Розробка складу емульсійної білково-жирової системи
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.321856Ключові слова:
емульсійна білково-жирова система, насіння льону, соєвий шрот, альфа-ліноленова кислота, технологічні показникиАнотація
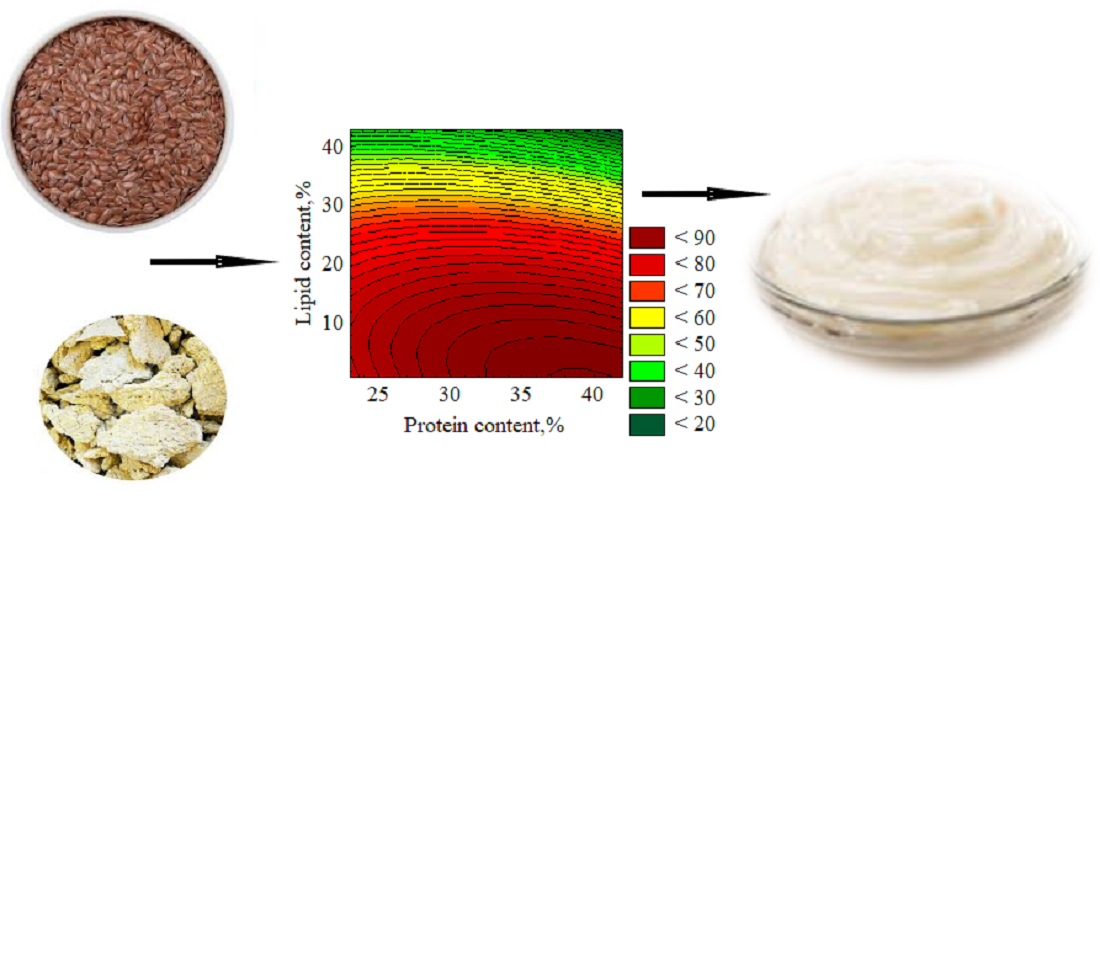
Об'єктом дослідження є технологічні показники емульсійної білково-жирової системи, розробленої на основі олійного насіння та продуктів його переробки. Проблематика дослідження полягає в необхідності стабілізації емульсії білково-жирової системи рослинного походження. Розглянуто шлях вирішення проблеми корегування технологічних показників емульсійних білково-жирових системах на основі насіння льону та соєвого шроту, зокрема стабільності емульсії та стійкості до окисного псування. Розроблено емульсійну білково-жирову систему з підвищеним вмістом ω-3 поліненасичених жирних кислот (ALA) на основі суміші насіння льону та соєвого шроту. Досліджено вплив співвідношення сировини на стабільність емульсійної системи. Встановлено, що раціональне співвідношення насіння льону (40 %) та соєвого шроту (60 %) забезпечує високу стійкість ліпідної компоненти до окисного псування, що підтверджується приростом пероксидного числа всього на 0,9 ммоль ½О/кг після 30 днів зберігання. Досліджено вплив стабілізаторів – ксантанової камеді (0,5 %) та поліоксиетилен (20) сорбітан монолаурату (0,2 %) – на стабільність емульсійної білково-жирової системи під час 30-добового зберігання за температури 4°C.
Емульсійна система розробленого складу характеризується нижчим вмістом білків відносно зразка порівняння (на 8%), однак цей недолік компенсується збалансованістю жирнокислотного складу, значно вищим вмістом ω-3 ПНЖК (9,8% проти 0%) та ліпідів (17,7% проти 1,1%). Такі характеристики суттєво підвищують її харчову цінність. Розроблена білково-жирова система має значний потенціал для впровадження у харчову промисловість, сприяючи створенню нових продуктів із підвищеним вмістом ALA та розширенню асортименту емульсійних продуктів, які відповідають сучасним стандартам здорового харчування
Посилання
- Petik, I., Litvinenko, O., Kalyna, V., Ilinska, O., Raiko, V., Filenko, O. et al. (2023). Development of extruded animal feed based on fat and oil industry waste. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2 (11 (122)), 112–120. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.275509
- Petik, I., Litvinenko, O., Stankevych, S., Zabrodina, I., Ponomarova, M., Kotliar, O. et al. (2024). Determination of the cellulose- and lipid-containing components influence on the extrudate technological indicators. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2 (6 (128)), 6–13. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.301843
- Belinska, A., Ryshchenko, I., Bliznjuk, O., Masalitina, N., Siedykh, K., Zolotarova, S. et al. (2024). Development of a method for inactivating lipoxygenases in linseed using chemical reagents. Technology Organic and Inorganic Substances, 4 (6 (130)), 14–21. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.309079
- Kunitsia, E., Kalyna, V., Haliasnyi, I., Siedykh, K., Kotliar, O., Dikhtyar, A. et al. (2023). Development of a flavored oil composition based on hemp oil with increased resistance to oxidation. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (11 (125)), 26–33. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.287436
- Elaine, E., Bhandari, B., Tan, C. P., Nyam, K. L. (2024). Recent Advances in the Formation, Stability, and Emerging Food Application of Water-in-Oil-in-Water Double Emulsion Carriers. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 17 (11), 3440–3460. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-024-03350-y
- El-Sayed, S. M., Hashim, A. F. (2024). Development of emulsion foams based on healthier oleogels and their application as low-fat replacers for whipped cream. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization, 18 (11), 9142–9155. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-024-02866-3
- Lingiardi, N., Galante, M., Spelzini, D. (2023). Emulsion Gels Based on Quinoa Protein Hydrolysates, Alginate, and High-Oleic Sunflower Oil: Evaluation of Their Physicochemical and Textural Properties. Food Biophysics, 19 (2), 298–309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-023-09817-3
- Singh, R., Sá, A. G. A., Sharma, S., Nadimi, M., Paliwal, J., House, J. D., Koksel, F. (2023). Effects of Feed Moisture Content on the Physical and Nutritional Quality Attributes of Sunflower Meal-based High-Moisture Meat Analogues. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 17 (7), 1897–1913. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-023-03225-8
- Didar, Z., Khodaparast, M. H. H., Goharjoo, B. (2024). Flaxseed mucilage - stabilized double emulsion for vitamin D delivery in Hazelnut milk ice cream: in vitro stability and storage. Journal of Food Science and Technology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-024-06078-x
- Zhu, T., Ma, L., Jiang, H., Li, W., Guo, X., Yang, C., Bu, G. (2023). Functional, structural properties of pea protein isolate-xylooligosaccharide glycosylated conjugate and its application in O/W emulsion preparation. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization, 17 (6), 6135–6143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-023-02102-4
- Li, X., Zhou, S., Chen, H., Zhang, R., Wang, L. (2024). Pomelo Fiber-Stabilized Oil-in-Water Emulsion Gels: Fat Mimetic in Plant-Based Ice Cream. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 18 (1), 422–432. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-024-03446-5
- Li, H., Zhang, L., Cao, H., Liu, T., Xi, Z., Li, H. et al. (2023). Whey Protein-Based High Internal Phase Emulsion Gel Characterization and Its Effect on the Textural and Melting Properties of Processed Cheese. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 17 (7), 2061–2075. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-023-03239-2
- Sulaiman, N. S., Zaini, H. M., Akanda, M. J. H., Heong, M. H., Chai, A., Pindi, W. (2024). Improving Functionality of Myofibrillar Protein: A Comparative Study on Fat Types on the Resulting Gelling and Microstructure Properties. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 17 (12), 5260–5272. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-024-03436-7
- Ashfaq, A., Osama, K., Yousuf, O., Younis, K. (2024). Protein-based Emulsion Hydrogels and Their Application in the Development of Sustainable Food Products. Plant Foods for Human Nutrition, 79 (4), 759–768. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11130-024-01214-6
- Lingiardi, N., Galante, M., Spelzini, D. (2024). Development of Bioactive Quinoa Protein Hydrolysate-based Emulsion Gels: Evaluation of Their Antioxidant and Rheological Properties. Food Biophysics, 20 (1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-024-09899-7
- Papchenko, V., Matveeva, T., Bochkarev, S., Belinska, A., Kunitsia, E., Chernukha, A. et al. (2020). Development of amino acid balanced food systems based on wheat flour and oilseed meal. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 3 (11 (105)), 66–76. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2020.203664
- Bui, A. T. H., Cozzolino, D., Zisu, B., Chandrapala, J. (2021). Influence of Fat Concentration on the Volatile Production in Model Whey Protein Systems as Affected by Low Frequency Ultrasound. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 14 (6), 1169–1183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-021-02619-w
- Kalyna, V., Stankevych, S., Zabrodina, I., Shubina, L., Chuiko, M., Mikheeva, O. et al. (2024). Development of the composition of anoxidation-stable dressing with high nutritional value. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (11 (127)), 29–37. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.296621
- Kunitsia, E., Popov, M., Gontar, T., Stankevych, S., Zabrodina, I., Stepankova, G. et al. (2024). Determination of the influence of hemp oil-based emulsion systems composition on the oxidation products content during storage. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 3 (6 (129)), 6–13. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.304466
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2025 Tatiana Matveeva, Serhii Stankevych, Viktoriia Kalyna, Tetiana Chaika, Aliona Dikhtyar, Svetlana Omelchenko, Oleh Kotliar, Lidiia Shubina, Tetiana Novozhylova, Olena Zolotukhina

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.
Ліцензійний договір – це документ, в якому автор гарантує, що володіє усіма авторськими правами на твір (рукопис, статтю, тощо).
Автори, підписуючи Ліцензійний договір з ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР», мають усі права на подальше використання свого твору за умови посилання на наше видання, в якому твір опублікований. Відповідно до умов Ліцензійного договору, Видавець ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР» не забирає ваші авторські права та отримує від авторів дозвіл на використання та розповсюдження публікації через світові наукові ресурси (власні електронні ресурси, наукометричні бази даних, репозитарії, бібліотеки тощо).
За відсутності підписаного Ліцензійного договору або за відсутністю вказаних в цьому договорі ідентифікаторів, що дають змогу ідентифікувати особу автора, редакція не має права працювати з рукописом.
Важливо пам’ятати, що існує і інший тип угоди між авторами та видавцями – коли авторські права передаються від авторів до видавця. В такому разі автори втрачають права власності на свій твір та не можуть його використовувати в будь-який спосіб.










