Визначення детермінантів ефективного використання інформаційних панелей у марокканських компаніях, що стикаються з проблемами цифровізації
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.326103Ключові слова:
інформаційні панелі, цифровізація, управління продуктивністю, поведінка користувачів, інформаційні технологіїАнотація
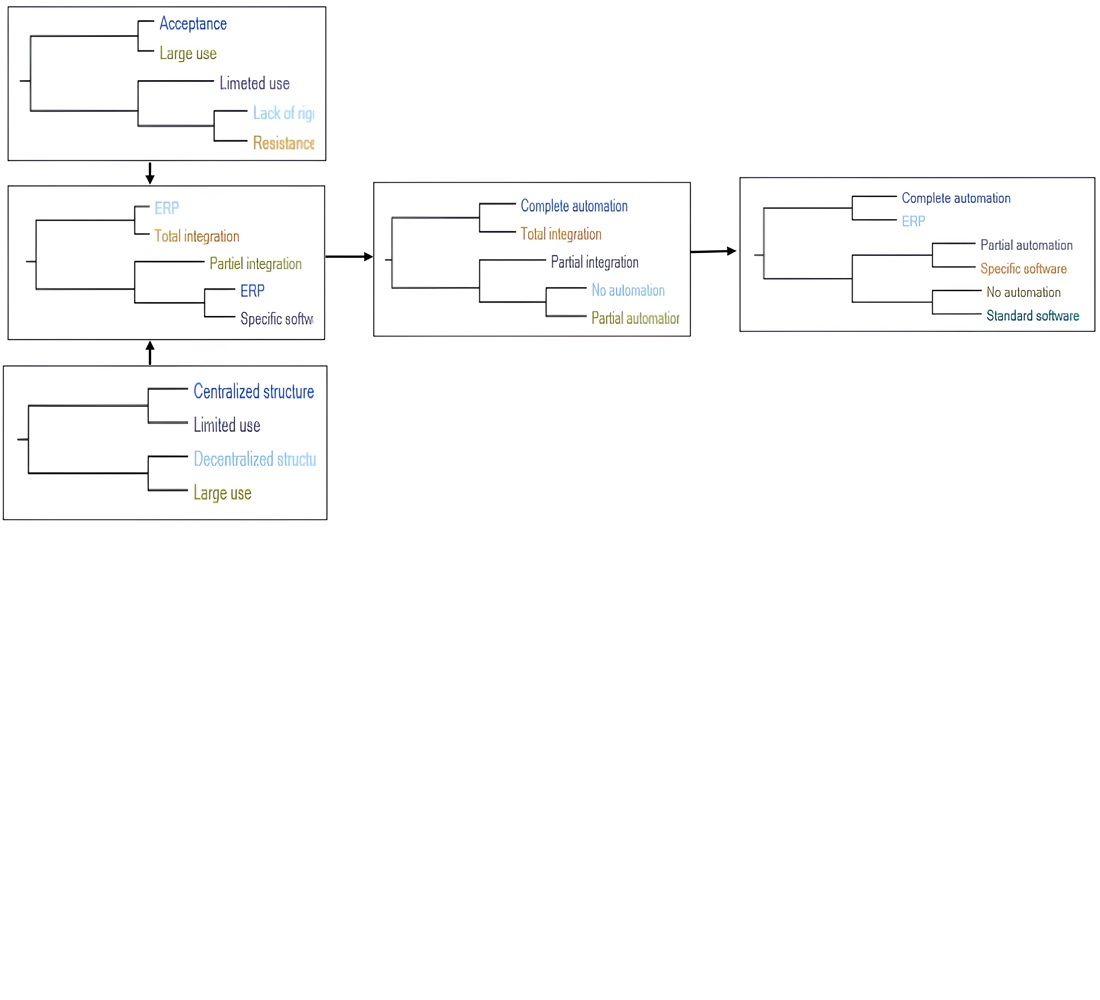
Рухи цифровізації спричиняють глибокі зміни, що впливають на організаційні структури та управлінську практику в компаніях, особливо після краху парадигми контролю ефективності та появи її пілотування за допомогою різних інструментів, з панелями інструментів, які використовуються найчастіше. Мета цього дослідження полягає в визначенні детермінанти ефективного використання інформаційних панелей менеджерами протягом усього пілотного процесу продуктивності для подолання викликів, пов’язаних із цифровізацією економічного та соціального середовища. Результати показують, що деяким компаніям вдалося здійснити цифровізований перехід і максимізувати цінність цифровізованих інформаційних панелей, тоді як інші стикаються із затримками, які перешкоджають досягненню мети. Це призводить до ідентифікації трьох ключових визначальних факторів для ефективного використання інформаційних панелей. Це необхідність впровадження інформаційних технологій, які об’єднують усі процеси, що сильно корелює (r>0,62) зі ступенем повної інтеграції та повної автоматизації інформаційних панелей, зобов’язання розвивати сприятливу поведінку щодо використання інформаційних технологій, яка має високу кореляцію (r=0,764146) із надмірним використанням цифровізованих інформаційних панелей керівниками, а також важливість прийняття гнучких структур для зменшення прийняття рішень обмеження для менеджерів з важливою кореляцією (r=0,673879) із широким використанням цифровізованих інформаційних панелей. Відмінною рисою цих результатів є те, що вони показують порівняння між високо цифровізованими компаніями та компаніями, які перебувають на початковому етапі цифровізації. Це дало б змогу останнім добре керувати переходом до цифровізації, спростивши для їхніх керівників пілотування своєї діяльності з метою отримання організаційних і конкурентних переваг, за умови, що протягом усього процесу цифровізації вони приймають політику реструктуризації, засновану на модернізації своїх структур та інтеграції інформаційної культури в свої стратегії, щоб розвивати пілотні компетенції своїх менеджерів і боротися з несприятливим ставленням до використання цифрових технологій
Посилання
- Lorino, P. (2003). Méthodes et pratiques de la performance: le pilotage par les processus et les compétences. Ed. d’organisation. Available at: https://d1wqtxts1xzle7.cloudfront.net/38508591/indicateurs_2-libre.pdf?1439933483=&response-content-disposition=inline%3B+filename%3DMETHODES_ET_PRATIQUES_DE_LA_PERFORMANCE.pdf&Expires=1743589406&Signature=I6uoLPmyAjGyG~~NFH3HsbsNg2bsFRhWyRNJJeyahhG4GPwABCy6d-~KxGNzzB96xS58GSxkXXph~HDeCDwmZ3VuHnagSJdCUTyBmY~oPl-Hmk6f4Yr3lCI7OHqR~2SvcSHq5yrhGAXKiweWQJ~8IY5UvPoRJSWnPQwRoEgHX9Kc80jPgcrKSOOShYlYSC6fJoHnCLB5TmhFO3FRHpFzVcolMrUb9-T5UJ-Uh28H6jLZ86GmTrzlw~JJYYP5Wm~MIEGEyeUxIHZ53l57bYLC1x-1OgXdI4XwZ2djYJbRN03THFvDzIxksijvf~lDQfFFPivt~ZVhufrMLc~Lut3B1g__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAJLOHF5GGSLRBV4ZA
- Pauwels, K., Ambler, T., Clark, B. H., LaPointe, P., Reibstein, D., Skiera, B. et al. (2009). Dashboards as a Service. Journal of Service Research, 12 (2), 175–189. https://doi.org/10.1177/1094670509344213
- Saeed, K. A., Wu, D., Xu, D. J. (2024). Effect of Designer- versus User-driven Network-monitoring Dashboard Design on User Flow Experience and Performance: The Role of Augmented Virtuality. Information & Management, 61 (3), 103926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2024.103926
- Kaplan, R. S., Norton, D. P. (2005). The balanced scorecard: measures that drive performance. Harvard Business Review Boston. Available at: https://hbr.org/2005/07/the-balanced-scorecard-measures-that-drive-performance
- Teplická, K., Steingartner, W., Kádárová, J., Hurná, S. (2020). Dashboards - effective instrument of decision in synergy with software support. Polish Journal of Management Studies, 22 (1), 565–582. https://doi.org/10.17512/pjms.2020.22.1.36
- Madsen, D. Ø. (2024). Balanced Scorecard. Reference Module in Social Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-443-13701-3.00566-1
- Soni, P., de Runz, C., Bouali, F., Venturini, G. (2024). A survey on automatic dashboard recommendation systems. Visual Informatics, 8 (1), 67–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.visinf.2024.01.002
- Chandrasekaran, H., Xuan, T. Y., Mang, T. K. (2023). High Performance Business Intelligence Dashboard. 2023 IEEE 8th International Conference On Software Engineering and Computer Systems (ICSECS), 158–163. https://doi.org/10.1109/icsecs58457.2023.10256421
- Santiago Rivera, D., Shanks, G. (2015). A Dashboard to Support Management of Business Analytics Capabilities. Journal of Decision Systems, 24 (1), 73–86. https://doi.org/10.1080/12460125.2015.994335
- Barney, J. B. (2000). Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. Economics Meets Sociology in Strategic Management, 203–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0742-3322(00)17018-4
- Davis, F. D., Granić, A. (2024). The Technology Acceptance Model. In Human-Computer Interaction Series. Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-45274-2
- Reinking, J. (2011). Contingency Theory in Information Systems Research. Information Systems Theory, 247–263. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-6108-2_13
- Yin, R. K. (2018). Case study research and applications: Design and Methods. Vol. 6. Sage Thousand Oaks, 319.
- Ajjan, H., Kumar, R. L., Subramaniam, C. (2016). Information technology portfolio management implementation: a case study. Journal of Enterprise Information Management, 29 (6), 841–859. https://doi.org/10.1108/jeim-07-2015-0065
- The Offshoring of Engineering (2008). Washington, DC: The National Academies Press. https://doi.org/10.17226/12067
- Progiciel De Gestion Intégré (2020). Office québécois de la langue française.
- Baaziz, A., Khelil, M. (2006). Balanced ScoreCard et pilotage de la performance: Cas de la Division Forage. In: Journées Scientifiques et Techniques de Sonatrach JST’7. Available at: https://hal.science/hal-00824497/document
- Reinking, J. (2013). The Diffusion Of Digital Dashboards: An Examination Of Dashboard Utilization And The Managerial Decision Environment. University of Central Florida. Available at: https://scispace.com/pdf/the-diffusion-of-digital-dashboards-an-examination-of-67eh029kuk.pdf
- Cebekhulu, B., Ozor, P. (2022). The influence of quality management and erp systems on organisational culture and performance. Proceedings on Engineering Sciences, 4 (1), 41–50. https://doi.org/10.24874/pes04.01.007
- Donaldson, L. (2006). The Contingency Theory of Organizational Design: Challenges and Opportunities. Organization Design, 19–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/0-387-34173-0_2
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2025 Mohamed Alami

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.
Ліцензійний договір – це документ, в якому автор гарантує, що володіє усіма авторськими правами на твір (рукопис, статтю, тощо).
Автори, підписуючи Ліцензійний договір з ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР», мають усі права на подальше використання свого твору за умови посилання на наше видання, в якому твір опублікований. Відповідно до умов Ліцензійного договору, Видавець ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР» не забирає ваші авторські права та отримує від авторів дозвіл на використання та розповсюдження публікації через світові наукові ресурси (власні електронні ресурси, наукометричні бази даних, репозитарії, бібліотеки тощо).
За відсутності підписаного Ліцензійного договору або за відсутністю вказаних в цьому договорі ідентифікаторів, що дають змогу ідентифікувати особу автора, редакція не має права працювати з рукописом.
Важливо пам’ятати, що існує і інший тип угоди між авторами та видавцями – коли авторські права передаються від авторів до видавця. В такому разі автори втрачають права власності на свій твір та не можуть його використовувати в будь-який спосіб.










