Identifying regularities of the structure and properties of 13ХFА pipe steel smelted on different charges in electric arc furnace
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.287043Keywords:
selection of metal waste, pipe steel, heat treatment, temper brittleness, cold resistance, oil and gas industryAbstract
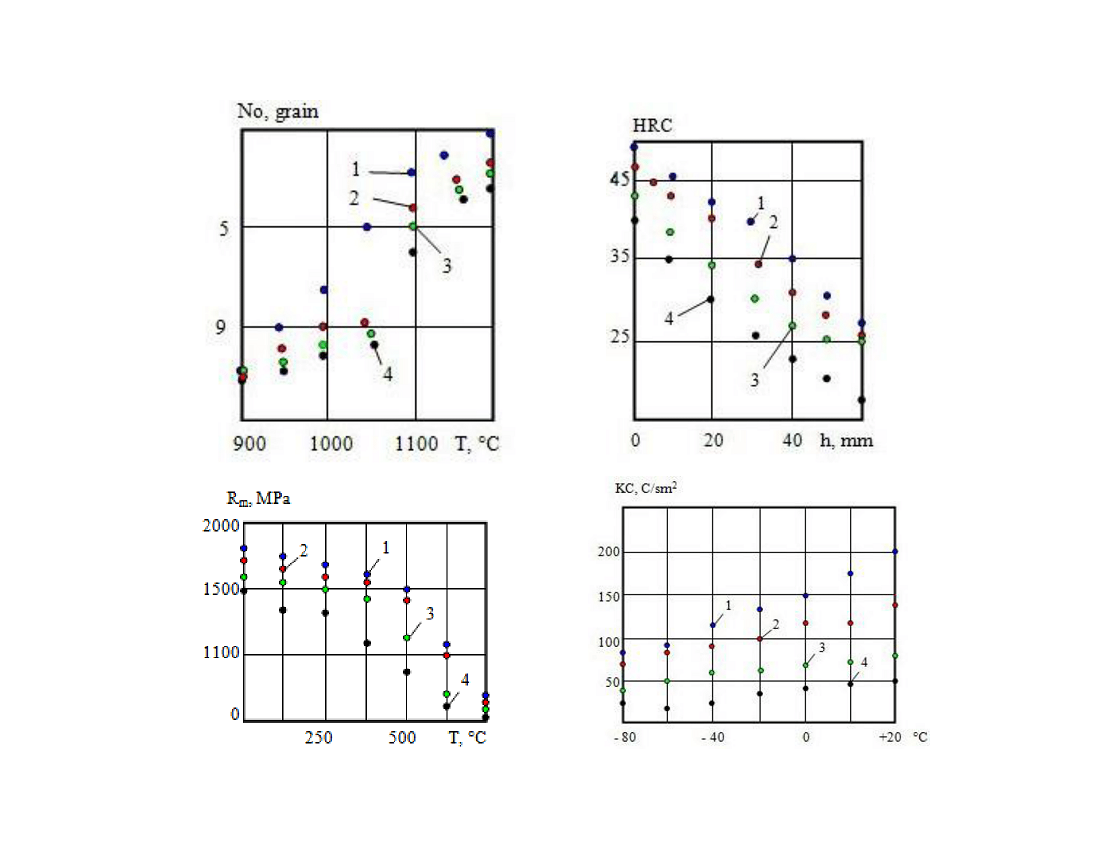
The problem of increasing the efficiency of 13ХFА pipe steel for oil and gas wells by using selective selection of charges for smelting them in an electric arc furnace is considered. 4 batches of different chemical heterogeneity were studied. It was found that melt 1 from a purer charge 1 contains a smaller amount of harmful impurities in the form of surface-active substances (surfactants), which affect grain growth when samples are heated for quenching. Thus, melts 1 and 2, containing a smaller amount of surfactants in the charge, have a greater tendency to austenite grain growth and lower hardenability compared to melts 3 and 4, the charge of which is relatively heavily contaminated with surfactants. This is due to the low relatively free energy of melts 3 and 4. The study showed that at a relatively low tempering temperature (300 °С) there was an insignificant change in the mechanical properties of the samples (Rm, KC, etc.). Hydrogenation of steels significantly reduces the strength of steels from all melts, however, an increase in tempering time leads to an increase in long-term strength. In this case, the maximum impact strength (KC) of all melts is observed after normalization, but samples from melt 1 have a higher IC. When the samples were held (570 °С), the near-boundary layers of steel grains were enriched with P, Sb, Sn, As, leading to embrittlement and weakening of intergrain cohesion and a decrease in the energy of boundaries. In the process of testing at –80 °С, cracks along the grain boundaries are visible on the fractures of the samples after brittle tempering. By increasing the purity of metal waste for smelting pipe steel, it is possible to improve the complex of its properties, and hence the durability of seamless pipes for the oil and gas industry produced from it.
References
- Raxmanov, S. R., Mamedov, A. T., Bespalko, B. N., Topolov, V. A., Azimov, A. A. (2017). Maşinostroitelnıye materialı. Baku: «Sabax», 410.
- Qoldenşteyn, M. İ., Qrachov, S. V., Veksler, Yu. B. (1999). Specialnıye stali. Мoscow: МİSİS, 408.
- Kərimov, R. İ., Quliyev, F. T. (2017). Baku Steel Company MMC-də elektroqövs sobasında isti briketlənmiş (HBİ) yuvarlar istifadə etməklə əritmə intensivliyinin artırılması və prosesin təhlili. Metallurgiya və materialşunaslığın problemləri. Mövzusunda 2-ci Beynəlxalq elmi-texniki konfransın materialları. Bakı, 39–41.
- Kerimov, R. I. oglu. (2019). Improving steel melting intensity in the process of electrosmelting from waste and pellets (HBI). Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 3 (1 (99)), 35–42. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2019.168352
- Chubukov, M. Yu. (2019). İssledovanie staley s razlichnımi variantami ximicheskoqo sostava, obespechivayushimi povısheniye kachestva neprerıvnolitıx zaqotovok dlya nefteqazoprovodnıx trub. Volqoqrad, 153.
- Kərimov, R. İ. (2021). Elektroəritmə və fasiləsiz tökmə polad pəstahların resurslara qənaətli texnologiyasının nəzəri əsaslandırılması və tətbiqi. Bakı, 304.
- Yakovleva, İ. L., Tereshenko, N. A., Urtsev, N. V. (2020). Nablyudenie martensitno-austenitnoy sostavlyayushey v structure nizkouqlerodistoy i nizkolegirovannoy trubnoy stali. Fizika metallov i metallovedenie, 121 (4), 396–402. doi: https://doi.org/10.31857/s0015323020040178
- Mekerov, S. K., Kincharov, A. İ., Stepanov, P. P., Saxnevich, A. N. (2019). Opit ecspluatachii trubnoy stali novoqo pokoleniya v usloviyax volqo-uralskiy nefteqazonosniy provintsii. İnjenernaya praktika, 10, 152–163.
- Zavalishin, A. N., Rumyantsev, M. I., Kojevnikova, E. V. (2023). Effect of quenching and tempering on the structure and properties of hot-rolled tube steels of strength categories K60 and K65. MiTOM, 1, 13–18. doi: https://doi.org/10.30906/mitom.2023.1.13-18
- Putilova, Е. А. (2018). Study of the main features of the structure, physical and mechanical properties of the tube steel of durability class P110. Mejdunarodniy nauchno-issledovatelskiy jurnal, 12 (78), 128–132. doi: https://doi.org/10.23670/IRJ.2018.78.12.022
- Şərifov, Z. Z. (2014). Materialşünaslıq və materiallar texnologiyası. Bakı: ADDA, 660.
- Laxtin, Yu. М., Leonteva, V. P. (1990). Materialovedeniye. Uchebnik dlya vishix texnicheskix uchebnix zavedeniy. Мoscow: Mashinostroyenie, 528.
- Kuzin, О. А., Yachyuk, R. А. (2002). Metaloznavstvo ta termichna obrobka metaliv. Lviv: Afisha, 30.
- Solnsev, Yu. P., Paryaxin, Е. İ. (2020). Materialovedeniye. Sankt-Peterburg, 784.
- Тaran, Yu. N., Тubenko, S. İ., Bolshakov, V. İ. et al. (2001). Noviye materiali. Dnepropetrovsk, 54.
- Velychko, O. H., Stoianov, O. M., Boichenko, B. M., Niyazev, K. H. (2016). Tekhnolohiyi pidvyshchenyia yakosti stali. Dnepropetrovsk: Seredniak T.K, 196.
- Velichko, А. Т., Raxmanov, S. R., Babnli, М. В., Mamedov, А. Т., Bayramov, А. Т. (2021). Vnepechnaya obrabotka pri proizvodstve visokokachestvennix staley. Baku, 467.
- Velichko, А. Q. (2005). Vnepechnaya obrabotka stali. Dnepropetrovsk, 199.
- Misnev, P. A., Adigamov, R. A., Baraboshkin, K. A., Varkhaleva, T. S., Fedotov, E. S., Karlina, A. I. (2022). Mathematical models for pediction of korrozion resistance of pipe steel qrades in CO2 environment. Ferrois Metallurgy. Bulletin of Scientitic, Techical and Economic information, 78 (7), 611–619.
- Serqeev, A. N., Serqeev, N. N., Aqeev, V. S. (2022). Vodorodnnoe oxrupchivanie i rastreskivanie visokoprochnoy armaturnoy stali 20ХГС2. Litovskaya respublika, 158.
- Astafjev, V. I., Artamoshkin, S. V., Tetjueva, T. V. (1993). Influence of microstructure and non-metallic inclusions on sulphide stress corrosion cracking in low-alloy steels. International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 55 (2), 243–250. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/0308-0161(93)90032-o
- Botvina, L. R., Tetyueva, T. V., İoffe, A. V. (1998). Stadiynost mnojestvennoqo razrusheniya nizkoleqirovannix staley v srede serodoroda. Metallovedenie i termicheskaya obrabotka metallov, 2, 14–22.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Arif Mammadov, Agil Babaev, Nizami Ismailov, Mukhtar Huseinov, Faiq Guliyev

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








