Розробка прогнозної оптимізаційної моделі для мінімізування затримок та неефективності в спеціальних портах
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.323188Ключові слова:
Анотація
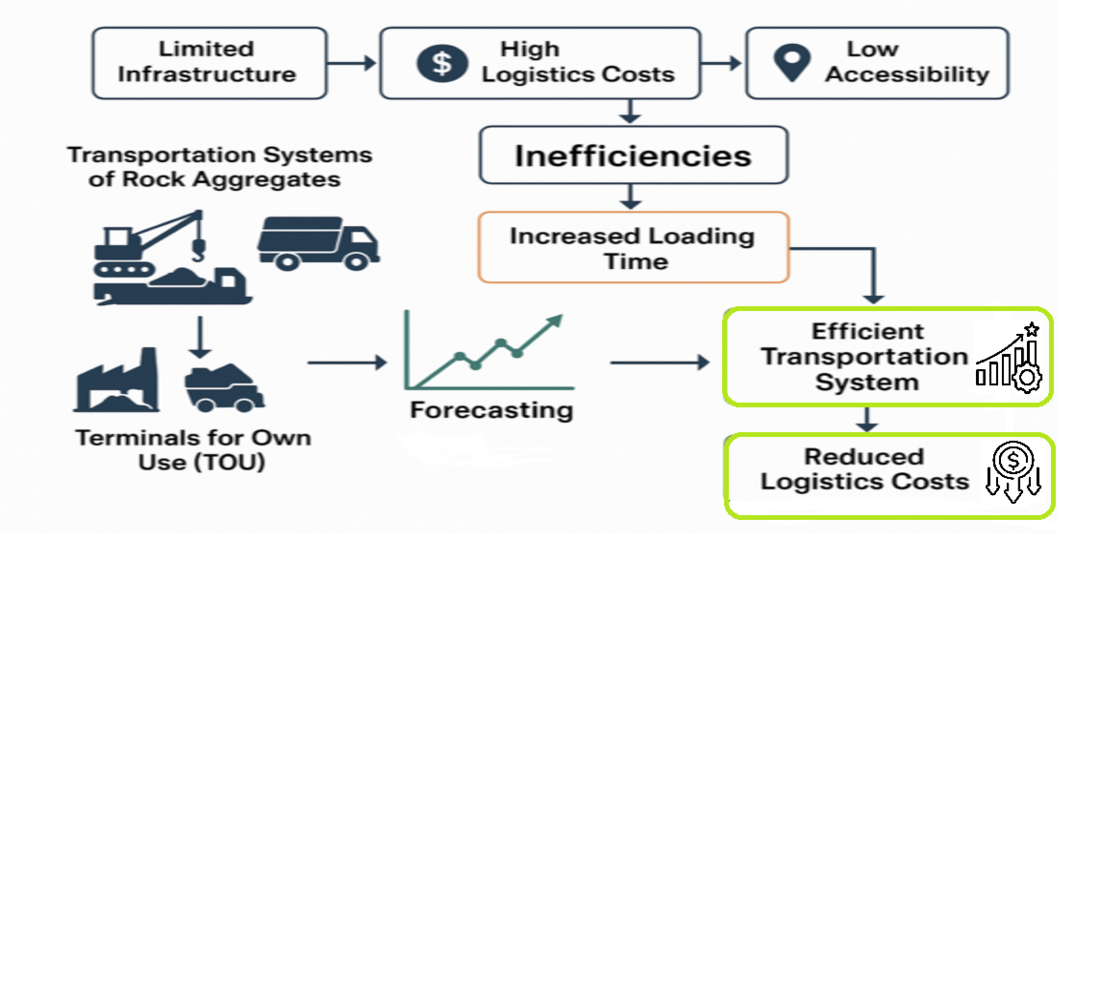
Об’єктом цього дослідження є система транспортування кам’яних заповнювачів в контексті архіпелагічної логістики, зосереджена на інтеграції морського та наземного транспортних засобів на терміналах для власного використання в Індонезії. У багатьох острівних країнах, таких як Індонезія, ефективність морської логістики відіграє вирішальну роль у підтримці економічної конкурентоспроможності. Однак такі проблеми, як обмежена інфраструктура, високі витрати на логістику та низька доступність, залишаються, особливо на терміналах для власного використання, де завантаження та розвантаження сипучих товарів, як-от кам’яних заповнювачів, може тривати 2–5 днів через обмеження обладнання. Ця неефективність збільшує час швартування та експлуатаційні витрати, послаблюючи продуктивність ланцюга поставок і промислову конкурентоспроможність. Оскільки попит на будівельні матеріали зростає, оптимізація портової інфраструктури та транспортного сполучення стає актуальною. У цьому дослідженні використовується модель довготривалої короткострокової пам’яті, оптимізована за допомогою оптимізації роєм частинок, щоб підвищити точність прогнозування попиту на сукупний порід. Модель досягає середньої абсолютної відсоткової похибки 0,46 % для даних навчання та 5,26 % для даних тестування, що свідчить про високу надійність прогнозу. Аналіз часових рядів визначає тенденцію до зниження попиту в 2022 році, що вказує на важливість точного прогнозування для зменшення неефективності. Краще прогнозування дає змогу краще планувати порти та керувати запасами, що веде до швидкої логістичної системи. Результати показують, що ефективна транспортна система, яка реагує на попит, значно скорочує час завантаження та загальні витрати на логістику. Дослідження підкреслює, що добре інтегрований підхід до прогнозування може сприяти кращому прийняттю рішень в управлінні портом і плануванні транспортування. Завдяки оптимізації транспортної ефективності та зв’язності запропонована модель пропонує зацікавленим сторонам зрозуміти, гарантуючи, що майбутнє планування інфраструктури узгоджується з цілями сталого розвитку
Посилання
- Tovar, B., Wall, A. (2022). The relationship between port-level maritime connectivity and efficiency. Journal of Transport Geography, 98, 103213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2021.103213
- Surury, F., Syauqi, A., Purwanto, W. W. (2021). Multi-objective optimization of petroleum product logistics in Eastern Indonesia region. The Asian Journal of Shipping and Logistics, 37 (3), 220–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajsl.2021.05.003
- Seyedan, M., Mafakheri, F. (2020). Predictive big data analytics for supply chain demand forecasting: methods, applications, and research opportunities. Journal of Big Data, 7 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-020-00329-2
- Interview on Operational Challenges at PT. Watu Meriba Jaya (2020). P. T. W. M. J. Mining Engineering Team Leader.
- Aldahmani, E., Alzubi, A., Iyiola, K. (2024). Demand Forecasting in Supply Chain Using Uni-Regression Deep Approximate Forecasting Model. Applied Sciences, 14 (18), 8110. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14188110
- Atmayudha, A., Syauqi, A., Purwanto, W. W. (2021). Green logistics of crude oil transportation: A multi-objective optimization approach. Cleaner Logistics and Supply Chain, 1, 100002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clscn.2021.100002
- Terrada, L., Khaili, M. E., Ouajji, H. (2022). Demand Forecasting Model using Deep Learning Methods for Supply Chain Management 4.0. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, 13 (5). https://doi.org/10.14569/ijacsa.2022.0130581
- Liu, W., Sun, D., Xu, T. (2019). Integrated Production and Distribution Planning for the Iron Ore Concentrate. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2019 (1). https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7948349
- Abolghasemi, M., Beh, E., Tarr, G., Gerlach, R. (2020). Demand forecasting in supply chain: The impact of demand volatility in the presence of promotion. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 142, 106380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2020.106380
- Gundu, V., Simon, S. P. (2020). PSO–LSTM for short term forecast of heterogeneous time series electricity price signals. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 12 (2), 2375–2385. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02353-9
- Cui, T., Shi, Y., Wang, J., Ding, R., Li, J., Li, K. (2025). Practice of an improved many-objective route optimization algorithm in a multimodal transportation case under uncertain demand. Complex & Intelligent Systems, 11 (2). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40747-024-01725-4
- Binsfeld, T., Hamdan, S., Jouini, O., Gast, J. (2024). On the optimization of green multimodal transportation: a case study of the West German canal system. Annals of Operations Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-024-06075-5
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2025 Syarifuddin Ishak, Ludfi Djakfa, Achmad Wicaksono, Moch Abdillah Nafis

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.
Ліцензійний договір – це документ, в якому автор гарантує, що володіє усіма авторськими правами на твір (рукопис, статтю, тощо).
Автори, підписуючи Ліцензійний договір з ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР», мають усі права на подальше використання свого твору за умови посилання на наше видання, в якому твір опублікований. Відповідно до умов Ліцензійного договору, Видавець ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР» не забирає ваші авторські права та отримує від авторів дозвіл на використання та розповсюдження публікації через світові наукові ресурси (власні електронні ресурси, наукометричні бази даних, репозитарії, бібліотеки тощо).
За відсутності підписаного Ліцензійного договору або за відсутністю вказаних в цьому договорі ідентифікаторів, що дають змогу ідентифікувати особу автора, редакція не має права працювати з рукописом.
Важливо пам’ятати, що існує і інший тип угоди між авторами та видавцями – коли авторські права передаються від авторів до видавця. В такому разі автори втрачають права власності на свій твір та не можуть його використовувати в будь-який спосіб.










