Development of conditions for obtaining oil from sunflower oil hydration waste
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.301418Keywords:
waste of the oil and fat industry, phosphatide concentrate, sodium chloride, rational hydration conditionsAbstract
The object of the study is the process of treatment of sunflower phosphatide concentrate using sodium chloride solution.
Hydration is a stage of oil refining. The waste of the process is a phosphatide concentrate, the disposal of which is dangerous to the environment. The concentrate contains valuable components – oil and phosphatides. An important task is to separate these components for effective use in various industries.
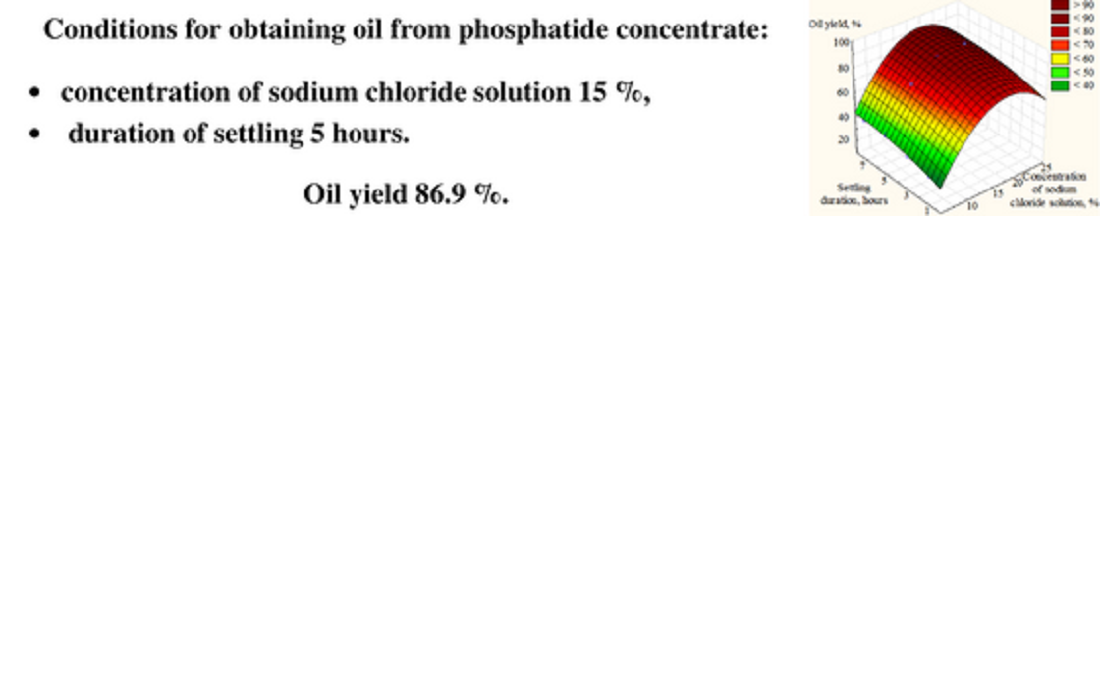
The process of extracting oil from phosphatide concentrate by hydration in the presence of sodium chloride solution was investigated. The influence of the concentrate treatment conditions on the oil yield was determined.
A sample of concentrate according to SOU 15.4-37-212:2004 (CAS 3436-44-0) was used: mass fraction of moisture and volatile substances – 2.8 %, mass fraction of phosphatides – 41.5 %. The concentrate was treated with sodium chloride solution with a concentration of (5–20) %. The hydration time was 25 min., the temperature was 45 °C, and the mass ratio of the sodium chloride solution to the concentrate was 1:1.
Conditions for the concentrate treatment were determined: the concentration of sodium chloride solution was 15 %, settling time was 5 hours. At the same time, the yield of oil was 86.9 %.
The parameters of the extracted oil were determined: acid value 2.8 mg KOH/g, peroxide value 3.2 ½ O mmol/kg, mass fraction of moisture and volatile substances 0.12 %. According to these indicators, the extracted oil corresponds to first-grade unrefined unfrozen sunflower oil according to DSTU 4492. The mass fraction of phosphorus-containing substances in terms of stearooleolecithin was 1.7 %, which slightly exceeds the standard value.
The research results make it possible to process hydration waste and obtain oil, which is a raw material for the products of many industries. This will help solve the problem of disposal of environmentally hazardous waste and improve the state of the environment
References
- Lamas, D. L., Constenla, D. T., Raab, D. (2016). Effect of degumming process on physicochemical properties of sunflower oil. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 6, 138–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2016.03.007
- Wang, M., Yan, W., Zhou, Y., Fan, L., Liu, Y., Li, J. (2021). Progress in the application of lecithins in water-in-oil emulsions. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 118, 388–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2021.10.019
- Vambol, S., Vambol, V., Sobyna, V., Koloskov, V., Poberezhna, L. (2019). Investigation of the energy efficiency of waste utilization technology, with considering the use of low-temperature separation of the resulting gas mixtures. Energetika, 64 (4). https://doi.org/10.6001/energetika.v64i4.3893
- Ahmad, T., Belwal, T., Li, L., Ramola, S., Aadil, R. M., Xu, Y., Zisheng, L. (2020). Utilization of wastewater from edible oil industry, turning waste into valuable products: A review. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 99, 21–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2020.02.017
- Kovaliova, O., Tchoursinov, Y., Kalyna, V., Koshulko, V., Kunitsia, E., Chernukha, A. et al. (2020). Identification of patterns in the production of a biologically-active component for food products. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2 (11 (104)), 61–68. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2020.200026
- Dijkstra, A. J. (2018). Enzymatic Gum Treatment. Lipid Modification by Enzymes and Engineered Microbes, 157–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-813167-1.00008-6
- Cai, Z., Wang, H., Li, W., Lee, W. J., Li, W., Wang, Y., Wang, Y. (2020). Preparation of l-α-glyceryl phosphorylcholine by hydrolysis of soy lecithin using phospholipase A1 in a novel solvent-free water in oil system. LWT, 129, 109562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109562
- Qu, Y., Sun, L., Li, X., Zhou, S., Zhang, Q., Sun, L. et al. (2016). Enzymatic degumming of soybean oil with magnetic immobilized phospholipase A2. LWT, 73, 290–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2016.06.026
- Li, Z., Wang, W., Liu, X., Qi, S., Lan, D., Wang, Y. (2023). Effect of different degumming processes on the retention of bioactive components, acylglycerol and phospholipid composition of rapeseed oil. Process Biochemistry, 133, 190–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2023.08.019
- Adhami, K., Asadollahzadeh, H., Ghazizadeh, M. (2019). A novel process for simultaneous degumming and deacidification of Soybean, Canola and Sunflower oils by tetrabutylphosphonium phosphate ionic liquid. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 76, 245–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2019.03.048
- Garba, U., Singanusong, R., Jiamyangyuen, S., Thongsook, T. (2020). Extracting lecithin from water degumming by-products of rice bran oil and its physicochemical, antioxidant and emulsifying properties. Food Bioscience, 38, 100745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbio.2020.100745
- Xie, M., Dunford, N. T. (2019). Fractionating of canola lecithin from acid degumming and its effect. Food Chemistry, 300, 125217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125217
- More, N. S., Gogate, P. R. (2018). Intensified degumming of crude soybean oil using cavitational reactors. Journal of Food Engineering, 218, 33–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2017.08.029
- Zhang, L., Akhymetkan, S., Chen, J., Dong, Y., Gao, Y., Yu, X. (2022). Convenient method for the simultaneous production of high-quality fragrant rapeseed oil and recovery of phospholipids via electrolyte degumming. LWT, 155, 112947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112947
- Sytnik, N., Kunitsia, E., Mazaeva, V., Chernukha, A., Kovalov, P., Grigorenko, N. et al. (2020). Rational parameters of waxes obtaining from oil winterization waste. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (10 (108)), 29–35. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2020.219602
- Bliznjuk, O., Masalitina, N., Myronenko, L., Zhulinska, O., Denisenko, T., Nekrasov, S. et al. (2022). Determination of rational conditions for oil extraction from oil hydration waste. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (6 (115)), 17–23. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.251034
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Dmytro Saveliev, Vasyl Rotar, Mikhail Kravtsov, Olena Petrova, Alla Ziuzko, Natalia Shevchuk, Svitlana Velma, Anzhela Rozumenko, Viktor Demenko, Taras Samchenko

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








