Construction of mathematical models of heat exchange in modern electronic devices with thermal active zones of canonical form
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.346809Keywords:
temperature field, thermal conductivity of material, thermal resistance of structures, thermally sensitive material, canonical regionAbstract
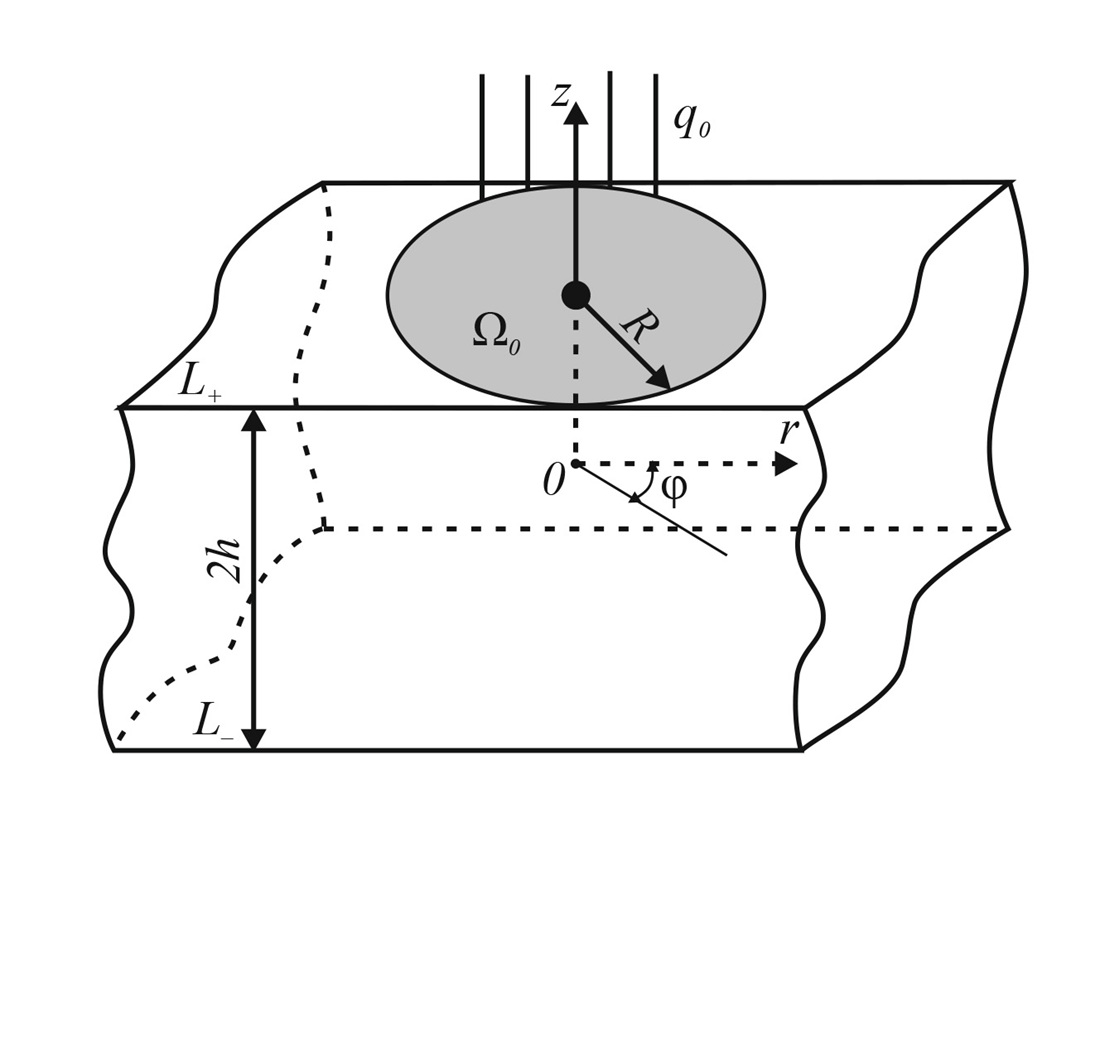
This study examines the heat exchange processes for thermally active and thermally sensitive individual nodes and elements in electronic devices that are subjected to thermal loads in the areas of canonical form. As a result of thermal loads, significant temperature gradients arise. To improve the accuracy of designing electronic devices and for their effective operation, linear and nonlinear mathematical models have been built to analyze their temperature regimes.
Based on the stated linear and nonlinear axisymmetric boundary value problems of heat conduction, their analytical and analytical-numerical solutions have been derived. Using these solutions has made it possible to establish the temperature distribution in spatial radial and axial coordinates for given geometric and thermophysical parameters (the chosen graphite has the ability to absorb a significant amount of heat at its thermal conductivity coefficient equal to 372 W/(m∙degree)).
To effectively describe canonical heating regions, the theory of generalized functions has been used. A technique for linearizing nonlinear mathematical models has been introduced. As a result, linear second-order differential equations with partial derivatives and a singular right-hand side have been derived.
The numerical results reflect the temperature distribution in the medium along the radial and axial coordinates for the given geometric and thermophysical parameters. The number of divisions of the interval (0; r*) was chosen to be 9, which made it possible to obtain numerical values of temperature with an accuracy of 10-6. The resulting numerical values of temperature for the selected materials with a linear temperature dependence of the thermal conductivity coefficient differ from the results obtained for its constant value by 5%.
The constructed mathematical models of heat transfer make it possible to analyze spatial isotropic media with respect to their thermal stability
References
- Nikitchuk, A. V. (2024). Impact of Electronic Components Thermal Resilience on the Reliability of Radio-Electronic Equipment. Visnyk NTUU KPI Seriia - Radiotekhnika Radioaparatobuduvannia, 98, 38–45. https://doi.org/10.20535/radap.2024.98.38-45
- Protsiuk, B. V. (2023). Nonstationary Problems of Heat Conduction for a Thermosensitive Plate with Nonlinear Boundary Condition on One Surface. Journal of Mathematical Sciences, 272 (1), 135–150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10958-023-06405-1
- Vovk, O. M. (2025). Thermal State of Two Contacting Thermosensitive Layers Under Complex Heat Exchange. Journal of Mathematical Sciences, 287 (2), 334–345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10958-025-07594-7
- Kozub, H. O., Kozub, Yu. H. (2020). Modeling of thermal processes in layered bodies. Geo-Technical Mechanics, 151, 234–244. https://doi.org/10.15407/geotm2020.151.234
- Fahmy, M. A. (2021). A new boundary element algorithm for modeling and simulation of nonlinear thermal stresses in micropolar FGA composites with temperature-dependent properties. Advanced Modeling and Simulation in Engineering Sciences, 8 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40323-021-00193-6
- Srinivas, V. B., Manthena, V. R., Bikram, J., Kedar, G. D. (2021). Fractional order heat conduction and thermoelastic response of a thermally sensitive rectangular parallelopiped. International Journal of Thermodynamics, 24 (1), 62–73. https://doi.org/10.5541/ijot.849663
- Brociek, R., Hetmaniok, E., Słota, D. (2024). Numerical Solution for the Heat Conduction Model with a Fractional Derivative and Temperature-Dependent Parameters. Symmetry, 16 (6), 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym16060667
- Povstenko, Y., Kyrylych, T., Woźna-Szcześniak, B., Yatsko, A. (2024). Fractional Heat Conduction with Heat Absorption in a Solid with a Spherical Cavity under Time-Harmonic Heat Flux. Applied Sciences, 14 (4), 1627. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14041627
- Peng, X., Li, X., Gong, Z., Zhao, X., Yao, W. (2022). A deep learning method based on partition modeling for reconstructing temperature field. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 182, 107802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2022.107802
- Basit, M. A., Imran, M., Mohammed, W. W., Ali, M. R., Hendy, A. S. (2024). Thermal analysis of mathematical model of heat and mass transfer through bioconvective Carreau nanofluid flow over an inclined stretchable cylinder. Case Studies in Thermal Engineering, 63, 105303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2024.105303
- Zhou, K., Ding, H., Steenbergen, M., Wang, W., Guo, J., Liu, Q. (2021). Temperature field and material response as a function of rail grinding parameters. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 175, 121366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2021.121366
- Mathew, J., Krishnan, S. (2021). A Review On Transient Thermal Management of Electronic Devices. Journal of Electronic Packaging. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4050002
- Liu, X., Peng, W., Gong, Z., Zhou, W., Yao, W. (2022). Temperature field inversion of heat-source systems via physics-informed neural networks. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 113, 104902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2022.104902
- Liu, H., Yu, J., Wang, R. (2023). Dynamic compact thermal models for skin temperature prediction of portable electronic devices based on convolution and fitting methods. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 210, 124170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2023.124170
- Coronel, A., Lozada, E., Berres, S., Huancas, F., Murúa, N. (2024). Mathematical Modeling and Numerical Approximation of Heat Conduction in Three-Phase-Lag Solid. Energies, 17 (11), 2497. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17112497
- Havrysh, V., Ovchar, I., Baranetskyj, J., Pelekh, J., Serduik, P. (2017). Development and analysis of mathematical models for the process of thermal conductivity for piecewise uniform elements of electronic systems. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (5 (85)), 23–33. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2017.92551
- Havrysh, V., Ivasyk, H., Kolyasa, L., Ovchar, I., Pelekh, Y., Bilas, O. (2017). Examining the temperature fields in flat piecewise- uniform structures. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2 (5 (86)), 23–32. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2017.97272
- Havrysh, V. I., Kosach, A. I. (2012). Boundary-value problem of heat conduction for a piecewise homogeneous layer with foreign inclusion. Materials Science, 47 (6), 773–782. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11003-012-9455-4
- Gavrysh, V., Tushnytskyy, R., Pelekh, Y., Pukach, P., Baranetskyi, Y. (2017). Mathematical model of thermal conductivity for piecewise homogeneous elements of electronic systems. 2017 14th International Conference The Experience of Designing and Application of CAD Systems in Microelectronics (CADSM), 333–336. https://doi.org/10.1109/cadsm.2017.7916146
- Havrysh, V., Kochan, V. (2023). Mathematical Models to Determine Temperature Fields in Heterogeneous Elements of Digital Devices with Thermal Sensitivity Taken into Account. 2023 IEEE 12th International Conference on Intelligent Data Acquisition and Advanced Computing Systems: Technology and Applications (IDAACS), 983–991. https://doi.org/10.1109/idaacs58523.2023.10348875
- Sokolovskyy, Y., Nechepurenko, A., Samotii, T., Yatsyshyn, S., Mokrytska, O., Yarkun, V. (2020). Software and Algorithmic Support for Finite Element Analysis of Spatial Heat-and-Moisture Transfer in Anisotropic Capillary-Porous Materials. 2020 IEEE Third International Conference on Data Stream Mining & Processing (DSMP), 316–320. https://doi.org/10.1109/dsmp47368.2020.9204175
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Vasyl Havrysh, Svitlana Yatsyshyn, Mykhailo Semerak, Mihaylo Klymiuk, Fedir Honchar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








