Determining the dependence of potassium glyceroxide catalytic activity on storage conditions
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.322987Keywords:
potassium glyceroxide transesterification catalyst, palm olein, triglyceride composition, melting pointAbstract
The object of the study is the catalytic activity of potassium glyceroxide in the chemical transesterification reaction of palm olein.
Transesterification is an important method for obtaining fats with desired properties, surfactants, alternative biofuels, etc. Industrial catalysts for chemical transesterification are explosive, flammable, and quickly lose activity. Alkali metal glyceroxides are safer and more stable catalysts.
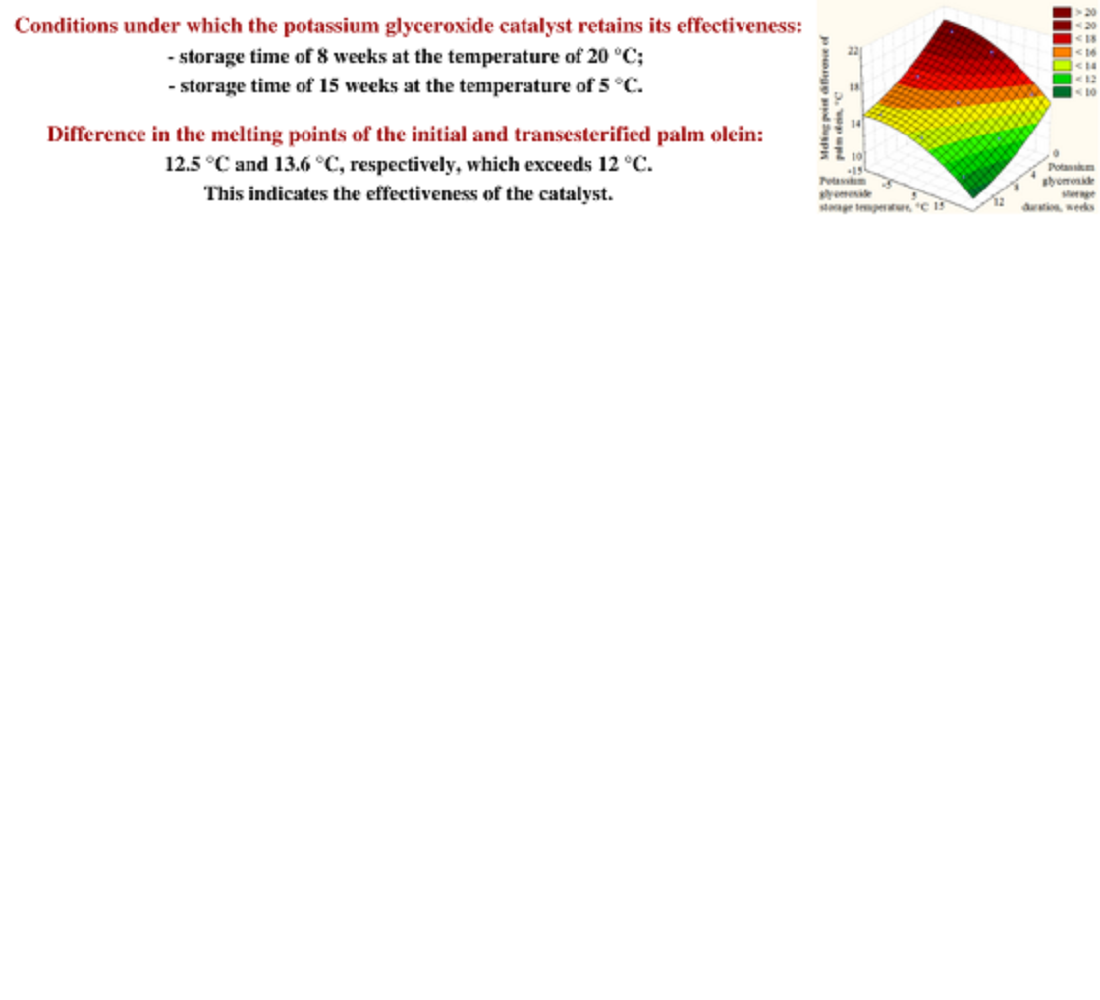
The dependence of potassium glyceroxide catalytic activity (CAS Number 43110-90-3) on storage conditions was examined. The criterion for the catalyst's effectiveness was an increase in palm olein melting point by more than 12 °C after transesterification. Refined, bleached, and deodorized palm olein (DSTU 4438:2005, CAS Number 93334-39-5) was used, with the following parameters: peroxide value 0.18 ½ O mmol/kg, acid value 0.12 mg KOH/g, melting point 22.2 °C.
The conditions under which potassium glyceroxide retains its effectiveness were determined: storage time of 8 weeks at a temperature of 20 °C; storage time of 15 weeks at 5 °C. The melting point difference between original and transesterified olein was 12.5 °C and 13.6 °C, respectively. The chromatographic analysis confirmed changes in the triglyceride composition of the transesterified olein.
It was found that the industrial catalyst sodium methoxide, stored under these conditions, lost its effectiveness. The melting point difference between original and transesterified olein was 7.5 °C and 9.7 °C, respectively.
The obtained data allow for efficient transesterification of fats using potassium glyceroxide as a more stable catalyst, which can be pre-produced and stored at the enterprise
References
- Sytnik, N., Demydov, I., Kunitsa, E. (2015). Effectiveness research of new catalyst for oil and fat interesterification by using chromatographic analysis. Technology Audit and Production Reserves, 6 (4 (26)), 8–13. https://doi.org/10.15587/2312-8372.2015.53285
- Malpartida, I., Maireles-Torres, P., Vereda, C., Rodríguez-Maroto, J. M., Halloumi, S., Lair, V. et al. (2020). Semi-continuous mechanochemical process for biodiesel production under heterogeneous catalysis using calcium diglyceroxide. Renewable Energy, 159, 117–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.05.020
- Sánchez, B. S., Benitez, B., Querini, C. A., Mendow, G. (2015). Transesterification of sunflower oil with ethanol using sodium ethoxide as catalyst. Effect of the reaction conditions. Fuel Processing Technology, 131, 29–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.10.043
- Catarino, M., Martins, S., Soares Dias, A. P., Costa Pereira, M. F., Gomes, J. (2019). Calcium diglyceroxide as a catalyst for biodiesel production. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 7 (3), 103099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103099
- Korchak, M., Bragin, O., Petrova, O., Shevchuk, N., Strikha, L., Stankevych, S. et al. (2022). Development of transesterification model for safe technology of chemical modification of oxidized fats. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (6 (120)), 14–19. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.266931
- Lau, P.-C., Kwong, T.-L., Yung, K.-F. (2022). Manganese glycerolate catalyzed simultaneous esterification and transesterification: The kinetic and mechanistic study, and application in biodiesel and bio-lubricants synthesis. Renewable Energy, 189, 549–558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2022.02.127
- Ferrero, G. O., Almeida, M. F., Alvim-Ferraz, M. C. M., Dias, J. M. (2015). Glycerol-enriched heterogeneous catalyst for biodiesel production from soybean oil and waste frying oil. Energy Conversion and Management, 89, 665–671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2014.10.032
- Lisboa, F. S., Ferreira, E. B., Silva, F. J. L. B., Silva, F. R. (2023). Structural stability and catalytic activity of calcium glycerolates in soybean oil methyl transesterification reactions. Reaction Kinetics, Mechanisms and Catalysis, 136 (2), 851–865. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-023-02391-2
- Ebadi Pour, N., Dumeignil, F., Katryniok, B., Delevoye, L., Revel, B., Paul, S. (2021). Investigating the active phase of Ca-based glycerol polymerization catalysts: On the importance of calcium glycerolate. Molecular Catalysis, 507, 111571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcat.2021.111571
- Fá, A., Bechthold, P., Juan, A., Marchetti, J. M. (2024). The formation of calcium glycerolate as an active species in the synthesis of biodiesel. A DFT study. Applied Surface Science Advances, 24, 100657. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsadv.2024.100657
- Bradley, D., Levin, E., Rodriguez, C., Williard, P. G., Stanton, A., Socha, A. M. (2016). Equilibrium studies of canola oil transesterification using a sodium glyceroxide catalyst prepared from a biodiesel waste stream. Fuel Processing Technology, 146, 70–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2016.02.009
- Santos, S., Braun, J., Espíndola, G., da Silva, J., Renner, R., Fontoura, L. (2024). Sodium Glyceroxide: An Efficient Homogeneous Alkaline Catalyst for Biodiesel Synthesis. Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society, 35 (7). https://doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20240013
- Wang, E., Shen, J., Wang, Y., Tang, S., Emami, S., Reaney, M. J. T. (2015). Production of biodiesel with lithium glyceroxide. Fuel, 160, 621–628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2015.07.101
- Liang, X., Fei, H., Zhou, C., Ye, X., Xie, Q., Wu, Z., Yu, S. et al. (2023). Zinc glycerolate: An unconventional heterogeneous catalyst for the glycerolysis of fatty acids in biodiesel production. Renewable Energy, 218, 119140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2023.119140
- Pradhan, S., Shen, J., Emami, S., Mohanty, P., Naik, S. N., Dalai, A. K., Reaney, M. J. T. (2017). Synthesis of potassium glyceroxide catalyst for sustainable green fuel (biodiesel) production. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 46, 266–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2016.10.038
- Erisna, D., Arita, S., Hadiah, F. (2024). Transesterification Process of Biodiesel with Potassium Glycerolate Catalyst. Indonesian Journal of Fundamental and Applied Chemistry, 9 (1), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.24845/ijfac.v9.i1.1
- Theam, K. L., Islam, A., Choo, Y. M., Taufiq-Yap, Y. H. (2015). Biodiesel from low cost palm stearin using metal doped methoxide solid catalyst. Industrial Crops and Products, 76, 281–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.06.058
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Liubov Morozova, Vita Glavatchuk, Oleksandr Minieiev, Tetiana Tkachenko, Larysa Marushko, Svitlana Korolchuk, Tanya Savchuk, Anastasiia Kolesnyk, Valentyna Mohutova, Roman Mylostyvyi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.









