Development of a method for reliability assessment of distribution power networks up to 110 kV
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.322920Keywords:
distribution networks, power reliability, Markov processes, redundancy assessment, failure rateAbstract
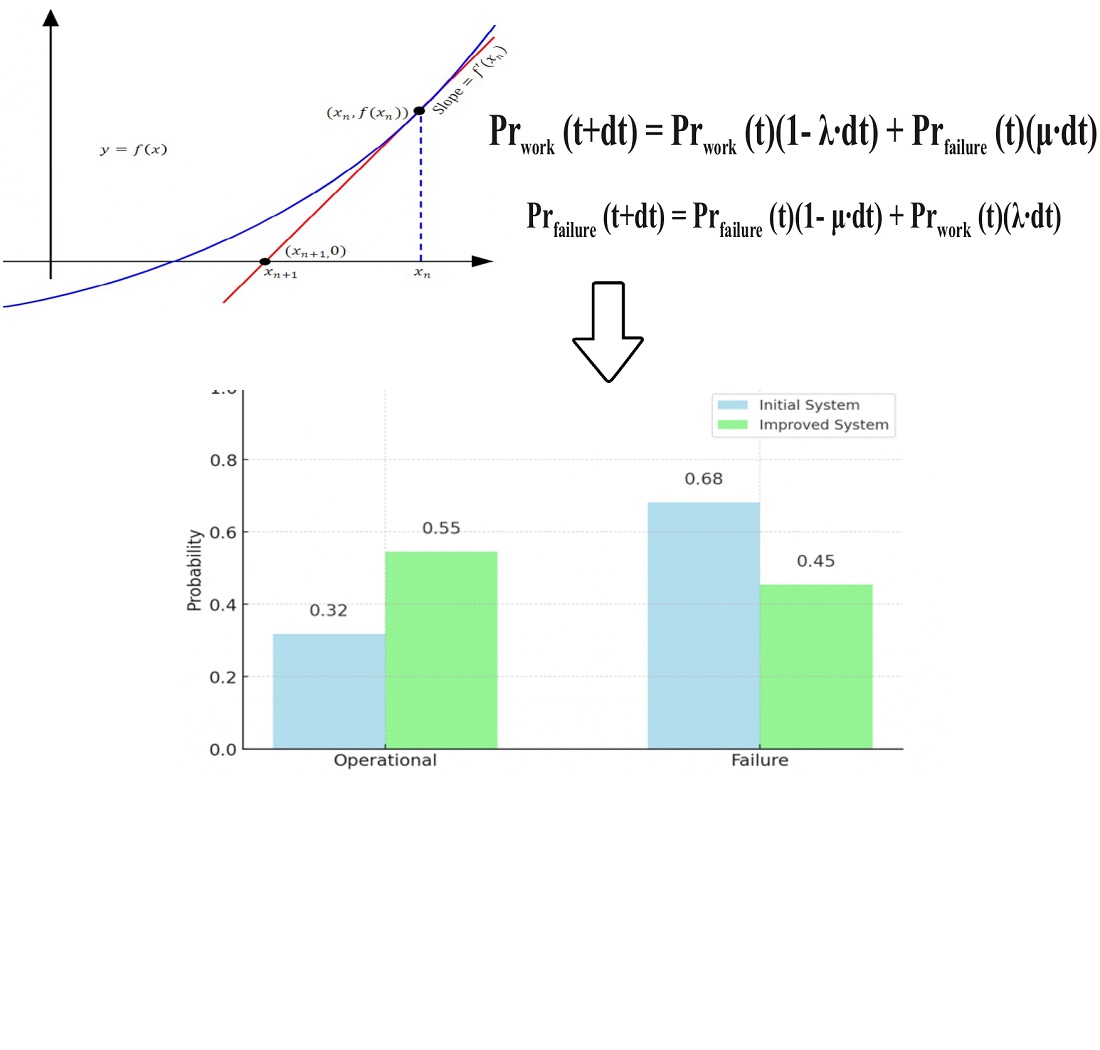
The study focuses on the reliability assessment of distribution power networks operating at voltages up to 110 kV, addressing the challenges of increasing loads, aging infrastructure, and the integration of renewable energy sources. A novel method and model for reliability assessment are proposed, incorporating failure rates, recovery times, and topological characteristics of networks. The research identifies critical factors influencing network reliability, including the level of redundancy, operational conditions, and climatic impacts. Notable findings show that network points with multiple feeder connections demonstrate the highest reliability, exceeding 99.99 %, while those with single-transformer configurations are the most vulnerable to failures. The average failure rate for overhead lines is calculated at 1.29 failures per 100 km annually, with recovery times reaching up to 40 hours for critical nodes.
The results are explained by the interplay of structural and operational factors, where redundancy significantly enhances reliability, and outdated equipment increases vulnerability. The study’s distinguishing feature lies in its use of Markov processes to dynamically model failures and recoveries, offering a comprehensive framework compared to traditional static methods. The practical applications of the results include improving network design through enhanced redundancy, optimizing maintenance strategies for critical elements, and supporting the integration of Smart Grid technologies. These findings contribute to the development of more resilient and efficient power distribution networks, adaptable to modern operational demands
References
- Singh, S., Singh, S. (2024). Advancements and Challenges in Integrating Renewable Energy Sources Into Distribution Grid Systems: A Comprehensive Review. Journal of Energy Resources Technology, 146 (9). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4065503
- Kaverin, V., Abisheva, D., Em, G., Kalinin, A., Yugay, V. (2022). Studying Partial Discharge Currents of High Voltage Power Line Suspension Insulators. International Journal on Energy Conversion (IRECON), 10 (3), 88. https://doi.org/10.15866/irecon.v10i3.21769
- Kayumov, D., Bulatbaev, F., Kayumova, I., Breido, J., Bulatbayeva, Y. (2023). An engineering approach for the qualitative assessment of the luminous flux of led lamps. International Journal of Energy for a Clean Environment, 24 (1), 31–43. https://doi.org/10.1615/interjenercleanenv.2022043776
- Wang, Y., Zheng, Q., Guo, M., Xiao, H., Si, C., Chen, W. (2022). Reliability Improvement of Distribution Network with Distributed Generation Sources and Diversified Loads. LOW VOLTAGE APPARATUS, 2, 63–67. Available at: http://www.eaes-seari.com/Jwk_dqynxgljs/EN/abstract/abstract480.shtml
- Soltan, S., Mazauric, D., Zussman, G. (2017). Analysis of Failures in Power Grids. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 4 (2), 288–300. https://doi.org/10.1109/tcns.2015.2498464
- Wu, Y., Fan, T., Huang, T. (2020). Electric Power Distribution System Reliability Evaluation Considering the Impact of Weather on Component Failure and Pre-Arranged Maintenance. IEEE Access, 8, 87800–87809. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2020.2993087
- Tatkeyeva, G., Bauyrzhanuly, M., Gaukhar, A., Assainov, G., Khabdullina, G., Tangirbergen, A. et al. (2024). Development of the logical system for forecasting wind characteristics in the urban conditions. EUREKA: Physics and Engineering, 2, 55–69. https://doi.org/10.21303/2461-4262.2024.003305
- Li, S., She, Y., Shi, K., Chen, Z. (2022). A Method for Evaluating Reliability and Failure Rate of DC Circuit Breakers. 2022 Global Conference on Robotics, Artificial Intelligence and Information Technology (GCRAIT), 578–581. https://doi.org/10.1109/gcrait55928.2022.00126
- Cao, H., Song, Y., Wang, S., Dai, F., Liu, J., Cheng, Q. (2024). Failure Mode Analysis and Identification Method Based on the External Characteristics of DC Circuit Breaker. 2024 China International Conference on Electricity Distribution (CICED), 01–05. https://doi.org/10.1109/ciced63421.2024.10754216
- Pande, P., Hussain, K., Pravallika, B., Al Ansari, M. S., Tharsanee, R. M., Acharya, S. (2024). Predictive Maintenance of Power Transformers in Distribution Network with Energy Management Using Deep Learning. 2024 5th International Conference on Intelligent Communication Technologies and Virtual Mobile Networks (ICICV), 581–586. https://doi.org/10.1109/icicv62344.2024.00098
- Biradar, V., Kakeri, D., Agasti, A. (2024). Machine Learning based Predictive Maintenance in Distribution Transformers. 2024 8th International Conference on Computing, Communication, Control and Automation (ICCUBEA), 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/iccubea61740.2024.10774993
- Reddy Shabad, P. K., Alrashide, A., Mohammed, O. (2021). Anomaly Detection in Smart Grids using Machine Learning. IECON 2021 – 47th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/iecon48115.2021.9589851
- Papaspiliotopoulos, V. A., Korres, G. N., Hatziargyriou, N. D. (2015). Protection coordination in modern distribution grids integrating optimization techniques with adaptive relay setting. 2015 IEEE Eindhoven PowerTech, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/ptc.2015.7232558
- Rêma, G. S., Bonatto, B. D., de Lima, A. C. S., de Carvalho, A. T. (2024). Emerging Trends in Power Transformer Maintenance and Diagnostics: A Scoping Review of Asset Management Methodologies, Condition Assessment Techniques, and Oil Analysis. IEEE Access, 12, 111451–111467. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2024.3441523
- Carletti, E., Amadei, F., Franzone, G., Rizzati, J., Cocchi, L., Bolognesi, M., Moschella, P. (2023). The reliability of the electrical distribution system using the Markov Modeling methodology. IET Conference Proceedings, 2023 (6), 1115–1119. https://doi.org/10.1049/icp.2023.0655
- Borges, C. L. T., Cantarino, E. (2011). Microgrids Reliability Evaluation with Renewable Distributed Generation and Storage Systems. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 44 (1), 11695–11700. https://doi.org/10.3182/20110828-6-it-1002.01090
- Song, H., Zhang, B., Wang, M., Xiao, Y., Zhang, L., Zhong, H. (2022). A Fast Phase Optimization Approach of Distributed Scatterer for Multitemporal SAR Data Based on Gauss–Seidel Method. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 19, 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/lgrs.2021.3077493
- Hu, W. J. (2021). Momentum Method for Improving the Convergence of Newton-Raphson Method for Nonlinear Circuit Transient Simulations. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Computer Science, Artificial Intelligence and Electronic Engineering (CSAIEE), 296–303. https://doi.org/10.1109/csaiee54046.2021.9543125
- Wei, J., Cai, H., Jiang, T., Westermann, D. (2021). Research on Power System Network Equivalent with Different Methods. PESS 2021; Power and Energy Student Summit.
- Gupta, A. P., Mohapatra, A., Singh, S. N. (2018). Power System Network Equivalents: Key Issues and Challenges. TENCON 2018 - 2018 IEEE Region 10 Conference, 2291–2296. https://doi.org/10.1109/tencon.2018.8650397
- Aghili, J., Franck, E., Hild, R., Michel-Dansac, V., Vigon, V. (2025). Accelerating the convergence of Newton’s method for nonlinear elliptic PDEs using Fourier neural operators. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 140, 108434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnsns.2024.108434
- Ramli, S. P., Usama, M., Mokhlis, H., Wong, W. R., Hussain, M. H., Muhammad, M. A., Mansor, N. N. (2021). Optimal directional overcurrent relay coordination based on computational intelligence technique: a review. Turkish Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences, 29 (3), 1284–1307. https://doi.org/10.3906/elk-2012-98
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Fariza Abilzhanova, Felix Bulatbaev, Aizada Kuanyshtaeva

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








