Change detection in side-scan sonar imagery based on deep learning feature matching methods
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.346940Keywords:
side-scan sonar, feature matching, deep learning, change detection, computer visionAbstract
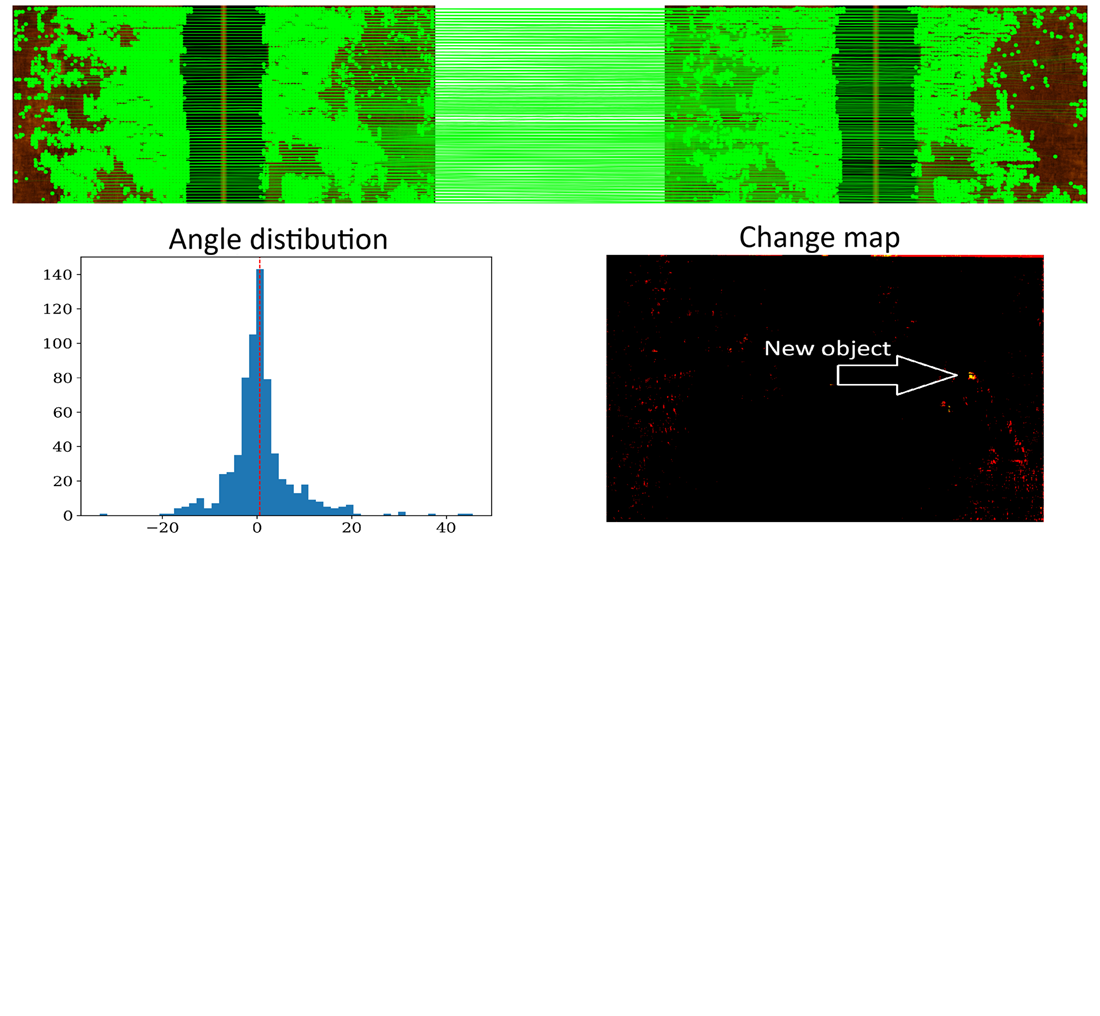
This paper explores change detection in repeat-track side-scan sonar imagery through feature matching. It addresses insufficient matching accuracy and stability in low-contrast, noisy, and geometrically distorted side-scan sonar imagery typically collected from surface vehicles. The experiment included a comparison of classical, convolutional, and transformer-based feature matching methods (SIFT, DISK, SuperPoint, LoFTR, and LightGlue) on two real-world datasets, Atlantic and Baltic. The results were evaluated quantitatively and qualitatively. Quantitative evaluation used displacement, angular stability, and reprojection error metrics, as well as resource consumption metrics like execution time and memory usage. In addition, matching maps and change maps for pairs of images were generated and analyzed qualitatively. All methods produced interpretable change maps for the low-noise Baltic dataset, whereas the wave-affected Atlantic dataset with stripe- and speckle noise only occasionally produced consistent maps. The SuperPoint + LightGlue method demonstrated the highest ratio of inlier correspondences after RANSAC filtering (43.4% and 65.6%) and the lowest mean reprojection error (36.0 and 3.9 px), while LoFTR provided the densest coverage (up to 97%) consuming up to 15× more computational resources. These results confirm the advantage of transformer-based matching methods under challenging conditions due to their global receptive field. In contrast, CNN-based methods performed better in low-noise, well-aligned images. Overall, the findings indicate that deep feature matchers can improve the applicability and reliability of change detection in tasks such as humanitarian demining, autonomous underwater navigation, image mosaicking, and related applications
References
- Zhou, X., Yuan, S., Yu, C., Li, H., Yuan, X. (2022). Performance Comparison of Feature Detectors on Various Layers of Underwater Acoustic Imagery. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10 (11), 1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10111601
- Shafique, A., Cao, G., Khan, Z., Asad, M., Aslam, M. (2022). Deep Learning-Based Change Detection in Remote Sensing Images: A Review. Remote Sensing, 14 (4), 871. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14040871
- Steiniger, Y., Schröder, S., Stoppe, J. (2022). Reducing the false alarm rate of a simple sidescan sonar change detection system using deep learning. 22nd International Symposium on Nonlinear Acoustics, 48, 070022. https://doi.org/10.1121/2.0001642
- Hedlund, W. (2024). Change Detection in Synthetic Aperture Sonar Imagery Using Segment Anything Model. Linköping University. Available at: https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/record.jsf?pid=diva2%3A1877741&dswid=6083
- Westman, E., Hinduja, A., Kaess, M. (2018). Feature-Based SLAM for Imaging Sonar with Under-Constrained Landmarks. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 3629–3636. https://doi.org/10.1109/icra.2018.8461004
- Alcantarilla, P., Nuevo, J., Bartoli, A. (2013). Fast Explicit Diffusion for Accelerated Features in Nonlinear Scale Spaces. Procedings of the British Machine Vision Conference 2013, 13.1-13.11. https://doi.org/10.5244/c.27.13
- Myers, V., Saebo, T. O., Hansen, R. (2018). Comparison of Co-Registration Techniques for Synthetic Aperture Sonar Images from Repeated Passes. Synthetic Aperture Sonar and Radar, 40 (2).
- Myers, V., Quidu, I., Zerr, B., Sabo, T. O., Hansen, R. E. (2020). Synthetic Aperture Sonar Track Registration With Motion Compensation for Coherent Change Detection. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 45 (3), 1045–1062. https://doi.org/10.1109/joe.2019.2909960
- Zhou, X., Yu, C., Yuan, X., Luo, C. (2021). Matching Underwater Sonar Images by the Learned Descriptor Based on Style Transfer Method. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2029 (1), 012118. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/2029/1/012118
- Zhang, J., Xie, Y., Ling, L., Folkesson, J. (2023). A fully‐automatic side‐scan sonar simultaneous localization and mapping framework. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 18 (5), 674–683. https://doi.org/10.1049/rsn2.12500
- Midtgaard, O., Hansen, R. E., Saebo, T. O., Myers, V., Dubberley, J. R., Quidu, I. (2011). Change detection using Synthetic Aperture Sonar: Preliminary results from the Larvik trial. OCEANS’11 MTS/IEEE KONA, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.23919/oceans.2011.6107272
- G-Michael, T., Marchand, B., Tucker, J. D., Marston, T. M., Sternlicht, D. D., Azimi-Sadjadi, M. R. (2016). Image-Based Automated Change Detection for Synthetic Aperture Sonar by Multistage Coregistration and Canonical Correlation Analysis. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1109/joe.2015.2465631
- Gode, S., Hinduja, A., Kaess, M. (2024). SONIC: Sonar Image Correspondence using Pose Supervised Learning for Imaging Sonars. 2024 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 3766–3772. https://doi.org/10.1109/icra57147.2024.10611678
- Lindenberger, P., Sarlin, P.-E., Pollefeys, M. (2023). LightGlue: Local Feature Matching at Light Speed. 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 17581–17592. https://doi.org/10.1109/iccv51070.2023.01616
- Barnes, C., Shechtman, E., Finkelstein, A., Goldman, D. B. (2009). PatchMatch. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 28 (3), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1145/1531326.1531330
- Zhang, J., Xie, Y., Ling, L., Folkesson, J. (2025). A Dense Subframe-Based SLAM Framework With Side-Scan Sonar. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 50 (2), 1087–1102. https://doi.org/10.1109/joe.2024.3503663
- Sun, J., Shen, Z., Wang, Y., Bao, H., Zhou, X. (2021). LoFTR: Detector-Free Local Feature Matching with Transformers. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 8918–8927. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr46437.2021.00881
- DeTone, D., Malisiewicz, T., Rabinovich, A. (2018). SuperPoint: Self-Supervised Interest Point Detection and Description. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). https://doi.org/10.1109/cvprw.2018.00060
- Tyszkiewicz, M. J., Fua, P., Trulls, E. (2020). DISK: Learning local features with policy gradient. arXiv. http://doi.org/10.48550/ARXIV.2006.13566
- Culjak, I., Abram, D., Pribanic, T., Dzapo H., Cifrek, M. (2012). A brief introduction to OpenCV. 2012 Proceedings of the 35th International Convention MIPRO, 1725–1730. Available at: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6240859/authors#authors
- Gutiérrez, G., Torres-Avilés, R., Caniupán, M. (2024). cKdtree: a Compact Kdtree for Spatial Data. Alberto Mendelzon Workshop on Foundations of Data Management. Available at: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/cKdtree%3A-a-Compact-Kdtree-for-Spatial-Data-Guti%C3%A9rrez-Torres-Avil%C3%A9s/1106acf86126909ec2ad8ffa174cbd6e4dcca329
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Oleksandr Katrusha, Dmytro Prylipko, Kostiantyn Yefremov

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








