Physico – chemical study of the adsorption properties of natural minerals for sorption treatment of wastewater from Pb+2, Ni+2, Zn+2 ions
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.298913Keywords:
water, adsorbent, metal, bentonite, diatomite, sorption, purification, minerals, extraction, kineticsAbstract
One of the urgent challenges is to clean up industrial wastewater from toxic and heavy metal ions in a more efficient and environmentally friendly way.
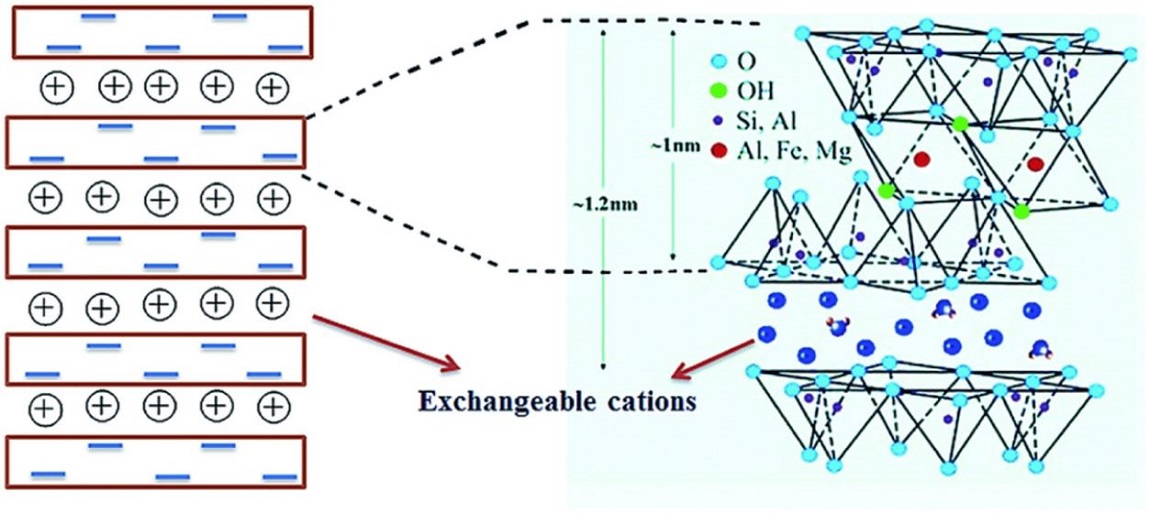
Bentonite montmorillonite, bentonite red, zeolite and diatomite of the Almaty region were selected as the materials of the study.
In this study was investigated the adsorption properties of natural minerals by physico-chemical methods for the sorption treatment of wastewater from Pb+2, Ni+2, Zn+2 ions.
X – ray phase analysis determines the chemical composition of the materials studied. The main component of diatomite is SiO2, in zeolite – Laumontite composition Ca4Al8Si16O48·14H2O (51.3 %). The base of bentonites is bedellite – montmorillonite, which has an amorphous structure. The method of atomic absorption spectrometry was used to investigate the sorption of heavy metal ions (Pb+2, Ni+2, Zn+2) by the natural adsorbents under investigation. Bentonites, Mukra and Medium Tentec have the best sorption properties. Here, the content of lead, nickel and zinc ions is reduced by an average of 82–85 %. In the case of diatomite, the ion content of the same metals is reduced by approximately 74–76 %, and for zeolite by 64 %. Generally speaking, the adsorption properties of these minerals are expected to be achieved by the high porosity in the case of diatomite and zeolite or the penetration of ions into the interpackage space between the bentonite layers. Mixing adsorbents, increasing their mass percentages and increasing the mass of the mixture leads to increased efficiency of the degree of cleaning from these ions.
In conclusion of the study, natural minerals of the Almaty region have sorption properties that can be used for practical purposes, in particular for wastewater treatment
References
- Politaeva, N., Taranovskaya, E., Mukhametova, L., Ilyashenko, S., Atamanyuk, I., Afif, R. A., Pfeifer, C. (2020). Cotton Fiber and Carbon Materials Filters for Efficient Wastewater Purification. International Journal of Technology, 11 (8), 1608. https://doi.org/10.14716/ijtech.v11i8.4538
- Carolin, C. F., Kumar, P. S., Saravanan, A., Joshiba, G. J., Naushad, Mu. (2017). Efficient techniques for the removal of toxic heavy metals from aquatic environment: A review. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 5 (3), 2782–2799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.05.029
- Wadhawan, S., Jain, A., Nayyar, J., Mehta, S. K. (2020). Role of nanomaterials as adsorbents in heavy metal ion removal from waste water: A review. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 33, 101038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.101038
- Atamanova, O. V., Tichomirova, E. I., Politayeva, N. A., Podolsky, A. L., Istrashkina, M. V. (2019). Innovative technologies for industrial wastewater treatment. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 288 (1), 012001. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/288/1/012001
- Kuznetsova, E., Akulova, A., Motovilov, A. (2016). Problems and solutions for processing and disposal of sewage galvanic production. Eurasian Union of Scientists, 3 (24), 109–112.
- Atamanova, O., Tikhomirova, E., Koshelev, A., Istrashkina, M., Politayeva, N., Podolsky, A. (2019). Wastewater treatment of industrial enterprises via adsorption method. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 337 (1), 012010. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/337/1/012010
- Boriskov, D., Efremova, S., Komarova, N., Tikhomirova, E., Bodrov, A. (2021). Applicability of the modified diatomite for treatment of wastewater containing heavy metals. E3S Web of Conferences, 247, 01052. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202124701052
- Obuzdina, M., Rush, E. (2019). New sorption materials based on modification of natural zeolites in metal wastewater treatment processes. E3S Web of Conferences, 140, 08001. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/201914008001
- Veprikova, E. V., Tereshchenkoa, E. A., Chesnokova, N. V., Shchipkova, M. L., Kuznetsova, B. N. (2010). Features of water purification from petroleum products using petroleum sorbents, filter materials and active carbons. Filtering Materials and Active Coals Journal of Siberian Federal University, 3 (3), 285–304.
- Feofanov, Yu. A., Mishukov, B. G., Podporin, A. V., Feofanov, M. Yu. (2017). Evaluation of the effectiveness of the use of various sorption materials for cleaning of oil-containing water. Water Magazine, 5 (117).
- Petukhova, Yu. N., Ilyina, S. I., Fursenko, A. V., Nosyrev, M. A. (2019). Ochistka stochnyh vod ot ionov tyazhelyh metallov s pomoshch'yu sorbentov. EurasianUnionScientists, 6 (64). https://doi.org/10.31618/esu.2413-9335.2019.6.64.254
- Kurilina, T. A., Andreeva, S. A., Kurilin, S. S. (2016). Sorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions with a modified sorbent. Eurasian Union of Scientists, 1 (22), 26–29.
- Surkova, T., Abdikerim, B., Berkinbayeva, A., Azlan, M. N., Baltabekova, Zh. A. (2022). Obtaining modified sorbents based on natural raw materials of Kazakhstan and research of their properties. Kompleksnoe Ispolʹzovanie Mineralʹnogo Syrʹâ/Complex Use of Mineral Resources/Mineraldik Shikisattardy Keshendi Paidalanu, 322 (3), 23–32. https://doi.org/10.31643/2022/6445.25
- Dehmani, Y., Ba Mohammed, B., Oukhrib, R., Dehbi, A., Lamhasni, T., Brahmi, Y. et al. (2024). Adsorption of various inorganic and organic pollutants by natural and synthetic zeolites: A critical review. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 17 (1), 105474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2023.105474
- Mudaber, S Batur, J. (2023). Differences in Heavy Metals Adsorption on Natural, Modified, and Synthetic Zeolites-A Review. Journal of the Turkish Chemical Society Section A: Chemistry, 10 (3), 847–860. https://doi.org/10.18596/jotcsa.1263041
- Bikulova, V. Zh., Latypova, F. M., Mukhametdinova, L. Kh. (2013). Adsorption treatment of industrial wastewater from zinc ions. Technologies of Industrial and Domestic Water Treatment, 3, 37–39.
- Gholikandi, G. B., Baneshi, M. M., Dehghanifard, E., Salehi, S., Yari, A. R. (2010). Natural zeolites application as sustainable adsorbent for heavy metals removal from drinking water. Iranian J. of Toxicology, 3 (3), 302–310. Available at: http://ijt.arakmu.ac.ir/article-1-53-en.html
- Ju, O., Ibe, E. (2014). Adsorption studies of heavy metals by low-cost adsorbents. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manage, 18 (3), 443–448. Available at: http://www.bioline.org.br/pdf?ja14060
- Surchi, K. M. S. (2011). Agricultural Wastes as Low Cost Adsorbents for Pb Removal: Kinetics, Equilibrium and Thermodynamics. International Journal of Chemistry, 3 (3). https://doi.org/10.5539/ijc.v3n3p103
- Khadhraoui, M., Watanabe, T., Kuroda, M. (2002). The effect of the physical structure of a porous Ca-based sorbent on its phosphorus removal capacity. Water Research, 36 (15), 3711–3718. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0043-1354(02)00096-9
- Khraisheh, M. A. M., Al‐Ghouti, M. A., Allen, S. J., Ahmad, M. N. M. (2004). The Effect of pH, Temperature, and Molecular Size on the Removal of Dyes from Textile Effluent Using Manganese Oxides‐Modified Diatomite. Water Environment Research, 76 (7), 2655–2663. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1554-7531.2004.tb00227.x
- Zhao, G. (2011). Sorption of Heavy Metal Ions from Aqueous Solutions: A Review. The Open Colloid Science Journal, 4 (1), 19–31. https://doi.org/10.2174/1876530001104010019
- Bokiev, B., Khujaev, P., Sharipov, Sh., Murodov, P. (2018). Sorption method for purification of industrial wastewater waters. Bulletin of Science and Practice, 4 (7), 203–209.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Manshuk Murzagaliyeva, Nazgul Ashimkhan, Ardak Sapiyeva, Gulnur Daribayeva

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.









