Interpretation of laboratory results through comprehensive automation of medical laboratory using OpenAI
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.286338Keywords:
information system, OpenAI, interpretation, laboratory analyzers, equipmentAbstract
In modern medicine, laboratory tests play an important role in the diagnosis, treatment and monitoring of patients. However, the volume and complexity of the data obtained can create challenges for interpreting the results. In this paper, we present a study on the application of integrated automation of a medical laboratory using OpenAI for a more accurate and effective interpretation of laboratory results.
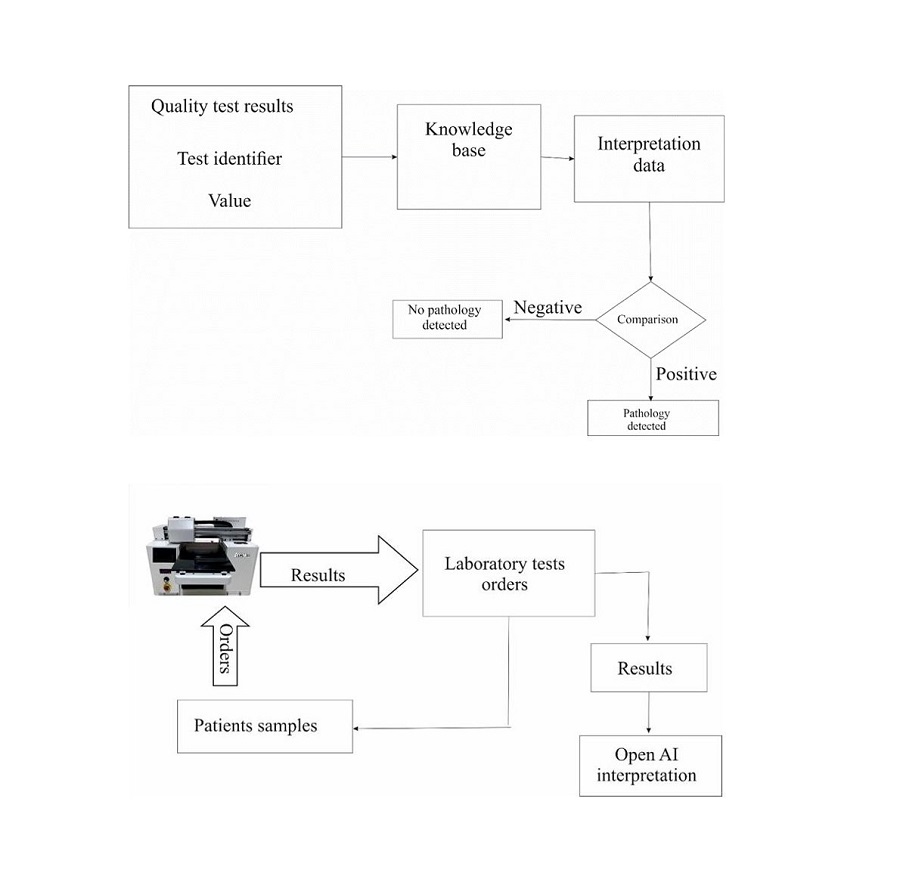
Interpreting laboratory results through integrated automation using artificial intelligence (AI) and other digital technologies automatically analyzes and interprets laboratory results. This approach aims to streamline the process of interpreting laboratory results and provide more accurate, consistent and timely results to healthcare providers. Comprehensive automation of the interpretation of laboratory results can improve the efficiency and accuracy of laboratory results, leading to improved patient outcomes and better clinical decision-making. However, it is essential to note that AI models are imperfect and can still make mistakes. Therefore, healthcare professionals should always review automated interpretation results before diagnosing or treating. The work presented results in applying OpenAI to interpret laboratory results in the laboratory information system smartLAB Kazakhstan, which provides a complete cycle of automation of all medical laboratory processes.
In the course of the study, an automated information system of a medical research complex using artificial intelligence was developed and implemented
References
- Abdumanonov, A. A. (2016). Osobennosti razrabotki avtomatizirovannykh rabochikh mest polzovatelei meditcinskikh informatcionnykh sistem. Simvol nauki, 1-2, 11–14. Available at: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/osobennosti-razrabotki-avtomatizirovannyh-rabochih-mest-polzovateley-meditsinskih-informatsionnyh-sistem
- Yu, K.-H., Beam, A. L., Kohane, I. S. (2018). Artificial intelligence in healthcare. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2 (10), 719–731. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-018-0305-z
- Herman, D. S., Rhoads, D. D., Schulz, W. L., Durant, T. J. S. (2021). Artificial Intelligence and Mapping a New Direction in Laboratory Medicine: A Review. Clinical Chemistry, 67 (11), 1466–1482. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/clinchem/hvab165
- Guliyev, Ya. I., Tsvetkov, A. A. (2016). Ensuring Information Security in Healthcare Organizations. Doctor and Information Technology, 6, 49–62. Available at: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/obespechenie-informatsionnoy-bezopasnosti-v-meditsinskih-organizatsiyah
- Demirci, F., Akan, P., Kume, T., Sisman, A. R., Erbayraktar, Z., Sevinc, S. (2016). Artificial Neural Network Approach in Laboratory Test Reporting. American Journal of Clinical Pathology, 146 (2), 227–237. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcp/aqw104
- Mencacci, A., De Socio, G. V., Pirelli, E., Bondi, P., Cenci, E. (2023). Laboratory automation, informatics, and artificial intelligence: current and future perspectives in clinical microbiology. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 13. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2023.1188684
- Evgina, S. A., Gusev, A. V., Shamanskiy, M. B., Godkov, M. A. (2022). Artificial intelligence on the doorstep of the laboratory. Laboratornaya Sluzhba, 11 (2), 18. doi: https://doi.org/10.17116/labs20221102118
- Rabbani, N., Kim, G. Y. E., Suarez, C. J., Chen, J. H. (2022). Applications of machine learning in routine laboratory medicine: Current state and future directions. Clinical Biochemistry, 103, 1–7. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2022.02.011
- Jackins, V., Vimal, S., Kaliappan, M., Lee, M. Y. (2020). AI-based smart prediction of clinical disease using random forest classifier and Naive Bayes. The Journal of Supercomputing, 77 (5), 5198–5219. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-020-03481-x
- Renjit, J. A., Shunmuganathan, K. L. (2010). Distributed and cooperative multi-agent based intrusion detection system. Indian Journal of Science and Technology, 3 (10), 1070–1074. doi: https://doi.org/10.17485/ijst/2010/v3i10.2
- Ilin, I. V., Levina, A. I., Iliashenko, O. Yu. (2017). Reengineering of high-tech and specialized Medical care delivery process for telemedicine system implementation. Proceedings of the 29th International Business Information Management Association Conference – Education Excellence and Innovation Management through Vision 2020: From Regional Development Sustainability to Global Economic Growth 2017, 1822–1831.
- Laboratory information system – a solution for automation of work processes in modern laboratories. Available at: www.lis.kz
- Health Level Seven International. Available at: https://wiki.hl7.org/Main_Page.
- International Association for Testing Materials. Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ASTM_International.
- Models. V4 of the OpenAI Typescript. Available at: https://platform.openai.com/docs/api-reference/models
- API reference. Available at: https://platform.openai.com/docs/api-reference
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Kuanysh Kadirkulov, Aisulu Ismailova, Aliya Beissegul, Sandugash Serikbayeva, Dinara Kazimova, Gulmira Tazhigulova

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








