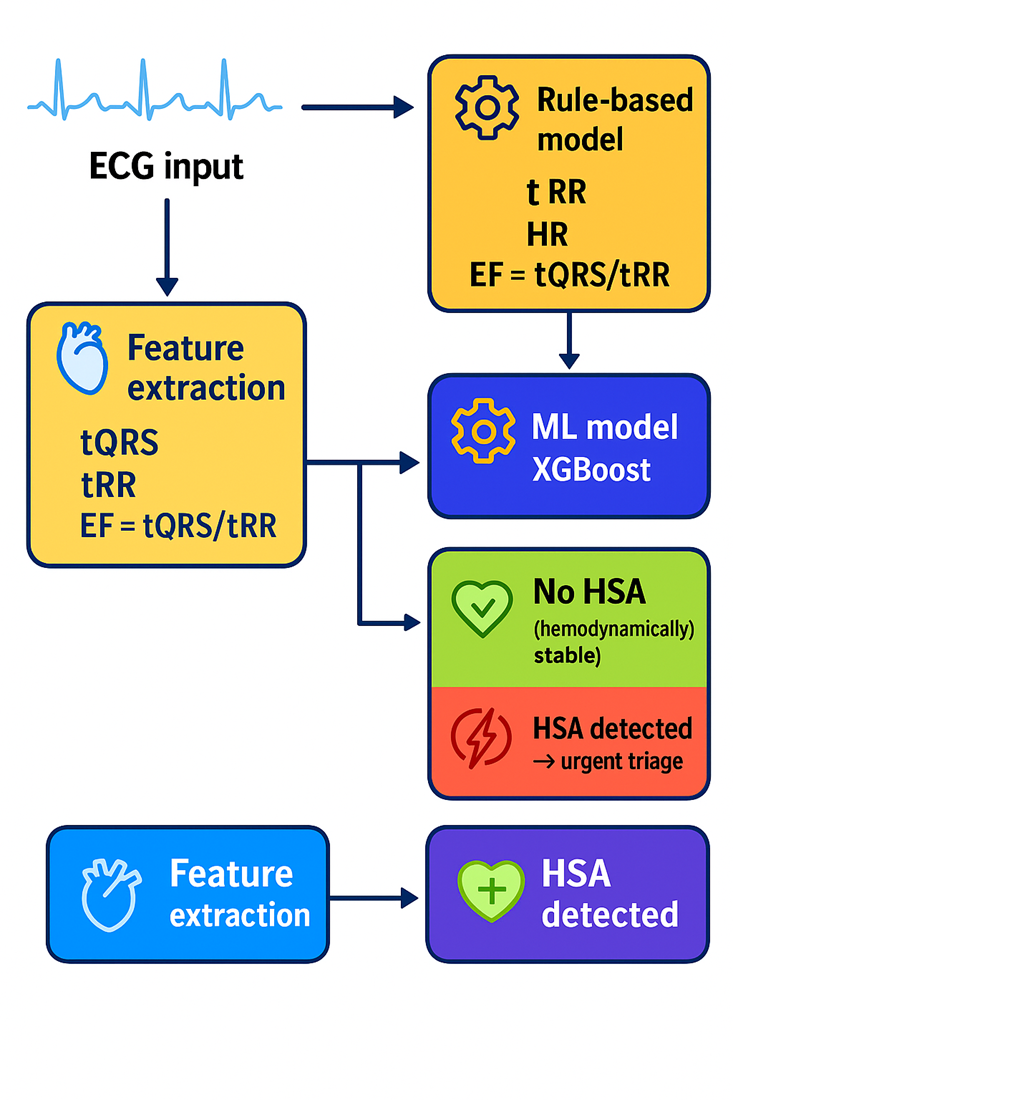
Основні результати показують, що моделі машинного навчання, такі як XGBoost, досягли високої діагностичної ефективності (F1-оцінка = 0,84, AUC = 0,91), тоді як класифікатори на основі правил забезпечили клінічно інтерпретовану точність. Ці результати дозволили частково компенсувати відсутність ехокардіографії та сприяли надійному сортуванню в гострих та чутливих до часу умовах.
Ця ефективність випливає з ключових особливостей методу: опори на інтерпретовані ознаки ЕКГ (tQRS, tRR, HR та EF, отримані з tQRS/tRR) та низької обчислювальної складності, що відрізняє його від більш непрозорих методів глибокого навчання. Результати пояснюються сильною кореляцією між цими характеристиками та як електричною, так і механічною функцією серця, що дозволяє проводити гемодинамічну оцінку без візуалізації. Це підтримує клінічну довіру до результатів алгоритму.
Запропонований підхід застосовується в первинному скринінгу, невідкладному сортуванні, телемедицині та дистанційному моніторингу, поєднуючи точність із поясненням та автономністю від інструментів візуалізації. Тому дослідження інтерпретованого виявлення гемодинамічно значущих аритмій на основі ЕКГ залишаються дуже актуальними, особливо в умовах відсутності доступу до спеціалізованої діагностики
Посилання
- Hannun, A. Y., Rajpurkar, P., Haghpanahi, M., Tison, G. H., Bourn, C., Turakhia, M. P., Ng, A. Y. (2019). Cardiologist-level arrhythmia detection and classification in ambulatory electrocardiograms using a deep neural network. Nature Medicine, 25 (1), 65–69. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0268-3
- Ribeiro, A. H., Ribeiro, M. H., Paixão, G. M. M., Oliveira, D. M., Gomes, P. R., Canazart, J. A. et al. (2020). Automatic diagnosis of the 12-lead ECG using a deep neural network. Nature Communications, 11 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15432-4
- Attia, Z. I., Kapa, S., Lopez-Jimenez, F., McKie, P. M., Ladewig, D. J., Satam, G. et al. (2019). Screening for cardiac contractile dysfunction using an artificial intelligence–enabled electrocardiogram. Nature Medicine, 25 (1), 70–74. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0240-2
- Eleyan, A., Alboghbaish, E. (2024). Electrocardiogram Signals Classification Using Deep-Learning-Based Incorporated Convolutional Neural Network and Long Short-Term Memory Framework. Computers, 13 (2), 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers13020055
- Goto, S., Kimura, M., Katsumata, Y., Goto, S., Kamatani, T., Ichihara, G. et al. (2019). Artificial intelligence to predict needs for urgent revascularization from 12-leads electrocardiography in emergency patients. PLOS ONE, 14 (1), e0210103. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0210103
- Alamatsaz, N., Tabatabaei, L. S., Yazdchi, M., Payan, H., Alamatsaz, N., Nasimi, F. (2022). A lightweight hybrid CNN-LSTM model for ECG-based arrhythmia detection. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2209.00988
- Li, Q., Rajagopalan, C., Clifford, G. D. (2014). A machine learning approach to multi-level ECG signal quality classification. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 117 (3), 435–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2014.09.002
- Acharya, U. R., Fujita, H., Lih, O. S., Hagiwara, Y., Tan, J. H., Adam, M. (2017). Automated detection of arrhythmias using different intervals of tachycardia ECG segments with convolutional neural network. Information Sciences, 405, 81–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2017.04.012
- Samet, P. (1973). Hemodynamic Sequelae of Cardiac Arrhythmias. Circulation, 47 (2), 399–407. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.47.2.399
- Acharya, U. R., Fujita, H., Oh, S. L., Hagiwara, Y., Tan, J. H., Adam, M. (2017). Application of deep convolutional neural network for automated detection of myocardial infarction using ECG signals. Information Sciences, 415-416, 190–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2017.06.027
- Mailybayev, Y., Muratbekova, G., Altayeva, Z., Zhatkanbayev, O. (2022). Development of models and improvement of methods for formalization of design problems and automating technical and operational works of railway stations. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (3 (118)), 6–16. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.263167
- Annam, J. R., Surampudi, B. R. (2016). Inter-patient heart-beat classification using complete ECG beat time series by alignment of R-peaks using SVM and decision rule. 2016 International Conference on Signal and Information Processing (IConSIP), 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/iconsip.2016.7857480
- Smailov, N., Uralova, F., Kadyrova, R., Magazov, R., Sabibolda, A. (2025). Optymalizacja metod uczenia maszynowego do deanonimizacji w sieciach społecznościowych. Informatyka, Automatyka, Pomiary w Gospodarce i Ochronie Środowiska, 15 (1), 101–104. https://doi.org/10.35784/iapgos.7098
- Goettling, M., Hammer, A., Malberg, H., Schmidt, M. (2024). xECGArch: a trustworthy deep learning architecture for interpretable ECG analysis considering short-term and long-term features. Scientific Reports, 14 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-63656-x
- Zilberman, A., Rogel, S. (1990). Hemodynamic evaluation of common cardiac arrhythmias. International Journal of Cardiology, 27 (3), 341–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-5273(90)90291-c
- Smailov, N., Orynbet, M., Nazarova, A., Torekhan, Z., Koshkinbayev, S., Yssyraiyl, K. et al. (2025). Optymalizacja pracy światłowodowych czujników w warunkach kosmicznych. Informatyka, Automatyka, Pomiary w Gospodarce i Ochronie Środowiska, 15 (2), 130–134. https://doi.org/10.35784/iapgos.7200
- Hamo, C. E., DeJong, C., Hartshorne-Evans, N., Lund, L. H., Shah, S. J., Solomon, S., Lam, C. S. P. (2024). Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Nature Reviews Disease Primers, 10 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-024-00540-y
- Sabibolda, A., Tsyporenko, V., Smailov, N., Tsyporenko, V., Abdykadyrov, A. (2024). Estimation of the Time Efficiency of a Radio Direction Finder Operating on the Basis of a Searchless Spectral Method of Dispersion-Correlation Radio Direction Finding. Advances in Asian Mechanism and Machine Science, 62–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-67569-0_8
- Braunwald, E., Frahm, C. J., Ross, J. (1961). Studies on starling’s law of the heart. V. Left ventricular function in man. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 40 (10), 1882–1890. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci104412
- Smailov, N., Akmardin, S., Ayapbergenova, A., Ayapbergenova, G., Kadyrova, R., Sabibolda, A. (2025). Analiza wydajności VLC w optycznych systemach komunikacji bezprzewodowej do zastosowań wewnętrznych. Informatyka, Automatyka, Pomiary w Gospodarce i Ochronie Środowiska, 15 (2), 135–138. https://doi.org/10.35784/iapgos.6971
- deChazal, P., O’Dwyer, M., Reilly, R. B. (2004). Automatic Classification of Heartbeats Using ECG Morphology and Heartbeat Interval Features. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 51 (7), 1196–1206. https://doi.org/10.1109/tbme.2004.827359
- Yildirim, O., Baloglu, U. B., Tan, R.-S., Ciaccio, E. J., Acharya, U. R. (2019). A new approach for arrhythmia classification using deep coded features and LSTM networks. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 176, 121–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2019.05.004
- Abdykadyrov, A., Smailov, N., Sabibolda, A., Tolen, G., Dosbayev, Z., Ualiyev, Z., Kadyrova, R. (2024). Optimization of distributed acoustic sensors based on fiber optic technologies. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (5 (131)), 50–59. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.313455
- Acharya, U. R., Oh, S. L., Hagiwara, Y., Tan, J. H., Adam, M., Gertych, A., Tan, R. S. (2017). A deep convolutional neural network model to classify heartbeats. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 89, 389–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2017.08.022
- Bekbay, A., Ozhikenov, K., Ozhikenova, A., Bodin, O., Bezborodova, O., Rakhmatullov, F. (2019). Heart State Monitoring Using Multi-Agent Technology. 2019 8th Mediterranean Conference on Embedded Computing (MECO), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/meco.2019.8760007
- Bekbay, A., Alimbayeva, Z., Alimbayev, C., Bayanbay, N., Ozhikenov, K., Mukazhanov, Y. (2022). Development of an atrioventricular block prediction of method for portable heart monitoring system. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 3 (5 (117)), 15–27. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.258791
- Smailov, N., Tsyporenko, V., Sabibolda, A., Tsyporenko, V., Abdykadyrov, A., Kabdoldina, A. et al. (2024). Usprawnienie cyfrowego korelacyjno-interferometrycznego ustalania kierunku za pomocą przestrzennego sygnału analitycznego. Informatyka, Automatyka, Pomiary w Gospodarce i Ochronie Środowiska, 14 (3), 43–48. https://doi.org/10.35784/iapgos.6177
- Smailov, N., Tsyporenko, V., Ualiyev, Z., Issova, А., Dosbayev, Z., Tashtay, Y. et al. (2025). Improving accuracy of the spectral-correlation direction finding and delay estimation using machine learning. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2 (5 (134)), 15–24. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.327021
- Rahman, H. U., Ahmad, J., Akhmediyarova, A., Oralbekova, D., Mamyrbayev, O. (2024). Deciphering the Role of Circadian Clock in Inflammatory Response and Immune Disorders Using Model Checking and Petri Nets. IEEE Access, 12, 196576–196590. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2024.3521499
- Zilgarayeva, A., Smailov, N., Pavlov, S., Mirzakulova, S., Alimova, M., Kulambayev, B., Nurpeissova, D. (2024). Optical sensor to improve the accuracy of non-invasive blood sugar monitoring. Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, 34 (3), 1489. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijeecs.v34.i3.pp1489-1498
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2025 Ainur Bekbay, Lashin Bazarbay, Zhanar Bigaliyeva, Vinera Baiturganova, Akezhan Sabibolda, Yersaiyn Mailybayev, Nurzhigit Smailov

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.
Ліцензійний договір – це документ, в якому автор гарантує, що володіє усіма авторськими правами на твір (рукопис, статтю, тощо).
Автори, підписуючи Ліцензійний договір з ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР», мають усі права на подальше використання свого твору за умови посилання на наше видання, в якому твір опублікований. Відповідно до умов Ліцензійного договору, Видавець ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР» не забирає ваші авторські права та отримує від авторів дозвіл на використання та розповсюдження публікації через світові наукові ресурси (власні електронні ресурси, наукометричні бази даних, репозитарії, бібліотеки тощо).
За відсутності підписаного Ліцензійного договору або за відсутністю вказаних в цьому договорі ідентифікаторів, що дають змогу ідентифікувати особу автора, редакція не має права працювати з рукописом.
Важливо пам’ятати, що існує і інший тип угоди між авторами та видавцями – коли авторські права передаються від авторів до видавця. В такому разі автори втрачають права власності на свій твір та не можуть його використовувати в будь-який спосіб.









