Design of diamond drill heads with a hydrojet effect of rock destruction
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.265304Keywords:
drill heads, hydraulic jet destruction, informative core, diamond matrix, stepped, multistageAbstract
It follows from the analysis of materials related to the design and operation of drilling equipment that an important direction in the search for effective solutions appears to be the improvement of the structure of the working matrix of diamond drilling heads and the enhancement of their technological capabilities by using in their schemes physical effects that are unconventional in the field of well drilling technology.
The tasks to be solved are to reduce the energy costs of the process of deepening wells, to obtain a structurally integral, informative core, and to ensure the stability of well walls.
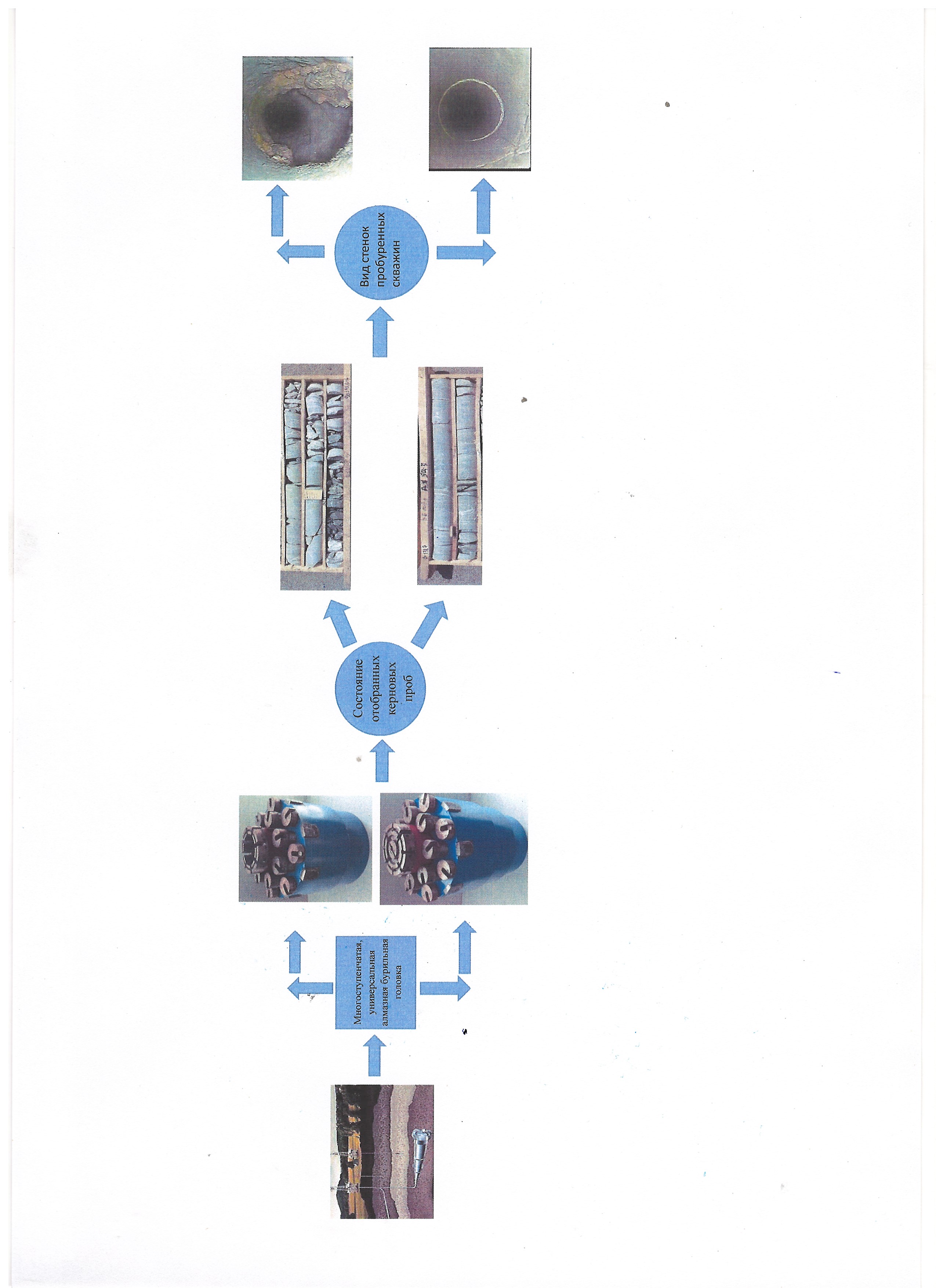
Following the concept, diamond drill heads with a separate system of washing channels and a hydrojet effect of rock destruction were designed and tested during the drilling of wells.
The novelty of the structure of drill heads is the direction of the pressure flow of liquid to the steps of the bottom of the wells, repeating the shape of the matrix, the removal of sludge along the grooves and radial grooves, the treatment of the well wall.
A special technology for the manufacture of diamond drill heads with a complex geometry of the matrix has been devised.
The performance of diamond drill heads of various designs was tested under the industrial conditions of drilling wells for water and at polymetal deposits. It has been established that in terms of the quality of the tasks to be solved and technical and economic indicators, they have a significant advantage in comparison with standard equipment in terms of the mechanical speed of drilling wells, energy costs, and structural integrity of the core.
The comparative states of the shape, the transverse size of the hydrogeological well, the purity of the treatment of the wall of the latter, drilled by diamond drill heads and standard equipment with ball bits, are indicative. The structural integrity of the core selected by the regular column set HQ in an assembly with drill heads with a hydrojet effect of rock destruction is ensured
References
- Niu, S., Zheng, H., Yang, Y., Tong, X., Chen, L., Liu, Y., Bao, Z. (2019). Experimental research on torque characteristic and weight distribution of the polycrystalline diamond compact–roller hybrid bit. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 11 (5), 168781401984974. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/1687814019849740
- Tan, Q., Guan, S. (2017). Application of Wellbore Stability Mechanics in Offshore Drilling With Complex Pressure. 4th ISRM Young Scholars Symposium on Rock Mechanics. Jeju.
- Fan, Y., Cui, S., Liu, H., Wu, P., Wang, X., Zhong, C., Meng, Y. (2021). Borehole wall tensile caving instability in the horizontal well of deep brittle shale. Science Progress, 104 (1), 003685042110023. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/00368504211002330
- Parshukova, L. A. (2017). Kompleksnyy podkhod k probleme ustoychivosti glinistykh porod pri burenii skvazhin. Bulatovskie chteniya, 3, 222–230.
- Berle, A., Adestål, V. (2018). Advances in Instrumented Coring. 80th EAGE Conference and Exhibition 2018. doi: https://doi.org/10.3997/2214-4609.201801554
- Isonkin, A. M. (2018). Vliyanie intensivnosti razrusheniya gornoy porody na effektivnost' primeneniya almaznykh burovykh koronok. Zhurnal «Veles», 12-1 (66), 20–32.
- Ivasiv, V., Yurych, A., Zabolotnyi, S., Yurych, L., Bui, V., Ivasiv, O. (2020). Determining the influence of the condition of rock-destroying tools on the rock cutting force. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (1 (103)), 15–20. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2020.195355
- Wang, J., Qian, D., Sun, Y., Peng, F. (2021). Design of Diamond Bits Water Passage System and Simulation of Bottom Hole Fluid Are Applied to Seafloor Drill. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9 (10), 1100. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9101100
- Regotunov, A. S. (2020). On the influence of some factors on the value of the energy intensity indicator for rock destruction during roller-bit drilling of blastholes. Setevoe periodicheskoe nauchnoe izdanie «Problemy nedropol'zovaniya», 3, 41–51. doi: https://doi.org/10.25635/2313-1586.2020.03.041
- Bugakov, V. I., Laptev, A. I. (2017). Manufacture of drill bits from new diamond materials at high pressures and temperatures. Steel in Translation, 47 (1), 12–16. doi: https://doi.org/10.3103/s0967091217010041
- Stoxreiter, T., Wenighofer, R., Portwood, G., Pallesi, S., Bertini, A., Galler, R., Grafinger, S. (2019). Rock fracture initiation and propagation by mechanical and hydraulic impact. Open Geosciences, 11 (1), 783–803. doi: https://doi.org/10.1515/geo-2019-0061
- Gao, Y., Xiang, X., Li, Z., Guo, X., Han, P. (2021). An experimental and simulation study of the flow pattern characteristics of water jet impingements in boreholes. Energy Exploration & Exploitation, 40 (2), 852–872. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/01445987211052063
- Brenner, V. A., Zhabin, A. B., Pushkarev, A. E. (2002). Perspektivy razvitiya gidrostruynykh tekhnologiy v gornodobyvayuschey promyshlennosti i podzemnom stroitel'stve. Gornye mashiny i avtomatika, 5, 2–10.
- Brenner, V. A., Zhabin, A. B., Pushkarev, A. E. (2005). Razrushenie gornykh porod pri pomoschi gidrostruynykh tekhnologiy. Nauchnye raboty Donetskogo natsional'nogo tekhnicheskogo universiteta, 99.
- Gorelikov, V. G. (2012). Konstruktivnye osobennosti almaznykh koronok dlya bureniya treschinovatykh gornykh porod. Zapiski gornogo instituta, 197, 29–33.
- Mendebaev, T. N., Izakov, B. K., Kalambaeva, A. S. (2018). Resursosberegayuschaya tekhnologiya bureniya skvazhin zaboynoy komponovkoy s gidroraspredelitelem i tonkostennymi almaznymi koronkami. Razvedka i okhrana nedr, 3, 41–43.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Toktamys Mendebaev, Nurlan Smashov

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








