Development of superposition-based quantum key distribution protocol in decentralized full mesh networks
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.318588Keywords:
quantum cryptography, quantum key distribution, quantum mechanics, qubit, decentralized protocolsAbstract
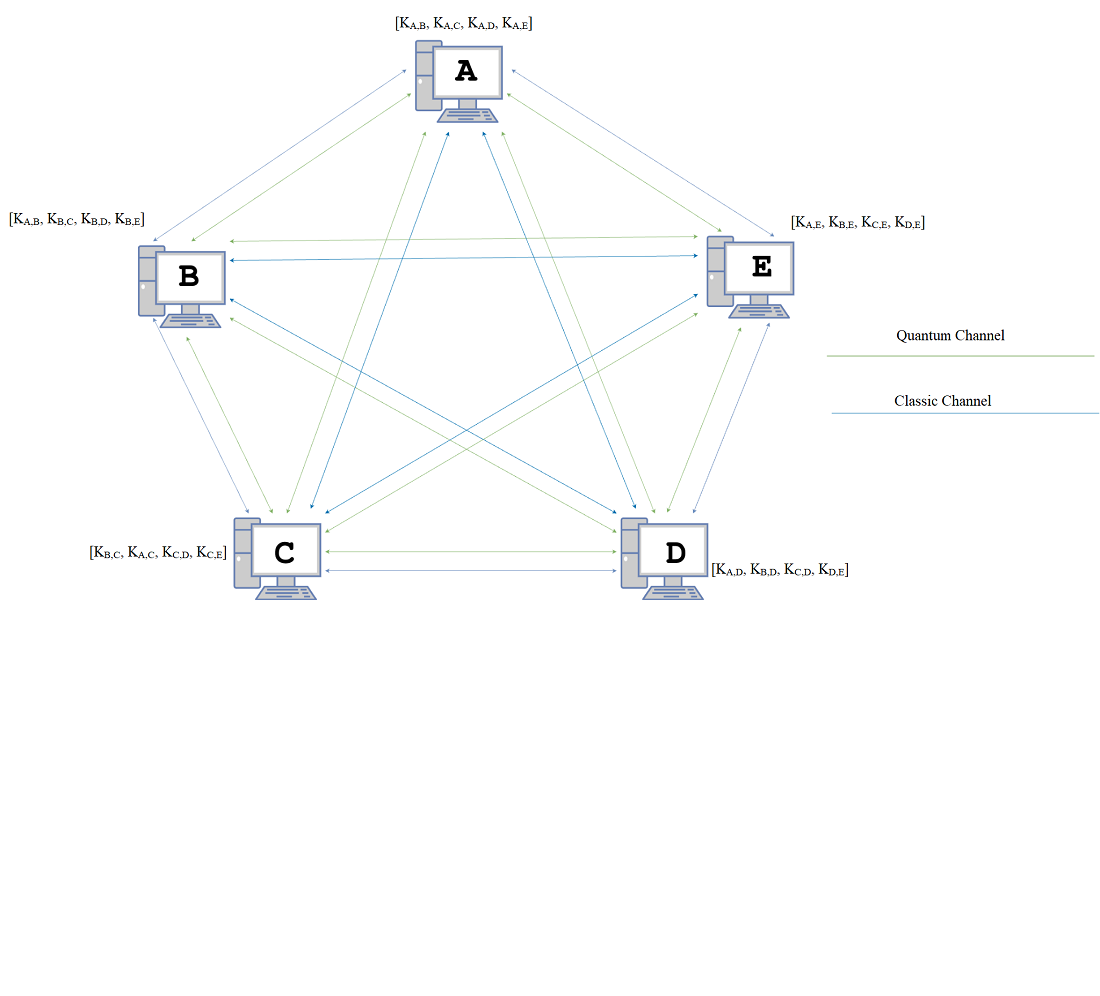
The object of this research is the security of communication networks, particularly in decentralized, multi-user environments where robust data protection and integrity are critical. The issue under discussion is the rising vulnerability of conventional cryptography systems resulting from ever complex cyberattacks and the expected risks presented by quantum computing possibilities. The development of a QKD protocol employing quantum superposition to improve data security and resilience against both present and future quantum-based cyber-attacks is demonstrated by the achieved results of this work. Achieving scalability and autonomous eavesdropping detection, this protocol lets several communication nodes securely exchange randomly produced keys without centralized management. A quick analysis of the results reveals that main elements influencing the great durability, security, and adaptability of the protocol are quantum superposition and its distributed character. Without centralized authority, the characteristics of the obtained results – especially the use of optical components, detectors, and quantum sources in conjunction with classical communication channels – solve the problem of ensuring data confidentiality and integrity in a multi-user environment. This protocol's practical reach covers safe communication applications in both public and private sectors, therefore addressing situations calling for strong data protection against modern cyberattacks. Conditions for practical application include settings like government, financial, or health-related interactions when safe information flow is crucial. This QKD system offers a future-ready security solution for high-stakes environments and represents notable advancement toward protecting data from quantum and conventional attacks
References
- Global Data Breaches and Cyber Attacks in 2024 (2024). IT Governance. Available at: https://www.itgovernance.co.uk/blog/global-data-breaches-and-cyber-attacks-in-2024
- Data generated per day, 2024. Exploding Topics. Available at: https://explodingtopics.com/
- Rivest, R. L., Shamir, A., Adleman, L. (1978). A method for obtaining digital signatures and public-key cryptosystems. Communications of the ACM, 21 (2), 120–126. https://doi.org/10.1145/359340.359342
- Shor, P. W. (1994). Algorithms for quantum computation: discrete logarithms and factoring. Proceedings 35th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, 124–134. https://doi.org/10.1109/sfcs.1994.365700
- Algazy, K., Sakan, K., Khompysh, A., Dyusenbayev, D. (2024). Development of a New Post-Quantum Digital Signature Algorithm: Syrga-1. Computers, 13 (1), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers13010026
- Wiesner, S. (1983). Conjugate coding. ACM SIGACT News, 15 (1), 78–88. https://doi.org/10.1145/1008908.1008920
- Brassard, G. (2005). Brief history of quantum cryptography: a personal perspective. IEEE Information Theory Workshop on Theory and Practice in Information-Theoretic Security, 2005., 19–23. https://doi.org/10.1109/itwtpi.2005.1543949
- Bennett, C. H., Brassard, G. (1984). An Update on Quantum Cryptography. Advances in Cryptology, 475–480. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-39568-7_39
- Ekert, A. K. (1991). Quantum cryptography based on Bell’s theorem. Physical Review Letters, 67 (6), 661–663. https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevlett.67.661
- Bennett, C. H., Brassard, G. (2014). Quantum cryptography: Public key distribution and coin tossing. Theoretical Computer Science, 560, 7–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcs.2014.05.025
- Muller, A., Herzog, T., Huttner, B., Tittel, W., Zbinden, H., Gisin, N. (1997). “Plug and play” systems for quantum cryptography. Applied Physics Letters, 70 (7), 793–795. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.118224
- Wang, J., Qin, X., Jiang, Y., Wang, X., Chen, L., Zhao, F. et al. (2016). Experimental demonstration of polarization encoding quantum key distribution system based on intrinsically stable polarization-modulated units. Optics Express, 24 (8), 8302. https://doi.org/10.1364/oe.24.008302
- Mo, X.-F., Zhu, B., Han, Z.-F., Gui, Y.-Z., Guo, G.-C. (2005). Faraday-Michelson system for quantum cryptography. Optics Letters, 30 (19), 2632. https://doi.org/10.1364/ol.30.002632
- Zhang, C.-H., Zhou, X.-Y., Ding, H.-J., Zhang, C.-M., Guo, G.-C., Wang, Q. (2018). Proof-of-Principle Demonstration of Passive Decoy-State Quantum Digital Signatures Over 200 km. Physical Review Applied, 10 (3). https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevapplied.10.034033
- Matsumoto, R. (2007). Multiparty quantum-key-distribution protocol without use of entanglement. Physical Review A, 76 (6). https://doi.org/10.1103/physreva.76.062316
- Razavi, M. (2012). Multiple-Access Quantum Key Distribution Networks. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 60 (10), 3071–3079. https://doi.org/10.1109/tcomm.2012.072612.110840
- Epping, M., Kampermann, H., Macchiavello, C., Bruß, D. (2017). Multi-partite entanglement can speed up quantum key distribution in networks. New Journal of Physics, 19 (9), 093012. https://doi.org/10.1088/1367-2630/aa8487
- Yu, K.-F., Gu, J., Hwang, T., Gope, P. (2017). Multi-party semi-quantum key distribution-convertible multi-party semi-quantum secret sharing. Quantum Information Processing, 16 (8). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-017-1631-x
- Pivoluska, M., Huber, M., Malik, M. (2018). Layered quantum key distribution. Physical Review A, 97 (3). https://doi.org/10.1103/physreva.97.032312
- Li, L., Li, Z. (2019). A multi-party quantum key distribution protocol based on phase shift operation. Laser Physics, 29 (10), 105201. https://doi.org/10.1088/1555-6611/ab3845
- Li, L., Li, Z. (2020). A verifiable multiparty quantum key agreement based on bivariate polynomial. Information Sciences, 521, 343–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2020.02.057
- Ma, X., Wang, C., Li, Z., Zhu, H. (2021). Multi-Party Quantum Key Distribution Protocol with New Bell States Encoding Mode. International Journal of Theoretical Physics, 60 (4), 1328–1338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-021-04758-4
- Shan, R.-T., Chen, X., Yuan, K.-G. (2021). Multi-party blind quantum computation protocol with mutual authentication in network. Science China Information Sciences, 64 (6). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-020-2977-x
- Doosti, M., Hanouz, L., Marin, A., Kashefi, E., Kaplan, M. (2024). Establishing Shared Secret Keys on Quantum Line Networks: Protocol and Security. 2024 International Conference on Quantum Communications, Networking, and Computing (QCNC), 176–183. https://doi.org/10.1109/qcnc62729.2024.00035
- Begimbayeva, Y., Zhaxalykov, T., Makarov, M., Ussatova, O., Tynymbayev, S., Temirbekova, Zh. (2024). Development of a Hybrid Quantum Key Distribution Concept for Multi-User Networks. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, 15 (9). https://doi.org/10.14569/ijacsa.2024.0150940
- Yevseiev, S., Pohasii, S., Milevskyi, S., Milov, O., Melenti, Y., Grod, I. et al. (2021). Development of a method for assessing the security of cyber-physical systems based on the Lotka-Volterra model. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (9 (113)), 30–47. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2021.241638
- Yevseiev, S., Havrylova, A., Milevskyi, S., Sinitsyn, I., Chalapko, V., Dukin, H. et al. (2023). Development of an improved SSL/TLS protocol using post-quantum algorithms. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 3 (9 (123)), 33–48. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.281795
- Rasool, A. A., Abbas, N. M., Sheikhyounis, K. (2022). Determination of optimal size and location of static synchronous compensator for power system bus voltage improvement and loss reduction using whale optimization algorithm. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (8 (115)), 26–34. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.251760
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Yenlik Begimbayeva, Olga Ussatova, Temirlan Zhaxalykov, Amir Akhtanov, Ruslan Pashkevich, Mukaddas Arshidinova

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








