Розробка алгоритмізації задачі маршрутизації транспортних засобів
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.326135Ключові слова:
оптимізація, машинне навчання, покриття множини, проблема маршрутизації транспортних засобів, вартістьАнотація
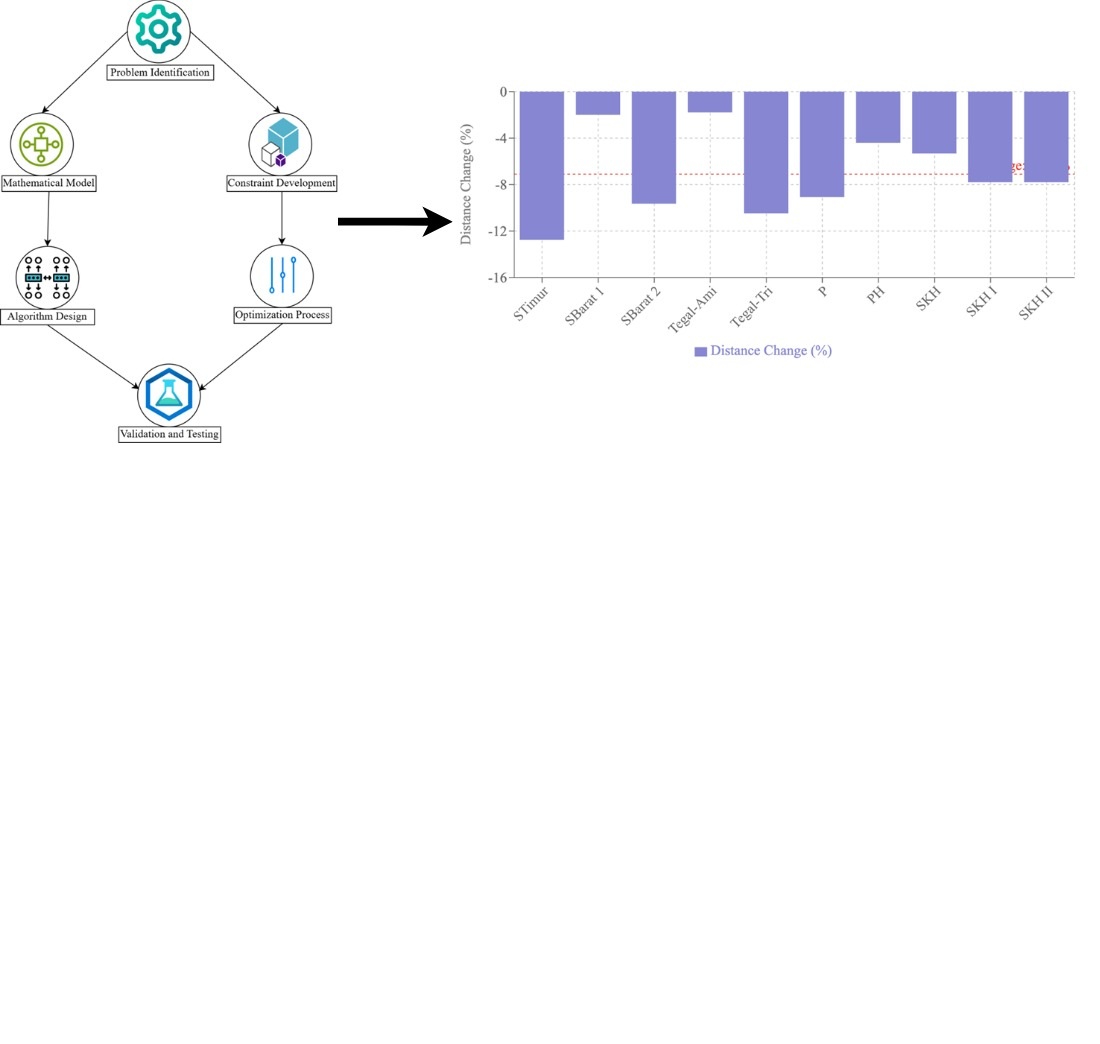
Проблема маршрутизації транспортних засобів з обмеженою пропускною здатністю та залежними від часу вимогами є значною проблемою оптимізації в галузі логістики та транспорту, що характеризується динамічними вимогами клієнтів, суворими часовими вікнами та неоднорідними автопарками. Це дослідження зосереджено на міських операціях доставки посилок як на основному об’єкті дослідження. Розглянута проблема полягає в неефективності традиційних стратегій маршрутизації транспортних засобів в адаптації до змінних у часі вимог клієнтів та операційних обмежень, що часто призводить до збільшення витрат та затримок обслуговування. Це дослідження має на меті мінімізувати загальні операційні витрати, забезпечуючи при цьому дотримання обмежень пропускної здатності, безперервність обслуговування та коливання попиту. Розроблено комплексну математичну модель на основі повністю зв’язаного, орієнтованого ациклічного графа G=(V, A), що включає змінні рішення, що представляють послідовності маршрутизації транспортних засобів, час та призначення типів транспортних засобів. Це дослідження розглядає проблему маршрутизації транспортних засобів з обмеженою пропускною здатністю та залежними від часу вимогами у міській доставці посилок, де традиційні методи маршрутизації мають труднощі з динамічними вимогами та операційними обмеженнями. Розроблено математичну модель з використанням орієнтованого ациклічного графа, оптимізовану за допомогою градієнтного методу з наближенням Гессе, розкладанням LU та квазіньютонівськими методами. Експерименти на наборах даних з кількістю клієнтів до 200 та 20 транспортними засобами зі скороченнями від 1,79% до 12,75%. Найбільш значне покращення спостерігалося в Сідораме Тімур, де відстань оптимізації зменшилася на 12,75%, що свідчить про високу точність оптимізації маршруту. Для задачі про покриття множини запропонований алгоритм досяг покращення якості рішення на 6,46% порівняно з традиційними жадібними алгоритмами
Посилання
- Anityasari, M., Rinardi, H. C., Warmadewanthi, I. D. A. A. (2024). Analysing medical waste transportation using periodic vehicle routing problem for Surabaya public health facilities. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management, 27 (2), 830–847. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-024-02124-0
- Rezaei, B., Gadelha Guimaraes, F., Enayatifar, R., C. Haddow, P. (2024). Exploring dynamic population Island genetic algorithm for solving the capacitated vehicle routing problem. Memetic Computing, 16 (2), 179–202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12293-024-00412-8
- Ambrosino, D., Cerrone, C. (2022). A Rich Vehicle Routing Problem for a City Logistics Problem. Mathematics, 10 (2), 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10020191
- Lim, H., Lee, G. M., Singgih, I. K. (2021). Multi-Depot Split-Delivery Vehicle Routing Problem. IEEE Access, 9, 112206–112220. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2021.3103640
- Wei, X., Niu, C., Zhao, L., Wang, Y. (2024). Combination of ant colony and student psychology based optimization for the multi-depot electric vehicle routing problem with time windows. Cluster Computing, 28 (2). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-024-04821-9
- Kim, G. (2024). Electric Vehicle Routing Problem with States of Charging Stations. Sustainability, 16 (8), 3439. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16083439
- Li, B., Wu, G., He, Y., Fan, M., Pedrycz, W. (2022). An Overview and Experimental Study of Learning-Based Optimization Algorithms for the Vehicle Routing Problem. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 9 (7), 1115–1138. https://doi.org/10.1109/jas.2022.105677
- Khorsi, M., Chaharsooghi, S. K., Husseinzadeh Kashan, A., Bozorgi-Amiri, A. (2022). Solving the humanitarian multi-trip cumulative capacitated routing problem via a grouping metaheuristic algorithm. Annals of Operations Research, 319 (1), 173–210. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-022-04757-6
- Yue, B., Ma, J., Shi, J., Yang, J. (2024). A Deep Reinforcement Learning-Based Adaptive Search for Solving Time-Dependent Green Vehicle Routing Problem. IEEE Access, 12, 33400–33419. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2024.3369474
- Thakur, G., Pal, A., Mittal, N., Yajid, M. S. A., Gared, F. (2024). A significant exploration on meta-heuristic based approaches for optimization in the waste management route problems. Scientific Reports, 14 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-64133-1
- Shahbazian, R., Pugliese, L. D. P., Guerriero, F., Macrina, G. (2024). Integrating Machine Learning Into Vehicle Routing Problem: Methods and Applications. IEEE Access, 12, 93087–93115. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2024.3422479
- Pan, B., Zhang, Z., Lim, A. (2021). Multi-trip time-dependent vehicle routing problem with time windows. European Journal of Operational Research, 291 (1), 218–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2020.09.022
- Azad, T., Rahman, H. F., Chakrabortty, R. K., Ryan, M. J. (2022). Optimization of integrated production scheduling and vehicle routing problem with batch delivery to multiple customers in supply chain. Memetic Computing, 14 (3), 355–376. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12293-022-00372-x
- Huang, G., Qi, Y., Cai, Y., Luo, Y., Huang, H. (2024). A Grey Wolf Optimizer Algorithm for Multi-Objective Cumulative Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem Considering Operation Time. Biomimetics, 9 (6), 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9060331
- Hesam Sadati, M. E., Çatay, B., Aksen, D. (2021). An efficient variable neighborhood search with tabu shaking for a class of multi-depot vehicle routing problems. Computers & Operations Research, 133, 105269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cor.2021.105269
- Akbarpour, N., Salehi-Amiri, A., Hajiaghaei-Keshteli, M., Oliva, D. (2021). An innovative waste management system in a smart city under stochastic optimization using vehicle routing problem. Soft Computing, 25 (8), 6707–6727. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-021-05669-6
- Chen, C.-M., Lv, S., Ning, J., Wu, J. M.-T. (2023). A Genetic Algorithm for the Waitable Time-Varying Multi-Depot Green Vehicle Routing Problem. Symmetry, 15 (1), 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15010124
- Park, S., Ha, C., Seok, H. (2023). Vehicle Routing Problem Model with Practicality. Processes, 11 (3), 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11030654
- Fernández Gil, A., Lalla-Ruiz, E., Gómez Sánchez, M., Castro, C. (2023). The cumulative vehicle routing problem with time windows: models and algorithm. Annals of Operations Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-022-05102-7
- Mancini, S., Gansterer, M. (2024). Bundle generation for the vehicle routing problem with occasional drivers and time windows. Flexible Services and Manufacturing Journal, 36 (4), 1189–1221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10696-023-09529-3
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2025 Muhammad Amin, Syahril Efendi, Mahyuddin K. M. Nasution, Marischa Elveny

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.
Ліцензійний договір – це документ, в якому автор гарантує, що володіє усіма авторськими правами на твір (рукопис, статтю, тощо).
Автори, підписуючи Ліцензійний договір з ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР», мають усі права на подальше використання свого твору за умови посилання на наше видання, в якому твір опублікований. Відповідно до умов Ліцензійного договору, Видавець ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР» не забирає ваші авторські права та отримує від авторів дозвіл на використання та розповсюдження публікації через світові наукові ресурси (власні електронні ресурси, наукометричні бази даних, репозитарії, бібліотеки тощо).
За відсутності підписаного Ліцензійного договору або за відсутністю вказаних в цьому договорі ідентифікаторів, що дають змогу ідентифікувати особу автора, редакція не має права працювати з рукописом.
Важливо пам’ятати, що існує і інший тип угоди між авторами та видавцями – коли авторські права передаються від авторів до видавця. В такому разі автори втрачають права власності на свій твір та не можуть його використовувати в будь-який спосіб.









