Development of a stabilization system composition for sauces and dressings
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.325772Keywords:
stabilization system, sauces-dressings, esters of fatty acids and sucrose, pH of the aqueous phase, emulsion stabilityAbstract
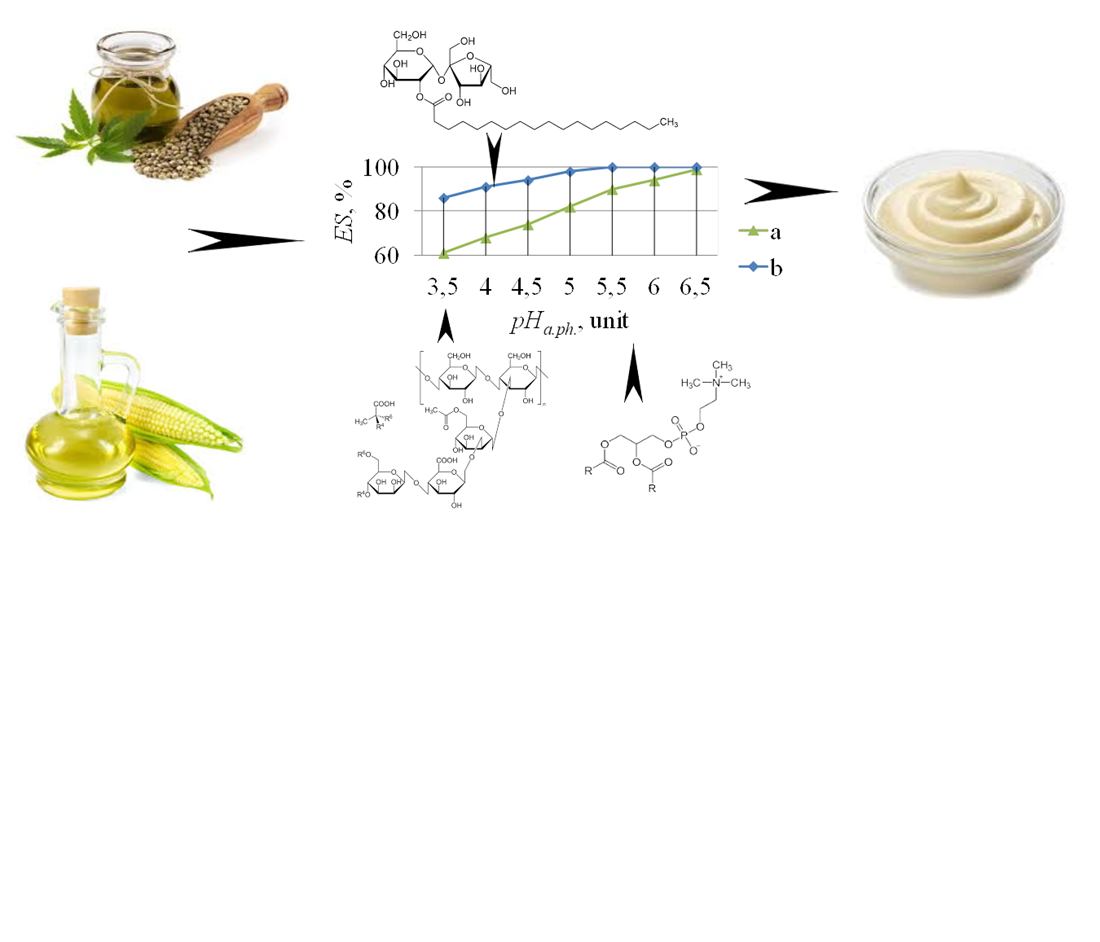
The object of the study is the stability of a model emulsion with a stabilization system including liquid soy lecithin, xanthan gum, and esters of fatty acids and sucrose (E 473) under the influence of changes in the pH of the aqueous phase. A way to solve the problem of stabilizing emulsion systems in an acidic environment (pH from 4.0 to 5.5) is considered by rationalizing the composition of the stabilization system of sauces-dressings. It is determined that the stability of the emulsion system stabilized by soy lecithin and xanthan gum increases with increasing pH. At the same time, in the pH range of 3.5–5.0 it remains at a relatively low level (60–82 %), which requires improvement of the stabilization system for sauces-dressings. A rational range of E 473 concentration in the stabilization system for sauces-dressings is substantiated. It was found that the introduction of E 473 at a concentration of 0.3 % contributes to a significant increase in the stability of model emulsion samples under conditions of low pH values. An approximate dependence of the stability of the emulsion system on the concentration of E 473 and the pH of the aqueous phase is proposed, which allows predicting the effectiveness of the stabilization system under given conditions. A feature of the results obtained is that the use of E 473 provides a significant increase in the stability of the emulsion system, which is critically important for preserving the physicochemical properties of dressing sauces, which most often have an acidic environment. From a practical point of view, the development allows for effective stabilization of food emulsion systems in a wide pH range, reducing the risk of phase separation. An applied aspect of using the obtained scientific result is the possibility of modeling and developing new formulations of emulsion products, in particular dressing sauces, with improved structural and mechanical characteristics
References
- Khalesi, H., Lu, W., Nishinari, K., Fang, Y. (2020). New insights into food hydrogels with reinforced mechanical properties: A review on innovative strategies. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 285, 102278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2020.102278
- Stankevych, S., Gorbunov, K., Zabrodina, I., Popov, M., Kalyna, V., Novozhylova, T. et al. (2024). Identification of the oxidation and hydrolysis products content influence on the rapeseed oil oxidation induction period. Technology Organic and Inorganic Substances, 4 (6 (130)), 6–13. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.308907
- Batchelor, D. V. B., Armistead, F. J., Ingram, N., Peyman, S. A., Mclaughlan, J. R., Coletta, P. L., Evans, S. D. (2021). Nanobubbles for therapeutic delivery: Production, stability and current prospects. Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science, 54, 101456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cocis.2021.101456
- Zhang, A.-Q., Li, X.-Y., Han, Y.-N., Liu, B.-H., Zhang, H.-L., Gao, J.-H., Zhang, Y.-H. (2022). Improving interface properties of zein hydrolysis and its application in salad dressing through dispersion improvement assisted by potassium oleate aqueous solution. Food Hydrocolloids, 130, 107719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2022.107719
- Putyatin, B., Bliznjuk, O., Masalitina, N., Bezpal’ko, V., Zhukova, L., Filenko, O. et al. (2024). Identifying the influence of the concentration of surfactants on the technological indicators of aerosol emulsion. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (6 (132)), 6–15. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.317819
- Sukumar, A., Gurumoorthi, P., Athmaselvi, K. A. (2023). Effect of ultrasonication on emulsion formulation, encapsulation efficiency, and oxidative stability of spray dried chia seed oil. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 60 (6), 1761–1771. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-023-05716-0
- Sivabalan, S., Sablani, S. (2022). Design of β-Carotene Encapsulated Emulsions for Thermal Processing and Storage. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 15 (2), 338–351. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-021-02754-4
- Kunitsia, E., Popov, M., Gontar, T., Stankevych, S., Zabrodina, I., Stepankova, G. et al. (2024). Determination of the influence of hemp oil-based emulsion systems composition on the oxidation products content during storage. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 3 (6 (129)), 6–13. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.304466
- Kalyna, V., Stankevych, S., Zabrodina, I., Shubina, L., Chuiko, M., Mikheeva, O. et al. (2024). Development of the composition of anoxidation-stable dressing with high nutritional value. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (11 (127)), 29–37. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.296621
- Felix-Sagaste, K. G., Garcia-Carrasco, M., Picos-Corrales, L. A., Gonzalez-Ruelas, T., Rodriguez-Mercado, J. A. (2023). Plant-animal extracts and biocompatible polymers forming oil-in-water emulsions: Formulations for food and pharmaceutical industries. Hybrid Advances, 3, 100072. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hybadv.2023.100072
- Shirvani, A., Goli, S. A. H., Varshosaz, J., Salvia-Trujillo, L., Martín-Belloso, O. (2023). Edible Wax-Based Nanoparticles as Novel Stabilizers for Oil-in-Water Pickering Emulsion. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 16 (6), 1356–1373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-023-03014-3
- Ashfaq, A., Osama, K., Yousuf, O., Younis, K. (2024). Protein-based Emulsion Hydrogels and Their Application in the Development of Sustainable Food Products. Plant Foods for Human Nutrition, 79 (4), 759–768. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11130-024-01214-6
- Zhu, T., Ma, L., Jiang, H., Li, W., Guo, X., Yang, C., Bu, G. (2023). Functional, structural properties of pea protein isolate-xylooligosaccharide glycosylated conjugate and its application in O/W emulsion preparation. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization, 17 (6), 6135–6143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-023-02102-4
- Vélez-Erazo, E. M., Silva, I. L., Comunian, T., Kurozawa, L. E., Hubinger, M. D. (2020). Effect of chia oil and pea protein content on stability of emulsions obtained by ultrasound and powder production by spray drying. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 58 (10), 3765–3779. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04834-3
- Liu, X., McClements, D. J., Cao, Y., Xiao, H. (2016). Chemical and Physical Stability of Astaxanthin-Enriched Emulsion-Based Delivery Systems. Food Biophysics, 11 (3), 302–310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-016-9443-6
- Tirgarian, B., Farmani, J., Farahmandfar, R., Milani, J. M., Van Bockstaele, F. (2023). Switchable pH-responsive Biopolymeric Stabilizers Made by Sonothermal Glycation of Sodium Caseinate with κappa-carrageenan. Food Biophysics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-023-09778-7
- Shi, L., Cheng, Y., Jia, C., Lin, H., Zhang, W., He, J. (2024). Stable complex of sodium caseinate and hexaglycerol monooleate with improved oil-in-water emulsion stability and curcumin encapsulation. Food Biophysics, 19 (2), 321–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-024-09828-8
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Katerina Kunitsa, Aliona Dikhtyar, Oleh Kotliar, Svitlana Andrieieva, Tatiana Gontar, Serhii Stankevych, Iryna Balandina, Larysa Obolentseva, Oleg Kolontaievskyi, Anton Ryabev

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








