A technique for approximating a tubular helical surface with strips of toruses
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.343193Keywords:
line of curvature, tangent strip, geodesic curvature, sweeping surface, numerical integrationAbstract
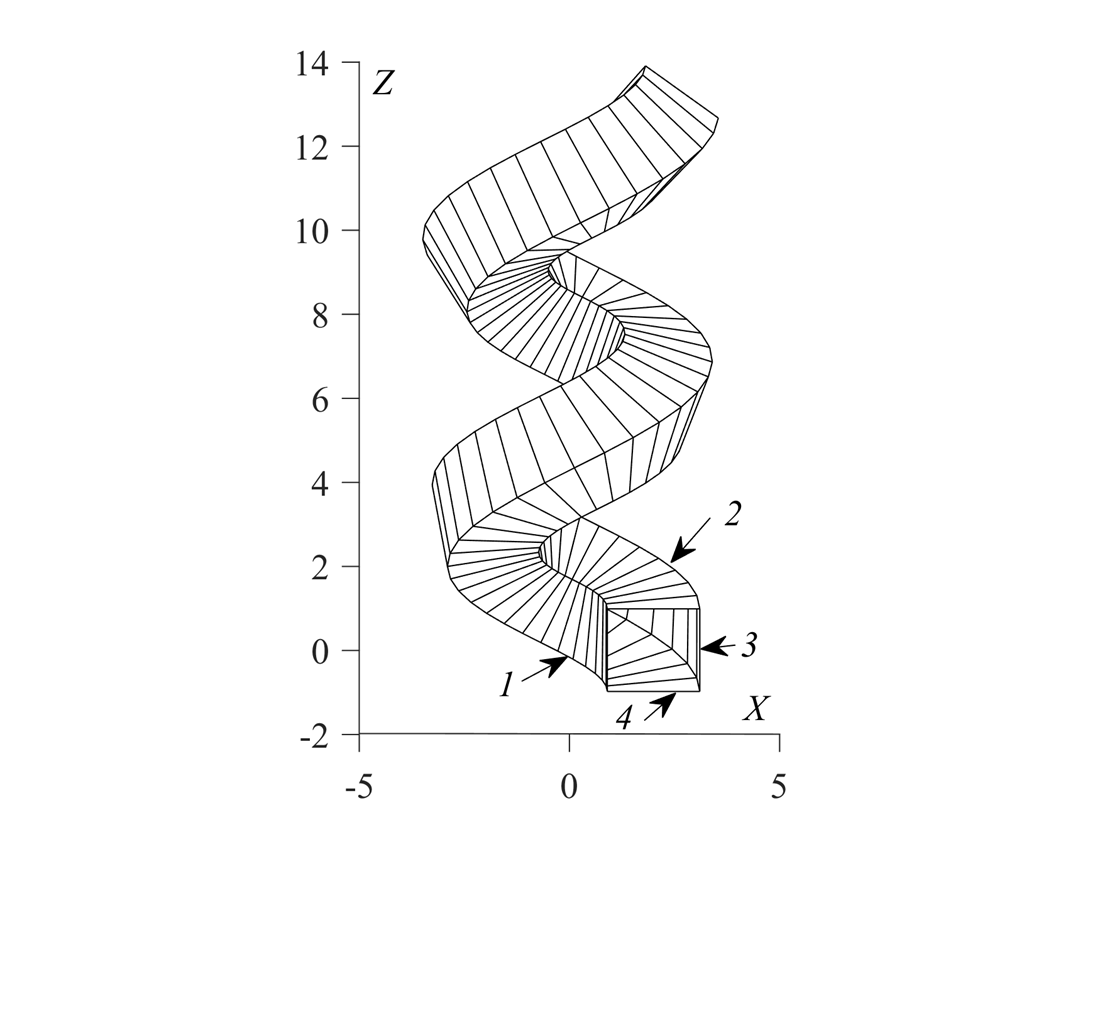
This study’s object is the approximation of a non-swept helical tubular surface by strips of sweeping surfaces (toruses) and the construction of sweeps of these strips.
Approximating non-swept tubular surfaces by sections of sweep ones is a common practice in the design of various types of pipelines. A clear example of such an approximation is a sports ball whose outer shell consists of a certain number of separate elements. These elements must fit most tightly to the non-swept surface along its certain lines. Such lines are the lines of curvature. The task is to find these lines on the surface in order to subsequently analytically describe the torus strip, which is tangent to the non-swept surface along this line.
As is known, there are two families of mutually perpendicular lines of curvature on surfaces. This paper considers a family of curvature lines that has advantages over another one in terms of approximation. This explains the results reported here. Their special feature is that in order to find the desired family of curvature lines, it is necessary to solve a differential equation.
The solution to this equation was borrowed from a scientific article and used for further calculations. The results were visualized in the form of an approximated tubular surface with four and six strips.
The sweeps of these strips were constructed for a tubular surface, in which the center line is a helical line r = 1. All dimensions are given in linear units. Instead of a circle generatrix, it is given by the radius of the cylinder a = 2, which hosts it, and the helical parameter b = 1.5 (step H = 9.4). The radius of the circle generatrix of the tubular surface of the original tubular surface in the approximated surface in the given examples is a polygon (square or equilateral hexagon).
References
- Hruban, V., Drobitko, A., Khramov, M., Tovpyha, M. (2025). Strength analysis and optimisation of trailer agricultural machinery structures using finite element methods. Machinery & Energetics, 16 (2), 117–130. https://doi.org/10.31548/machinery/2.2025.117
- Nazarenko, V., Ostroushko, B. (2025). Comparative research of 3D printer main control parameters and characteristics utilising Klipper firmware. Machinery & Energetics, 16 (1), 81–90. https://doi.org/10.31548/machinery/1.2025.81
- Duhanets, V., Semenyshena, R., Fedirko, P., Pukas, V., Volynkin, M. (2025). Application of automated welding processes in the restoration of pipelines of power facilities. Machinery & Energetics, 16 (1), 91–103. https://doi.org/10.31548/machinery/1.2025.91
- Zakharova, I., Shchetynin, S., Shchetynina, V., Zusin, A., Volenko, I. (2025). Use of robotic and automated systems in welding and restoration of parts. Machinery & Energetics, 16 (1), 117–129. https://doi.org/10.31548/machinery/1.2025.117
- Selvaraju, P. (2024). Developability Approximation for Neural Implicits Through Rank Minimization. 2024 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV). IEEE, 780–789. https://doi.org/10.1109/3dv62453.2024.00041
- Pan, Y., Xu, Z., Wang, B., Deng, B. (2025). Piecewise Ruled Approximation for Freeform Mesh Surfaces. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 44 (4), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1145/3730866
- Baharami, H., Piovarci, M., Tarini, M., Bickel, B., Pietroni, N. (2025). Fabricable Discretized Ruled Surfaces. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 44 (3), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1145/3734519
- Binninger, A., Verhoeven, F., Herholz, P., Sorkine‐Hornung, O. (2021). Developable Approximation via Gauss Image Thinning. Computer Graphics Forum, 40 (5), 289–300. https://doi.org/10.1111/cgf.14374
- Zeng, Z., Jia, X., Shen, L., Bo, P. (2022). Developable mesh segmentation by detecting curve-like features on Gauss images. Computers & Graphics, 109, 42–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cag.2022.10.003
- Ion, A., Rabinovich, M., Herholz, P., Sorkine-Hornung, O. (2020). Shape approximation by developable wrapping. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 39 (6), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1145/3414685.3417835
- Nesvidomin, A., Ahmed, A. K., Pylypaka, S., Volina, T., Nesvidomin, V., Vereshchaga, V. et al. (2023). Construction of a mathematical model for approximating the sphere by strips of unfolding surfaces. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (1 (126)), 78–84. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.291554
- Mukvych, M. M. (2009). Konstruiuvannia trubchastykh poverkhon iz prostorovoiu vissiu, opysanykh simiamy koordynatnykh linii kryvyny. Prykladna heometriia ta inzhenerna hrafika, 81, 195–200. Available at: https://scholar.google.ru/citations?view_op=view_citation&hl=ru&user=CiktFzQAAAAJ&citation_for_view=CiktFzQAAAAJ:IjCSPb-OGe4C
- Kresan, Т., Ahmed, A. K., Pylypaka, S., Volina, T., Voloshko, T. (2024). Construction of the working surfaces of the tillage screw body from the compartments of the developable helicoid. Machinery & Energetics, 15 (3), 9–21. https://doi.org/10.31548/machinery/3.2024.09
- Nesvidomin, A., Pylypaka, S., Volina, T., Shtyka, Y., Rybenko, I. (2025). Optimisation of a developable surface model passing through a helical curve with variable pitch. Machinery & Energetics, 16 (2), 49–57. https://doi.org/10.31548/machinery/2.2025.49
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Andrii Nesvidomin, Serhii Pylypaka, Victor Nesvidomin, Vitaliy Babka, Olga Shoman, Oleksandr Savoiskyi, Taras Pylypaka, Mykola Lokhonia, Svetlana Semirnenko, Yana Borodai

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








