Cache invalidation based on a declarative approach for separating business logic of microservices from cache update rules
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.325932Keywords:
cache invalidation, Redis, Memcached, declarative approach, cache management, performance optimizationAbstract
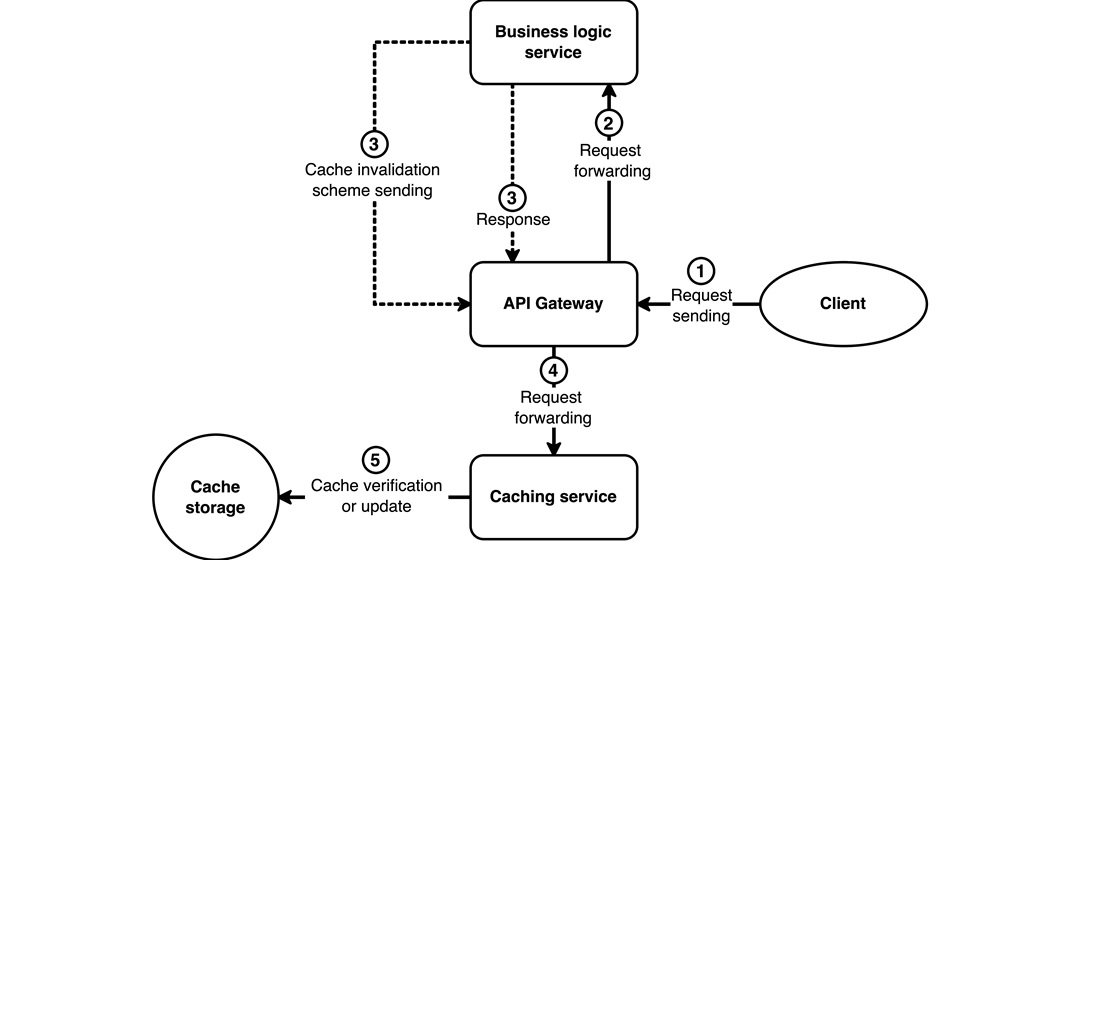
The object of this study is the mechanisms of cache invalidation within a microservice architecture. The research addresses the challenge of reducing inter-service dependences, enhancing system performance, and ensuring data consistency in distributed high-load environments by optimizing cache management strategies. The study's findings include the development of a declarative approach to cache invalidation, which ensures the decoupling of microservice business logic from cache update mechanisms. The proposed solution is based on a centralized cache management strategy utilizing YAML configurations in conjunction with asynchronous message exchange between services.
Optimization of the mechanisms for adding, updating, and deleting cache elements enables efficient management of cached data, warranting the avoidance of residual entries after deletion, updating all lists in which the element appeared, as well as maintaining cache consistency when updating or deleting data.
The proposed approach contributes to increasing the autonomy of microservices, reducing inter-service dependences, and more efficient use of the cache. The features and distinctive characteristics of the results relate to the fact that the proposed approach uses a declarative cache management model, which differs from conventional imperative solutions. This enables flexibility in configuring cache update mechanisms without the need to modify the business logic of microservices.
The practical implications of the study extend to high-load distributed systems where rapid data retrieval, scalability, and resilience to varying workloads are critical. The proposed approach could be applied in the design of effective caching strategies within microservice-based architectures
References
- Falkevych, V., Lisniak, A. (2024) Client state management using backend for frontend pattern architecture in B2B segment. Artificial Intelligence, 29 (2), 49–60. https://doi.org/10.15407/jai2024.02.049
- Falkevych, V. G., Lisniak, A. O. (2023). Methodology of cache invalidation in microservices architecture of the web applications. Scientific Notes of Taurida National V.I. Vernadsky University. Series: Technical Sciences, 1, 131–135. https://doi.org/10.32782/2663-5941/2023.1/20
- Faridi, M. T., Singh, K., Soni, K., Negi, S. (2023). Memcached vs Redis Caching Optimization Comparison using Machine Learning. 2023 2nd International Conference on Automation, Computing and Renewable Systems (ICACRS), 1153–1159. https://doi.org/10.1109/icacrs58579.2023.10404339
- Carra, D., Michiardi, P. (2014). Memory partitioning in Memcached: An experimental performance analysis. 2014 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), 1154–1159. https://doi.org/10.1109/icc.2014.6883477
- Zhang, H., Kallas, K., Pavlatos, S., Alur, R., Angel, S., Liu, V. (2024). MuCache: A General Framework for Caching in Microservice Graphs. Proceedings of the 21st USENIX Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation (NSDI 24), 221–238. Available at: https://www.usenix.org/system/files/nsdi24-zhang-haoran.pdf
- Chen, S., Tang, X., Wang, H., Zhao, H., Guo, M. (2016). Towards Scalable and Reliable In-Memory Storage System: A Case Study with Redis. 2016 IEEE Trustcom/BigDataSE/ISPA. https://doi.org/10.1109/trustcom.2016.0255
- Liu, Q. (2019). A High Performance Memory Key-Value Database Based on Redis. Journal of Computers, 14 (3), 170–183. https://doi.org/10.17706/jcp.14.3.170-183
- Fukuda, E. S., Inoue, H., Takenaka, T., Dahoo Kim, Sadahisa, T., Asai, T., Motomura, M. (2014). Caching memcached at reconfigurable network interface. 2014 24th International Conference on Field Programmable Logic and Applications (FPL), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/fpl.2014.6927487
- Ji, Z., Ganchev, I., O’Droma, M., Ding, T. (2014). A Distributed Redis Framework for Use in the UCWW. 2014 International Conference on Cyber-Enabled Distributed Computing and Knowledge Discovery, 241–244. https://doi.org/10.1109/cyberc.2014.50
- Yang, J., Yue, Y., Vinayak, R. (2021). Segcache: a memory-efficient and scalable in-memory key-value cache for small objects. 18th USENIX Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation (NSDI 21), 503–518. Available at: https://www.usenix.org/conference/nsdi21/presentation/yang-juncheng
- Rahul, Singh, K., Vrinda, Dipanshu (2024). Review Paper on Machine Learning Based Memcached Cluster Auto Scaling. Emerging Trends in IoT and Computing Technologies, 330–337. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781003535423-55
- Almeida, D., Lopes, M., Saraiva, L., Abbasi, M., Martins, P., Silva, J., Váz, P. (2023). Performance Comparison of Redis, Memcached, MySQL, and PostgreSQL: A Study on Key-Value and Relational Databases. 2023 Second International Conference On Smart Technologies For Smart Nation (SmartTechCon), 902–907. https://doi.org/10.1109/smarttechcon57526.2023.10391649
- Chopade, R., Pachghare, V. (2021). A data recovery technique for Redis using internal dictionary structure. Forensic Science International: Digital Investigation, 38, 301218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsidi.2021.301218
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Vitalii Falkevych, Andrii Lisniak

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.









