Analytical point-form description of the technique for graphical differentiation of a plane curve
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.343387Keywords:
point polynomial, strip of diffprojections, approximation, analytical chord method, drawings analytizationAbstract
This study considers graphic differentiation, in particular, a chord method, as one of the options for graphic differentiation in terms of replacing graphic operations with analytical ones in point form.
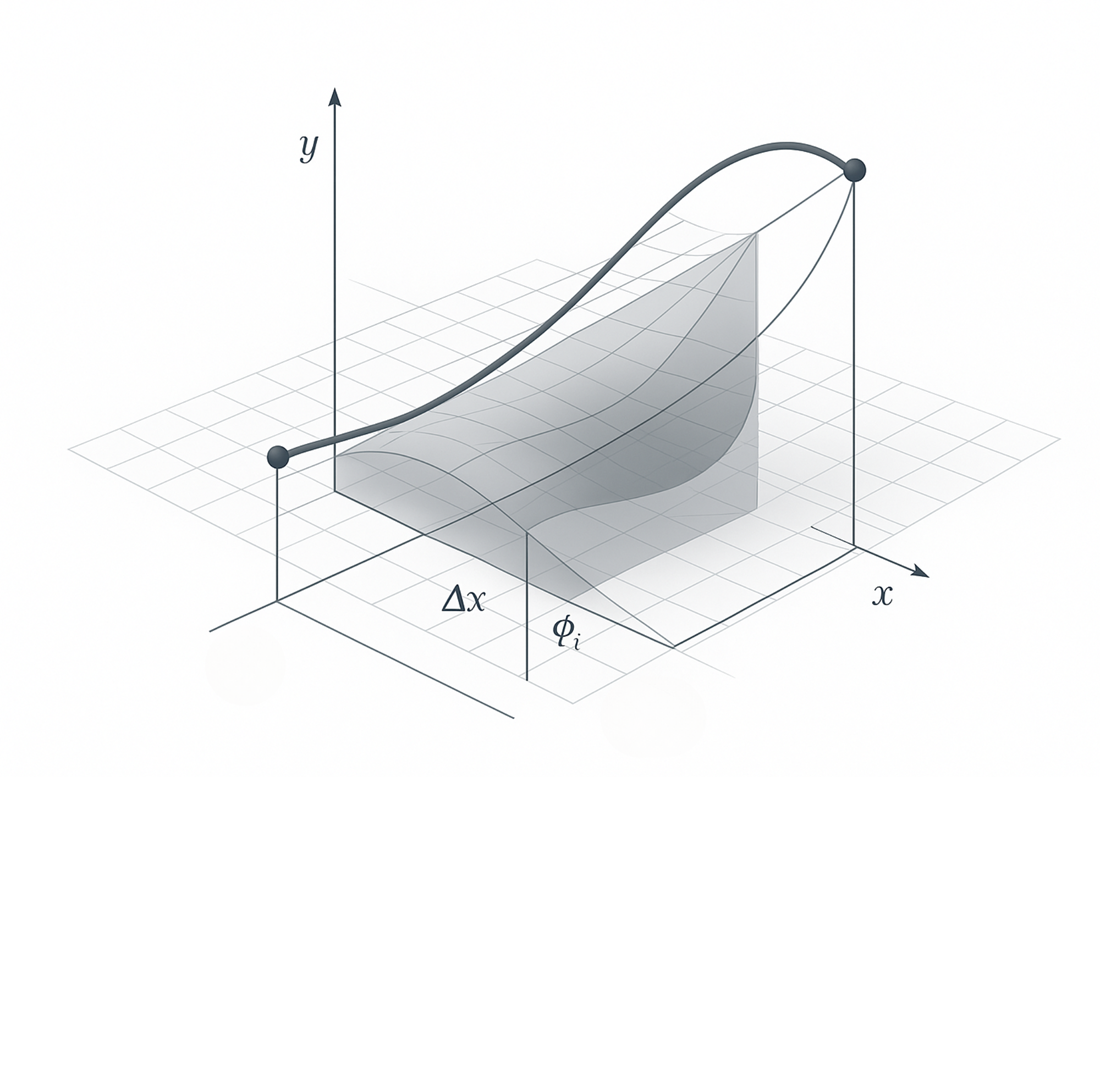
Determining the reference point and the center of projection for constructing a strip of differential projection correlates its positions with respect to the values of the derivative of the function, which is graphically represented by a discrete series of points. The reference point, the right differential projection of the first and left differential projection of the second points have the same values in the field of derivatives. However, they do not coincide with the values of the derivatives of the original functions. To establish such a correspondence, the difference between the left and right differential projections of the first point is divided in half and subtracted from the first derivative of the original function – the point polynomial.
Relative to the reference point, parallel to the first link of the accompanying broken line of the discretely represented curve, a straight line is drawn that intersects the abscissa axis at the center of the projection. Finding the reference point and the projection center is carried out analytically in point form without any graphic operations. Rays are drawn from the projection center parallel to one of the links of the accompanying polyline, thus forming a strip of differential projections, within which the values of the angles of inclination of the tangents to the curve at the base points are selected. Discrete derivative values are connected by straight line segments or remain separate points. The resulting derivative values coincide with the analytical values with a deviation of no more than 0.5–1.5 units.
The developed algorithms could be integrated into automated design and engineering analysis systems for effective calculation of derivatives of discretely given curves. In addition, they could serve as the basis for designing computationally productive modules in artificial intelligence and digital data processing systems that work with geometric and discrete information arrays.
References
- Fischer, M., Krause, C. M. (2025). Pivotal examples in graphical differentiation – an analysis of semiotic and theoretic control. Proceedings of the 48th Conference of the International Group for the Psychology of Mathematics Education: Research Reports, 1, 259–266. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/392626925_PIVOTAL_EXAMPLES_IN_GRAPHICAL_DIFFERENTIATION_-AN_ANALYSIS_OF_SEMIOTIC_AND_THEORETIC_CONTROL
- Zakharova, I., Shchetynin, S., Shchetynina, V., Zusin, A., Volenko, I. (2025). Use of robotic and automated systems in welding and restoration of parts. Machinery & Energetics, 16 (1), 117–129. https://doi.org/10.31548/machinery/1.2025.117
- Aghayeva, K., Krauklit, G. (2025). Automated methane emission monitoring systems based on satellite data: Radiation transfer model analysis. Machinery & Energetics, 16 (1), 146–156. https://doi.org/10.31548/machinery/1.2025.146
- Turchyn, O. (2024). Introduction of neural network technologies to optimise the control of the operating modes of a sucker-rod pump installation. Machinery & Energetics, 16 (1), 32–42. https://doi.org/10.31548/machinery/1.2025.32
- Andriievskyi, I., Spivak, S., Gogota, O., Yermolenko, R. (2024). Application of the regression neural network for the analysis of the results of ultrasonic testing. Machinery & Energetics, 15 (1), 43–55. https://doi.org/10.31548/machinery/1.2024.43
- Mukherjee, S., Claassen, M., Bürkner, P.-C. (2025). DGP-LVM: Derivative Gaussian process latent variable models. Statistics and Computing, 35 (5). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-025-10644-4
- Shahan, J. T., Walker, S. W. (2025). Exact shape derivatives with unfitted finite element methods. Journal of Numerical Mathematics. https://doi.org/10.1515/jnma-2024-0113
- Guo, P., Lan, Y., Qiao, J. (2025). Exact solutions of differential equations: renormalization group based polynomial scheme. Communications in Theoretical Physics, 77 (10), 105005. https://doi.org/10.1088/1572-9494/add24e
- Konopatskiy, E. V., Bezditnyi, A. A. (2019). Geometric modeling and optimization of multidimensional data in Radischev integrated drawing. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1260 (7), 072006. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1260/7/072006
- Konopatskiy, E. V., Mashtaler, S. N., Bezditnyi, A. A. (2019). Study of high-strength steel fiber concrete strength characteristics under elevated temperatures using mathematical modelling methods. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 687 (2), 022040. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/687/2/022040
- Konopatskiy, E. V., Bezditnyi, A. A. (2020). Geometric modeling of multifactor processes and phenomena by the multidimensional parabolic interpolation method. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1441 (1), 012063. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1441/1/012063
- Lako, A., Barko, O. (2024). Design and optimisation of automated hydraulic gate control systems for flood control. Machinery & Energetics, 15 (4), 58–68. https://doi.org/10.31548/machinery/4.2024.58
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Viktor Vereschaga, Kseniia Lysenko, Yevhen Adoniev, Ernest Murtaziiev, Ivan Vereshchaha, Tetiana Volina

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








