Розробка методу підвищення завадостійкості систем з ортогональним частотним поділом каналів в умовах міжканальної інтерференції
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.282100Ключові слова:
формуючий імпульс Найквіста, імпульс з селективним спектром, кусково-лінійна апроксимація, міжканальна інтерференція, OFDMАнотація
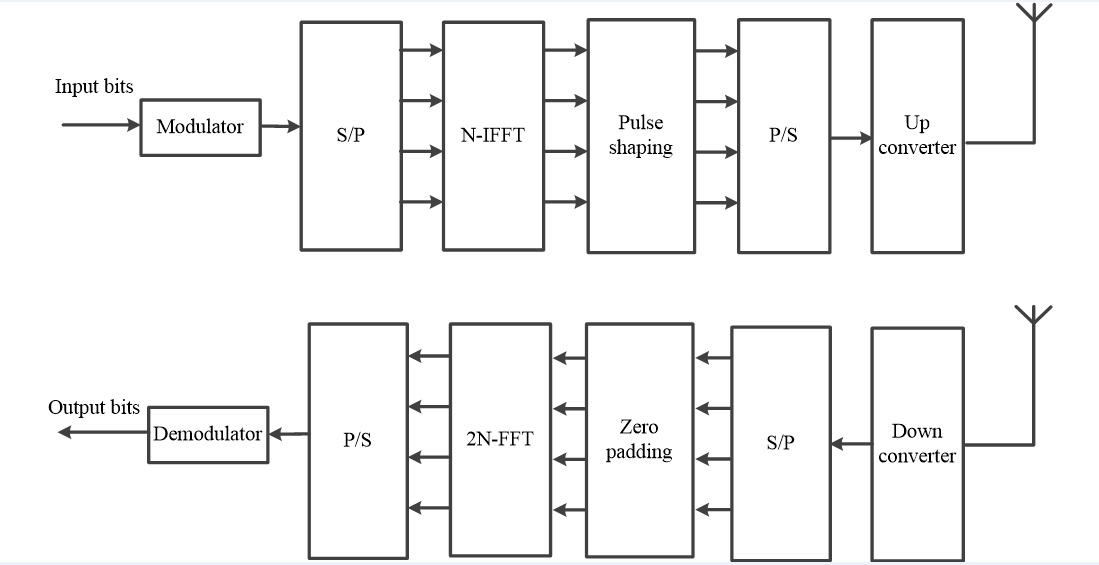
Сучасні системи зв’язку засновані на технології мультиплексування з ортогональним частотним поділом каналів (OFDM), яка дозволяє надійно передавати інформацію в умовах багатопроменевості. Необхідність збереження ортогональних властивостей піднесучих призводить до високої чутливості даних систем до частотних зсувів сигналу. У роботі удосконалений метод формування сигналу для OFDM системи. Досліджене застосування формуючих імпульсів з селективним спектром після етапу зворотнього швидкого перетворення Фур’є (IFFT) на стороні передавача для зменшення рівня міжканальних завад при зсуві частоти несучої. Синтезовані нові форми імпульсів, отримані з використанням оптимізованих багатопараметричних функцій з селективним спектром. Проаналізована ефективність застосування синтезованих імпульсів з селективним спектром щодо зменшення впливу частотного зсуву сигналу на завадостійкість OFDM системи. Проведене порівняння ймовірності бітової помилки з вже існуючими формами імпульсів Найквіста. У середовищі MATLAB розроблена модель передавача і приймача OFDM системи для експериментальної оцінки впливу запропонованих формуючих імпульсів на завадостійкість системи в умовах міжканальної інтерференції при різних видах модуляції. Встановлено, що найменший рівень ймовірності бітової помилки в умовах міжканальної інтерференції спостерігається для двопараметричного імпульсу з селективним спектром та кусково-лінійною апроксимацією перехідної області. Так, для відношення сигнал/шуму 15 дБ, модуляції BPSK та нормованого частотного зсуву 0,2 ймовірність бітової помилки для даного імпульсу становить 3∙10-4, для модуляції QPSK та нормованого частотного зсуву 0,1–10-6, для модуляції QAM-16 та нормованого частотного зсуву 0,03–2∙10-4
Посилання
- Singh, P., Sahu, O. P. (2015). An Overview of ICI Self Cancellation Techniques in OFDM Systems. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence & Communication Technology. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/cict.2015.113
- Kumar, N., Kaur, G., Sohi, B. S. (2015). Comparative Analysis of Various Inter-Carrier Interference Cancellation Methods. International Journal of Wireless and Microwave Technologies, 5 (3), 18–32. doi: https://doi.org/10.5815/ijwmt.2015.03.02
- Tan, P., Beaulieu, N. C. (2009). Analysis of the effects of Nyquist pulse-shaping on the performance of OFDM systems with carrier frequency offset. European Transactions on Telecommunications, 20 (1), 9–22. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/ett.1316
- Muschallik, C. (1996). Improving an OFDM reception using an adaptive Nyquist windowing. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 42 (3), 259–269. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/30.536046
- ETSI TS 136 211 V17.1.0 LTE. Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA). Physical channels and modulation. Available at: https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_ts/136200_136299/136211/17.01.00_60/ts_136211v170100p.pdf
- Muller-Weinfurtner, S. H., Huber, J. B. (2000). Optimum Nyquist windowing for improved OFDM receivers. Globecom ’00 - IEEE. Global Telecommunications Conference. Conference Record (Cat. No.00CH37137). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/glocom.2000.891232
- Song, R., Guo, X., Leung, S. H. (2011). Optimum Second Order Polynomial Nyquist Windows for Reduction of ICI in OFDM Systems. Wireless Personal Communications, 65 (2), 455–467. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-011-0267-x
- Kamal, S., Azurdia-Meza, C. A., Lee, K. (2016). Suppressing the effect of ICI power using dual sinc pulses in OFDM-based systems. AEU - International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 70 (7), 953–960. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeue.2016.04.013
- Kamal, S., Azurdia-Meza, C. A., Lee, K. (2017). Improved Nyquist-I Pulses to Enhance the Performance of OFDM-Based Systems. Wireless Personal Communications, 95 (4), 4095–4111. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4044-3
- Balan, A. L., Alexandru, N. D. (2012). Two improved nyquist filters with piece-wise rectangular-polynomial frequency characteristics. AEU - International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 66 (11), 880–883. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeue.2012.03.006
- Alexandru, N. D., Balan, A. L., Diaconu, F., Dimian, M. (2013). Development of Improved Nyquist Filters with piecewise linear frequency characteristics. 2013 36th International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing (TSP). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/tsp.2013.6614023
- Alexandru, N. D., Balan, A. L. (2014). Investigation of the mechanism of improvement in improved Nyquist filters. IET Signal Processing, 8 (1), 95–105. doi: https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-spr.2013.0050
- Sharique, M., Chaturvedi, A. K. (2015). Transmitter Pulse Shaping to Reduce OOB Power and ICI in OFDM Systems. Wireless Personal Communications, 83 (2), 1567–1578. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2464-5
- Xiao, J., Yu, J., Cao, Z., Li, F., Chen, L. (2013). Flipped-exponential Nyquist pulse technique to optimize the PAPR in optical direct detection OFDM system. Optics Communications, 286, 176–181. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2012.08.053
- Jayaprakash, A., Reddy, G. R. (2015). Discrete Ambiguity Function Based Analysis of Filter Bank Multicarrier Systems. IETE Technical Review, 32 (5), 330–346. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/02564602.2015.1015941
- Kongara, K. P., Smith, P. J., Mann, S. (2008). A comparison of CP-OFDM with IOTA-OFDM under typical system imperfections. IET Seminar Digests. doi: https://doi.org/10.1049/ic.2008.0694
- Sukachev, E. A. (2016). Vvedenie v teoriyu signalov Naykvista. Odessa: Osvita Ukrainy, 108.
- Proakis, J. G., Salehi, M. (2008). Digital Communications. McGraw-Hill. Available at: https://edisciplinas.usp.br/pluginfile.php/5636847/mod_resource/content/1/digital%20commun%205th%20-%20proakis%2C%20salehi.pdf
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2023 Rostyslav Bykov

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.
Ліцензійний договір – це документ, в якому автор гарантує, що володіє усіма авторськими правами на твір (рукопис, статтю, тощо).
Автори, підписуючи Ліцензійний договір з ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР», мають усі права на подальше використання свого твору за умови посилання на наше видання, в якому твір опублікований. Відповідно до умов Ліцензійного договору, Видавець ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР» не забирає ваші авторські права та отримує від авторів дозвіл на використання та розповсюдження публікації через світові наукові ресурси (власні електронні ресурси, наукометричні бази даних, репозитарії, бібліотеки тощо).
За відсутності підписаного Ліцензійного договору або за відсутністю вказаних в цьому договорі ідентифікаторів, що дають змогу ідентифікувати особу автора, редакція не має права працювати з рукописом.
Важливо пам’ятати, що існує і інший тип угоди між авторами та видавцями – коли авторські права передаються від авторів до видавця. В такому разі автори втрачають права власності на свій твір та не можуть його використовувати в будь-який спосіб.









