Determining the influence of structural and electromagnetic parameters on active losses in an electric motor with permanent magnets for unmanned aerial vehicles
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.344817Keywords:
high-speed motor, losses in the magnetic core, permanent magnet motorAbstract
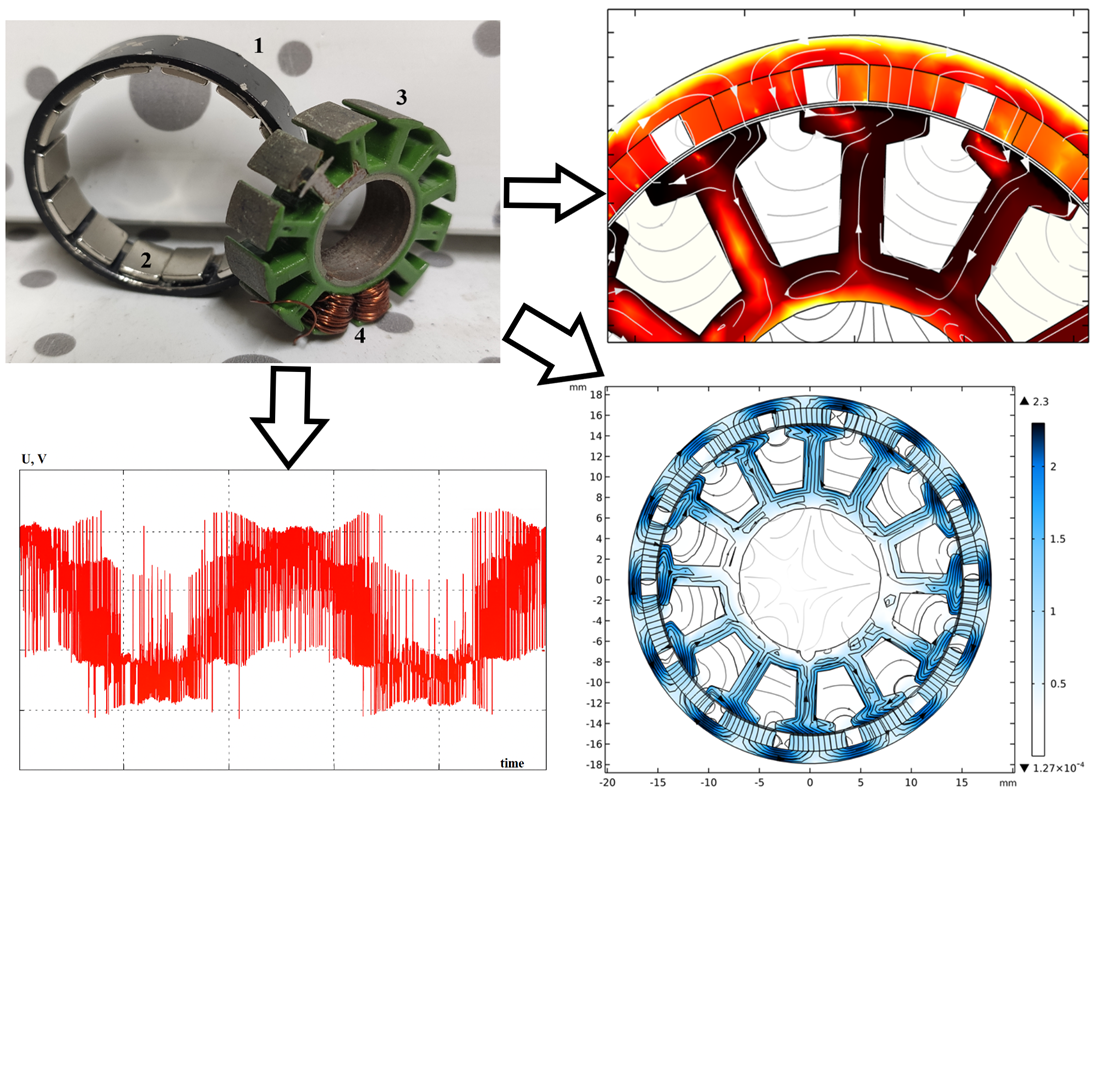
This study investigates a small-sized high-speed permanent magnet motor used in the drive of unmanned aerial vehicles.
As part of this study, a numerical simulation field mathematical model of a high-speed permanent magnet motor has been built, implemented by the finite element method. That made it possible to obtain the distribution of the electromagnetic field and forces, to estimate the total losses in all conductive and magnetically conductive media in individual structural elements of the permanent magnet motor under study. Unlike existing ones, the model built enables deriving the total losses in the calculation area; in permanent magnets, structural conductive elements, the armature winding, and in the magnetic core with hysteresis losses, eddy currents and additional losses caused by higher harmonics.
The task addressed is predetermined by the pressing scientific-practical issue related to increasing the energy efficiency of a high-speed permanent magnet motor used for electric transport systems and unmanned aerial vehicles. The use of a simplified, more technological rectangular shape of permanent magnets has been proposed. Applying permanent magnets of this configuration makes it possible to reduce the total losses in the motor by 23…41% depending on the type of power supply – sinusoidal or when powered by an inverter with PWM.
The use of a more technological form of permanent magnets leads to a decrease in the electromagnetic torque of the motor by approximately 18…30%, which is attributed to a decrease in the volume of active materials and an increase in the value of the equivalent air gap. At the same time, applying a modified form of permanent magnets makes it possible to reduce pulsations of the electromagnetic torque by 12%
References
- Ostroverkhov, M., Chumack, V., Falchenko, M., Kovalenko, M. (2022). Development of control algorithms for magnetoelectric generator with axial magnetic flux and double stator based on mathematical modeling. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (5 (120)), 6–17. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.267265
- Ji, W., Ni, F., Gao, D., Luo, S., Lv, Q., Lv, D. (2021). Electromagnetic Design of High-Power and High-Speed Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Considering Loss Characteristics. Energies, 14 (12), 3622. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14123622
- Tao, D., Zhou, K. L., Lv, F., Dou, Q., Wu, J., Sun, Y., Zou, J. (2020). Magnetic Field Characteristics and Stator Core Losses of High-Speed Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors. Energies, 13 (3), 535. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13030535
- Pan, B., Tao, D., Ge, B., Wang, L., Hou, P. (2022). Analysis of Eddy Current Loss of 120-kW High-Speed Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. Machines, 10 (5), 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10050346
- Cheng, M., Li, Z., Xu, S., Pei, R. (2024). Design and Calculation of Multi-Physical Field of Ultra-High-Speed Permanent Magnet Motor. Energies, 17 (13), 3072. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17133072
- Zhang, M., Luo, S., Liu, X., Li, W. (2021). The eddy current loss segmentation model of permanent magnet for temperature analysis in high‐speed permanent magnet motor. IET Power Electronics, 14 (4), 751–759. https://doi.org/10.1049/pel2.12009
- Bi, Q., Shao, D. (2023). Loss Analysis of High-Speed Permanent Magnet Motor for Cordless Vacuum Cleaner. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2488 (1), 012021. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/2488/1/012021
- Liu, Z., Zhang, G., Du, G. (2024). An Investigation into the Pole–Slot Ratio and Optimization of a Low-Speed and High-Torque Permanent Magnet Motor. Applied Sciences, 14 (10), 3983. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14103983
- Zeng, Y., Yang, S., Yang, X., Wang, Q., Zhang, L., Hao, J., Hua, W. (2023). Influence of Interference Fit and Temperature on High-Speed Permanent Magnet Motor. Applied Sciences, 13 (20), 11331. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132011331
- Wang, Y., Ge, B., Wang, L., Liu, S. (2023). Friction Loss Calculation and Thermal Analysis of Submerged Low Temperature High Speed Permanent Magnet Motor. IEEE Access, 11, 107116–107125. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2023.3320683
- Li, Z., Wang, P., Liu, L., Xu, Q., Che, S., Zhang, L. et al. (2022). Loss calculation and thermal analysis of ultra-high speed permanent magnet motor. Heliyon, 8 (11), e11350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11350
- Kovalenko, M., Tkachuk, I., Kovalenko, I., Zhuk, S., Kryshnov, O. (2024). Double stator axial flux magnetoelectric generator for conversion of low potential mechanical energy. Vidnovluvana Energetika, 2 (77), 13–20. https://doi.org/10.36296/1819-8058.2024.2(77).13-20
- Moradian, K., Sheikholeslami, T. F., Raghebi, M. (2022). Investigation of a spherical pendulum electromagnetic generator for harvesting energy from environmental vibrations and optimization using response surface methodology. Energy Conversion and Management, 266, 115824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2022.115824
- Chumack, V., Tsyvinskyi, S., Kovalenko, M., Ponomarev, A., Tkachuk, I. (2020). Mathemathical modeling of a synchronous generator with combined excitation. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (5 (103)), 30–36. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2020.193495
- Oh, Y., Sahu, M., Hajra, S., Padhan, A. M., Panda, S., Kim, H. J. (2022). Spinel Ferrites (CoFe2O4): Synthesis, Magnetic Properties, and Electromagnetic Generator for Vibration Energy Harvesting. Journal of Electronic Materials, 51 (5), 1933–1939. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-022-09551-5
- Kovalenko, M. A., Kovalenko, I. Y., Tkachuk, I. V., Harford, A. G., Tsyplenkov, D. V. (2024). Mathematical modeling of a magnetic gear for an autonomous wind turbine. Naukovyi Visnyk Natsionalnoho Hirnychoho Universytetu, 2, 88–95. https://doi.org/10.33271/nvngu/2024-2/088
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Mykhailo Kovalenko, Vadim Chumack, Viktor Grebenikov, Leonid Mazurenko, Ihor Tkachuk, Oleh Bazarov, Yehor Titov

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








