Optimized adaptive machine learning for dynamic data streams
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.343635Keywords:
adaptation model, computing performance, drift detection, streaming processing, rapid updatingAbstract
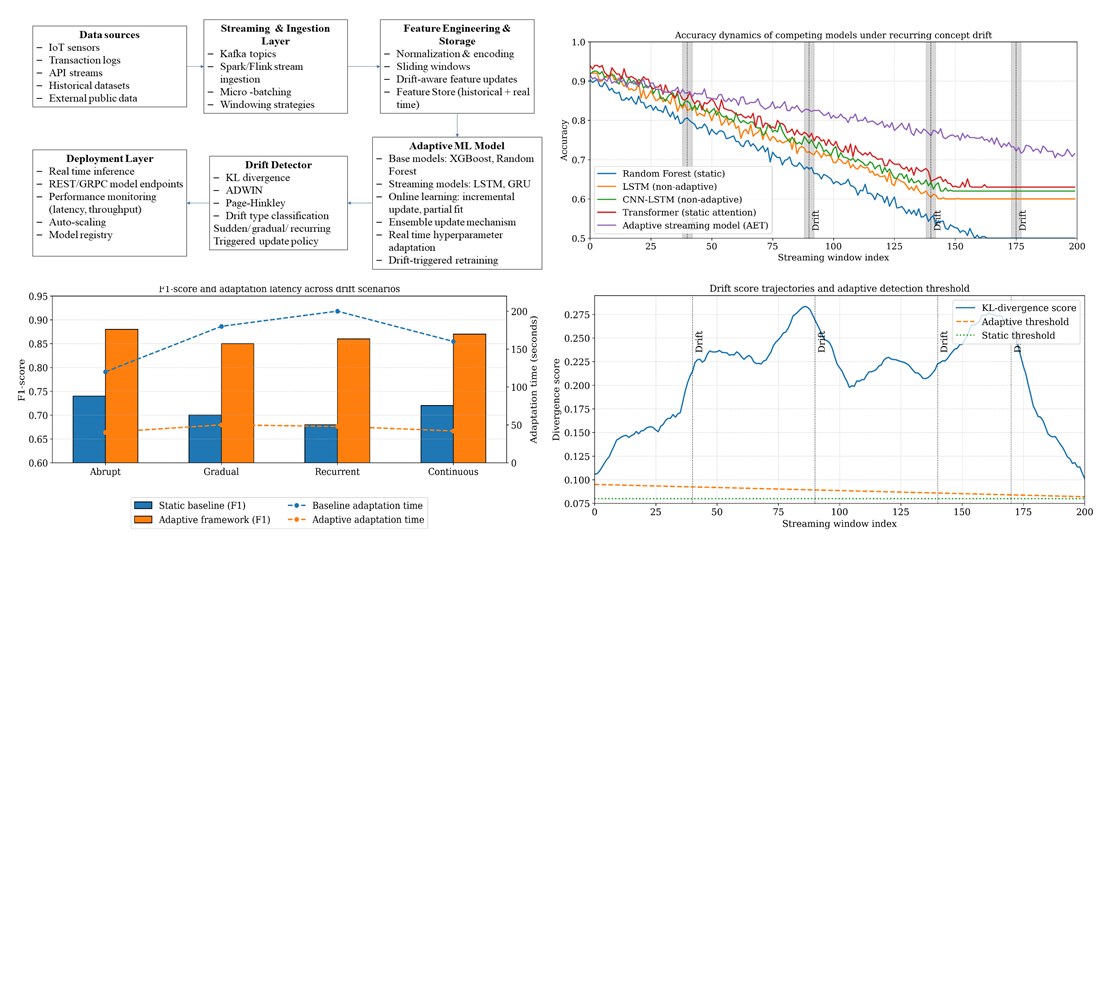
The object of the study is the adaptive machine learning systems that are able to process large amounts of rapidly changing streaming data in real time. The problem of maintaining prediction accuracy and computational efficiency in the presence of concept drift is treated. Concept drift refers to the overweighting of static models when stationary models are tried, and the nature of the underlying distributions changes. The adaptive architecture includes revision divergence-oriented concept drift detection, incremental model updating via hyper-dimensional statistical clustering of segments. Results from experiments using simulated and real-world datasets demonstrate that the adaptive architecture maintains predictive accuracy above 0.83 across abrupt, gradual, recurrent, and continuous drift scenarios. Compared with non-adaptive models, adaptation latency is reduced by approximately 2.6×, while unnecessary retraining operations are decreased by up to 40%. These results are possible due to the fact that proposed framework is able to retrain solutions if, and only if, distributional changes are determined to be statistically significant and meaningful to the model. This leads to the avoidance of processors being given redundant computations and providing a steady-state model during non-drift conditions. A principal contribution is that feature engineering is accomplished in a drift-aware manner, thresholding is made adaptive to the distributions indicated, and update mechanisms are employed which efficiently utilize resources in a unified high-performance streaming pipeline. The architecture performs well under abrupt, gradual, recurrent, and continuous drift and effective for real-time applications which include smart-city analytics, cyber security monitoring, roadways system works, and IoT for industrial systems
References
- Wang, J., Lu, T., Li, L., Huang, D. (2024). Enhancing Personalized Search with AI: A Hybrid Approach Integrating Deep Learning and Cloud Computing. Journal of Advanced Computing Systems, 4 (10), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.69987/jacs.2024.41001
- Navaux, P. O. A., Lorenzon, A. F., Serpa, M. da S. (2023). Challenges in High-Performance Computing. Journal of the Brazilian Computer Society, 29 (1), 51–62. https://doi.org/10.5753/jbcs.2023.2219
- Mektepbaeva, A., Medarov, A., Kulmuratova, A. (2024). Analysis of Penetration Testing Methods for Specific IoT Device: IP Camera. 2024 IEEE 4th International Conference on Smart Information Systems and Technologies (SIST), 76–82. https://doi.org/10.1109/sist61555.2024.10629431
- Jones, R., Davies, H. (2024). High-Performance Digital Forensic Framework for Anomalous Ransomware Detection in File System Log Data. https://doi.org/10.36227/techrxiv.172599923.38750111/v1
- Xing, S., Wang, Y. (2025). Proactive Data Placement in Heterogeneous Storage Systems via Predictive Multi-Objective Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Access, 13, 117986–117998. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2025.3586378
- Wilson, A., Anwar, M. R. (2024). The Future of Adaptive Machine Learning Algorithms in High-Dimensional Data Processing. International Transactions on Artificial Intelligence (ITALIC), 3 (1), 97–107. https://doi.org/10.33050/italic.v3i1.656
- Rane, N., Paramesha, M., Choudhary, S., Rane, J. (2024). Machine Learning and Deep Learning for Big Data Analytics: a Review of Methods and Applications. SSRN Electronic Journal. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4835655
- Kamila, N. K., Frnda, J., Pani, S. K., Das, R., Islam, S. M. N., Bharti, P. K., Muduli, K. (2022). Machine learning model design for high performance cloud computing & load balancing resiliency: An innovative approach. Journal of King Saud University - Computer and Information Sciences, 34 (10), 9991–10009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2022.10.001
- Ahmadi, S. (2023). Optimizing Data Warehousing Performance through Machine Learning Algorithms in the Cloud. International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR), 12 (12), 1859–1867. https://doi.org/10.21275/sr231224074241
- Ji, E., Wang, Y., Xing, S., Jin, J. (2025). Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning for Energy-Efficient API Traffic Optimization in Large-Scale Advertising Systems. IEEE Access, 13, 142493–142516. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2025.3598712
- Wang, S., Zheng, H., Wen, X., Fu, S. (2024). Distributed high-performance computing methods for accelerating deep learning training. Journal of Knowledge Learning and Science Technology ISSN: 2959-6386 (Online), 3 (3), 108–126. https://doi.org/10.60087/jklst.v3.n4.p22
- Cravero, A., Sepúlveda, S. (2021). Use and Adaptations of Machine Learning in Big Data – Applications in Real Cases in Agriculture. Electronics, 10 (5), 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10050552
- Naayini, P., Kamatala, S. (2023). High-Performance Data Computing: Parallel Frameworks, Execution Strategies, and Real-World Deployments. International Journal Of Scientific Advances, 4 (6). https://doi.org/10.51542/ijscia.v4i6.33
- Usman, S., Mehmood, R., Katib, I., Albeshri, A. (2022). Data Locality in High Performance Computing, Big Data, and Converged Systems: An Analysis of the Cutting Edge and a Future System Architecture. Electronics, 12 (1), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12010053
- Gadde, H. (2023). Leveraging AI for Scalable Query Processing in Big Data Environments. International Journal of Advanced Engineering Technologies and Innovations, 1 (02), 435–465. Available at: https://www.academia.edu/124871455/Leveraging_AI_for_Scalable_Query_Processing_in_Big_Data_Environments
- Sakhipov, A., Omirzak, I., Fedenko, A. (2025). Beyond Face Recognition: A Multi-Layered Approach to Academic Integrity in Online Exams. Electronic Journal of E-Learning, 23 (1), 81–95. https://doi.org/10.34190/ejel.23.1.3896
- Kaveh, M., Mesgari, M. S. (2022). Application of Meta-Heuristic Algorithms for Training Neural Networks and Deep Learning Architectures: A Comprehensive Review. Neural Processing Letters, 55 (4), 4519–4622. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-022-11055-6
- Mektepbayeva, A., Begisbayev, D., Seiitbek, R., Khaimuldin, N., Sakhipov, A., Rakhimzhanov, D. (2025). Adaptive Machine Learning Algorithms for Data Processing in Transportation Systems. 2025 IEEE 5th International Conference on Smart Information Systems and Technologies (SIST), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/sist61657.2025.11139286
- Jumagaliyeva, A., Abdykerimova, E., Turkmenbayev, A., Serimbetov, B., Muratova, G., Yersultanova, Z., Zhiyembayev, Z. (2024). Identifying patterns and mechanisms of AI integration in blockchain for e-voting network security. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (2 (130)), 6–18. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.305696
- Chinchanikar, S., Shaikh, A. A. (2022). A Review on Machine Learning, Big Data Analytics, and Design for Additive Manufacturing for Aerospace Applications. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 31 (8), 6112–6130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07125-4
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Aivar Sakhipov, Aruzhan Mektepbayeva, Amangul Talgat, Maxot Rakhmetov, Ainagul Adiyeva, Altynbek Seitenov, Nurzhan Ualiyev, Shynar Yelezhanova

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








