Numerical optimization of control strategies for coupled vibrational systems
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.326029Keywords:
Pontryagin’s maximum principle, wave equation, method of straight lines, functional convergenceAbstract
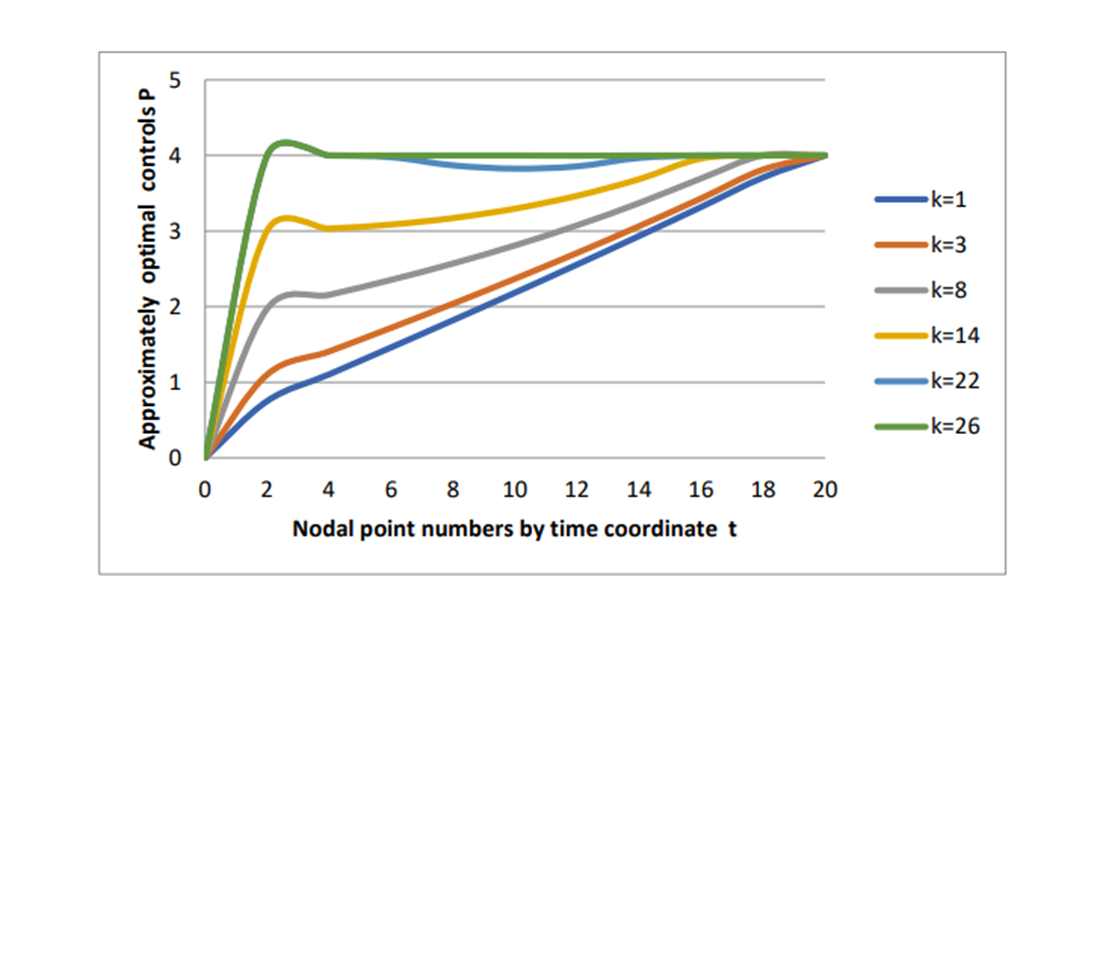
The study examines the numerical solution of vibration control problems in a coupled system consisting of two interacting objects. The problem is solved under the assumption that the left boundary of the distributed system is fixed, while an object with lumped parameters is attached to the right boundary, where a boundary control action is also applied to the distributed system. Special attention is given to obtaining a numerical solution to the problem. The solution is approached using two methods: the gradient projection method and, due to the linearity of the boundary problem concerning phase coordinates and control inputs, the method of successive approximations. By introducing an additional variable, the one-dimensional wave equation is approximated using the method of lines, transforming it into a system of ordinary differential equations of the 2n-th order. The resulting variational problem for the system with lumped parameters is then numerically solved based on Pontryagin’s maximum principle. The approximately optimal controls, obtained using the gradient projection method with a specially chosen step size, form a minimizing sequence of controls. Based on the numerical results, functional convergence is established. The method of successive approximations provides an optimal control solution as early as the second iteration, regardless of the initial control. This demonstrates the method’s efficiency and reliability for solving linear optimal control problems. The developed numerical techniques can be applied to optimize the dynamic behavior of complex mechanical structures, enhance system stability, and improve operational efficiency in various engineering applications
References
- Fagerholt, K., Psaraftis, H. N. (2015). On two speed optimization problems for ships that sail in and out of emission control areas. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 39, 56–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2015.06.005
- Entner, D., Fleck, P., Vosgien, T., Münzer, C., Finck, S., Prante, T., Schwarz, M. (2019). A Systematic Approach for the Selection of Optimization Algorithms including End-User Requirements Applied to Box-Type Boom Crane Design. Applied System Innovation, 2 (3), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/asi2030020
- Alharbi, F., Luo, S., Zhang, H., Shaukat, K., Yang, G., Wheeler, C. A., Chen, Z. (2023). A Brief Review of Acoustic and Vibration Signal-Based Fault Detection for Belt Conveyor Idlers Using Machine Learning Models. Sensors, 23 (4), 1902. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23041902
- Okba, A. C., Salah, K. (2022). Analytical and numerical-graphical optimization of dynamic vibration absorber based on two-fixed point theory. International Journal of Mechanics and Control, 22.
- Fayyaz, Bashmal, S., Nazir, A., Khan, S., Alofi, A. (2025). Damping Optimization and Energy Absorption of Mechanical Metamaterials for Enhanced Vibration Control Applications: A Critical Review. Polymers, 17 (2), 237. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17020237
- Lariviere, O., Chadefaux, D., Sauret, C., Thoreux, P. (2021). Vibration https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470411353Transmission during Manual Wheelchair Propulsion: A Systematic Review. Vibration, 4 (2), 444–481. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration4020029
- Alba, E., Blum, C., Isasi, P., León, C., Gómez, J. A. (Eds.) (2008). Optimization Techniques for Solving Complex Problems. John Wiley & Sons. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470411353
- Poley, R. (2020). Control Theory Fundamentals. CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform.
- Rodriguez-Loya, J., Lerma, M., Gardea-Torresdey, J. L. (2023). Dynamic Light Scattering and Its Application to Control Nanoparticle Aggregation in Colloidal Systems: A Review. Micromachines, 15 (1), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15010024
- Omar, N., Serra-Capizzano, S., Qaraad, B., Alharbi, F., Moaaz, O., Elabbasy, E. M. (2024). More Effective Criteria for Testing the Oscillation of Solutions of Third-Order Differential Equations. Axioms, 13 (3), 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms13030139
- Mamtiyev, K., Rzayeva, U. (2024). Finding and implementing the numerical solution of an optimal control problem for oscillations in a coupled objects system. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2 (2 (128)), 64–74. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.301714
- Liu, H., Cui, S., Liu, Y., Ren, Y., Sun, Y. (2018). Design and Vibration Suppression Control of a Modular Elastic Joint. Sensors, 18 (6), 1869. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18061869
- Ram, Y. M., Inman, D. J. (1999). Optimal control for vibrating systems. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 13 (6), 879–892. https://doi.org/10.1006/mssp.1999.1239
- Zhang, J. F. (2002). Optimal control for mechanical vibration systems based on second-order matrix equations. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 16 (1), 61–67. https://doi.org/10.1006/mssp.2001.1441
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Kamil Mamtiyev, Ulviyya Rzayeva, Rena Mikayilova

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








