Identifying the influence of nanomodifiers on the structure formation process regularities in the gypsum-alumina cement system
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.323295Keywords:
composite binder, mortar, ettringite, ettringite stabilization, aluminate cements, sulfoaluminate cements, nanomodifierAbstract
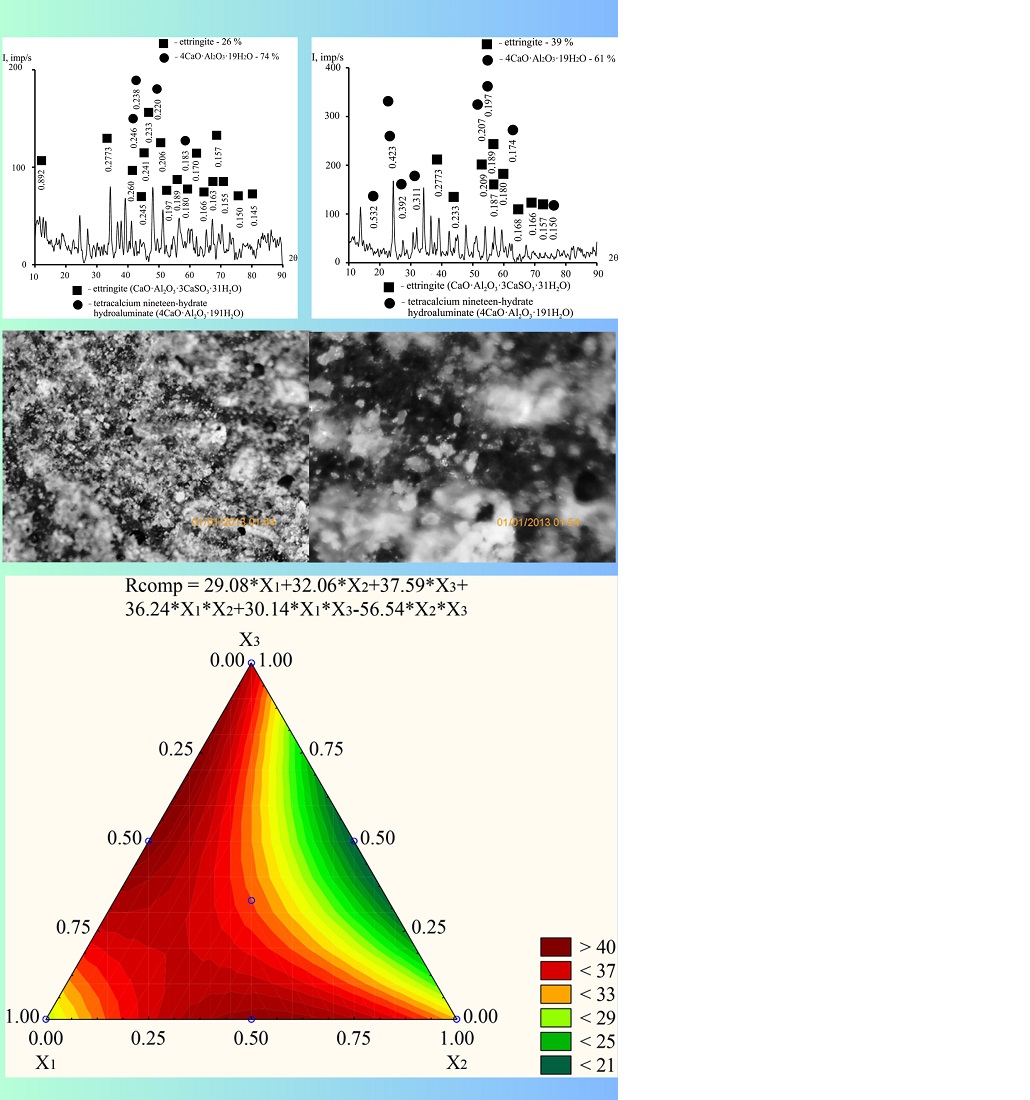
Gypsum alumina cement is resistant to magnesium solutions, seawater, and concentrated Na2SO4 and Mg2SO4 solutions, but it is less resistant to sodium chloride solutions. One of the ways to improve the gypsum alumina cement durability and enable its use in aggressive calcium chloride waters is to design a composition by incorporating modifiers. Thus, the composite is applicable for well-casing under conditions involving aggressive water exposure. However, such cements have their limitations: they are not suitable for processing at high temperatures in autoclaves. Up to now, the ettringite phase stability dependence on curing conditions and temperature has remained an unresolved issue.
It has been theoretically proven and experimentally confirmed that the optimal calcium sulfate content in gypsum alumina cement and gypsum grade G-5 (GAC+G5) compositions, according to calculations, ranges from 28 % to 38 % of the mass of the alumina binder. That makes it possible to increase ettringite formation and obtain cement stone structure with predefined characteristics. As a result of modification with nano additives, the strength indicators of the composite materials have been improved: gypsum alumina cement GAC gypsum grade G-5:G (70:30) %+0.18 % nanotubes+0.4 % Sika – up to 70.2 MPa compared to 14.67 MPa in the reference composition.
The scope of practical application includes the development of road surfaces and waterproofing materials, as well as hydraulic engineering. A condition for the practical implementation of results is the temperature range from –15 to 80 °С. Expected effects of application are shrinkage deformation reduction, improved crack resistance, increased strength, and enhanced durability of concrete articles under challenging operating conditions
References
- Rusyn, B. Н., Sanytskyі, М. А., Hohol, M. М., Kropyvnytskyі, T. S. (2023). Influence of ultrafine active mineral additives on the properties of low-carbon high-performance concretes. Bulletin National University of Water and Environmental Engineering, 4 (104), 66–75. https://doi.org/10.31713/vt420236
- Krivenko, P., Rudenko, I., Konstantynovskyi, O., Vaičiukynienė, D. (2022). Mitigation of Corrosion Initiated by Cl− and SO42−-ions in Blast Furnace Cement Concrete Mixed with Sea Water. Materials, 15 (9), 3003. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15093003
- Occhicone, A., Vukčević, M., Bosković, I., Mingione, S., Ferone, C. (2022). Alkali-Activated Red Mud and Construction and Demolition Waste-Based Components: Characterization and Environmental Assessment. Materials, 15 (4), 1617. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041617
- Alias, C., Zerbini, I., Abbà, A., Benassi, L., Gelatti, U., Sorlini, S. et al. (2023). Ecotoxicity Evaluation of Industrial Waste and Construction Materials: Comparison Between Leachates from Granular Steel Slags and Steel Slags-Containing Concrete Through a Plant-Based Approach. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 111 (1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-023-03764-y
- Khankhaje, E., Kim, T., Jang, H., Kim, C.-S., Kim, J., Rafieizonooz, M. (2024). A review of utilization of industrial waste materials as cement replacement in pervious concrete: An alternative approach to sustainable pervious concrete production. Heliyon, 10 (4), e26188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26188
- Qureshi, H. J., Ahmad, J., Majdi, A., Saleem, M. U., Al Fuhaid, A. F., Arifuzzaman, M. (2022). A Study on Sustainable Concrete with Partial Substitution of Cement with Red Mud: A Review. Materials, 15 (21), 7761. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15217761
- Azad, N. M., Samarakoon, S. M. S. M. K. (2021). Utilization of Industrial By-Products/Waste to Manufacture Geopolymer Cement/Concrete. Sustainability, 13 (2), 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13020873
- Derevianko, V., Hryshko, H., Dubov, T. (2019). Etringite phase stabilization. Building Materials and Products, 1-2 (103), 18–25. https://doi.org/10.48076/2413-9890.2023-103-04
- EN 197-1:2011. Cement - Part 1: Composition, specifications and conformity criteria for common cements.
- Hryshko, H., Derevianko, V., Vatazhyshyn, O., Dubov, T. (2024). Researching the influence of the CaO/Al2O3 ratio on ettringite formation and obtaining the structure of a cement paste with special properties. E3S Web of Conferences, 534, 01005. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202453401005
- Derevianko, V. M., Hryshko, H. M., Vatazhishin, O. V. (2023). Evaluation of the effectiveness of influence caused by ultra and nano-disperse additives for modification of sulfate phases and sulfoaluminate phases. Ukrainian Journal of Civil Engineering and Architecture, 4 (016), 71–76. https://doi.org/10.30838/j.bpsacea.2312.290823.71.972
- Akishev, K., Aryngazin, K., Tulegulov, A., Bayzharikova, M., Nurtai, Zh. (2024). Evaluation of the efficiency of the technological process for the production of building products with fillers from metallurgical slag. Metalurgija, 63 (2), 267–270. Available at: https://hrcak.srce.hr/file/451094
- Sanytsky, M., Kropyvnytska, T., Vakhula, O., Bobetsky, Y. (2023). Nanomodified Ultra High-Performance Fiber Reinforced Cementitious Composites with Enhanced Operational Characteristics. Proceedings of CEE 2023, 362–371. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-44955-0_36
- Occhicone, A., Vukčević, M., Bosković, I., Ferone, C. (2021). Red Mud-Blast Furnace Slag-Based Alkali-Activated Materials. Sustainability, 13 (20), 11298. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132011298
- Derevianko, V., Hryshko, H., Smolin, D., Zhurba, I., Dubov, T. (2024). Development of binders based on the СаО–Fe2O3 system. Technology Organic and Inorganic Substances, 4 (6 (130)), 49–58. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.309128
- Ministero Dello Sviluppo Economico. DECRETO 6 agosto 2020. Available at: https://www.gazzettaufficiale.it/eli/id/2020/10/05/20A05394/sg
- Vavouraki, A. I. (2020). Utilization of Industrial Waste Slags to Enhance Ground Waste Concrete-Based Inorganic Polymers. Journal of Sustainable Metallurgy, 6 (3), 383–399. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-020-00281-8
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Viktor Derevianko, Hanna Hryshko, Yevhen Zaiats, Andrii Drozd

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.









