Identification of patterns of non-stationary laminar flow of a viscous fluid at the inlet section of plane-parallel pressure flow
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.326379Keywords:
plane-parallel flow, inlet section, unsteady flow, viscous fluid, velocity distributionAbstract
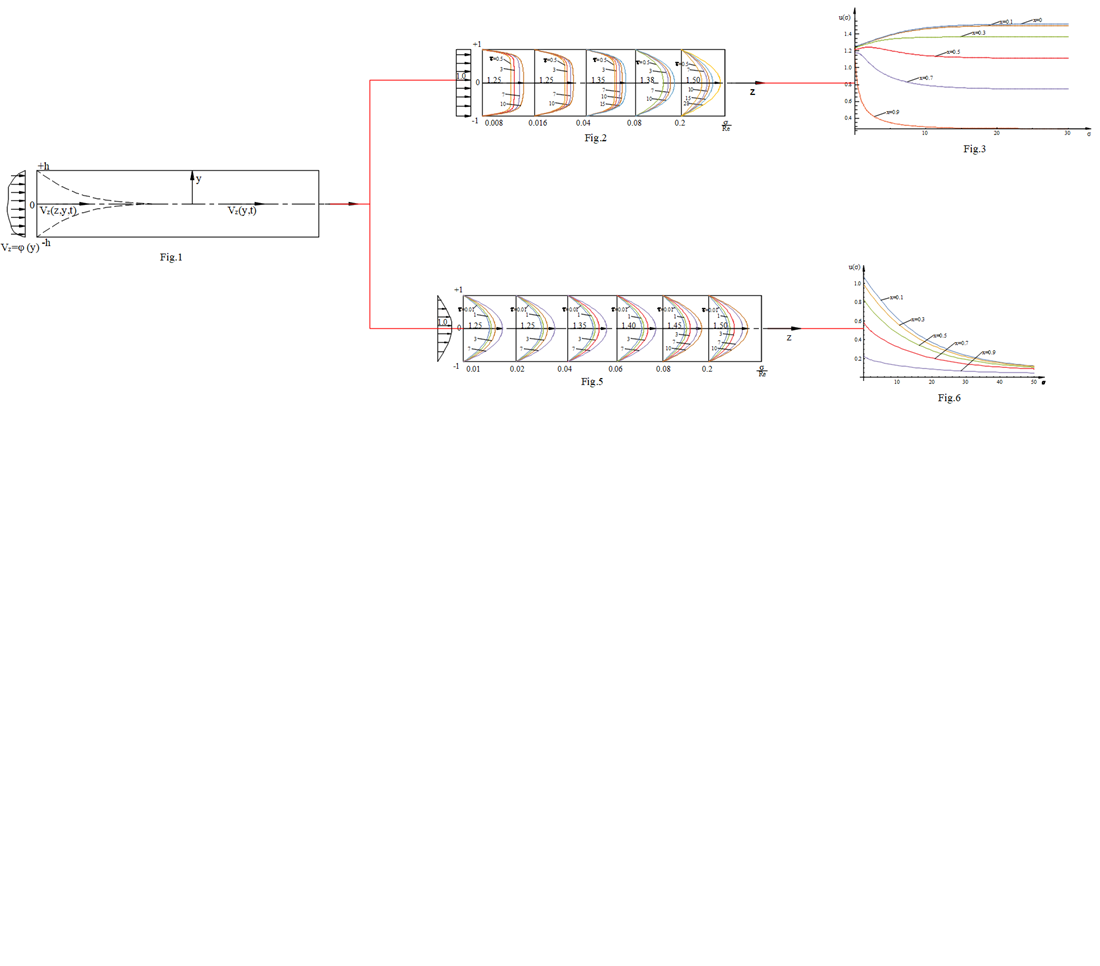
The inlet region of a plane-parallel pressure flow is the subject of this study. The patterns of variations in the hydrodynamic inlet region under unsteady plane-parallel pressure flow of a viscous fluid are examined in this research. Based on the boundary layer equation and flow characteristics, the boundary conditions of the problem were determined and a boundary value problem was formulated. The problem's boundary conditions were established and a boundary value problem was developed based on the boundary layer equation and flow characteristics. In order to find patterns of velocity change over time and over the length of the inlet region under general boundary conditions, a method for integrating the boundary value conditions was created. Solutions for scenarios with a constant and parabolic velocity distribution in the inlet region were derived from the general solutions. Regularities of pressure and velocity change were found along the entire hydrodynamic inlet region.
Using computer analysis, graphs of velocity changes over time at various points along the entire length of the inlet region are constructed. The patterns of velocity distribution along the entire length of the inlet region depending on time can be seen using graphs. This allows one to estimate the length of the hydrodynamic inlet region and calculate the fluid flow velocity at any point in this region. The findings enable revealing the essence of the processes running in an hydropneumatic automation system's transition sections. Based on the revealed regularities of the hydrodynamic parameters of viscous incompressible liquid during unsteady flows, it is possible to correctly design of the automatic systems' channels of regulating units ensuring their smooth and accurate operation
References
- Atabek, H. B., Chang, C. C., Fingerson, L. M. (1964). Measurement of Laminar Oscillatory Flow in the Inlet Length of a Circular Tube. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 9 (2), 219–227. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/9/2/309
- Avula, X. J. R. (1969). Analysis of suddenly started laminar flow in the entrance region of a circular tube. Applied Scientific Research, 21 (1), 248–259. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00411611
- Lew, H. S., Fung, Y. C. (1970). Entry flow into blood vessels at arbitrary Reynolds number. Journal of Biomechanics, 3 (1), 23–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9290(70)90048-5
- Mohanty, A. K., Asthana, S. B. L. (1979). Laminar flow in the entrance region of a smooth pipe. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 90 (3), 433–447. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0022112079002330
- Reci, A., Sederman, A. J., Gladden, L. F. (2018). Experimental evidence of velocity profile inversion in developing laminar flow using magnetic resonance velocimetry. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 851, 545–557. https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2018.512
- Urbanowicz, K., Firkowski, M., Bergant, A. (2018). Comparing analytical solutions for unsteady laminar pipe flow. Conference: BHR Pressure Surges. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/329759824_Comparing_analytical_solutions_for_unsteady_laminar_pipe_flow
- Ainola, L. Ya., Ruustal (1985). Development of flow at the inlet section of a round pipe during acceleration of liquid motion. Transactions of the Tallinn Polytechnic Institute, Tallinn, 95–107.
- Vardy, A. E., Brown, J. M. B. (2010). Laminar pipe flow with time-dependent viscosity. Journal of Hydroinformatics, 13 (4), 729–740. https://doi.org/10.2166/hydro.2010.073
- Sarukhanyan, A., Vardanyan, Y., Baljyan, P., Vermishyan, G. (2023). Pattern identification of the non-stationary laminar flow of a viscous fluid in the round pipe inlet section. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2 (7 (122)), 33–42. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.278001
- Sarukhanyan, A., Vermishyan, G., Kelejyan, H. (2023). Plane-Parallel Laminar Flow of Viscous Fluid in the Transition Zone of the Inlet Section. Journal of Architectural and Engineering Research, 4, 75–85. https://doi.org/10.54338/27382656-2023.4-008
- Sarukhanyan, A., Vartanyan, A., Vermishyan, G., Tokmajyan, V. (2020). The Study of Hydrodynamic Processes Occurring on Transition of Sudden Expanding of Hydraulic Section of Plane – Parallel Full Pipe Flow. TEM Journal, 1494–1501. https://doi.org/10.18421/tem94-23
- Pomerenk, O., Carrillo Segura, S., Cao, F., Wu, J., Ristroph, L. (2023). Hydrodynamics of finite-length pipes at intermediate Reynolds numbers. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 959. https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2023.99
- Daprà, I., Scarpi, G. (2017). Unsteady Flow of Fluids With Arbitrarily Time-Dependent Rheological Behavior. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 139 (5). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4035637
- Kannaiyan, A., Natarajan, S., Vinoth, B. R. (2022). Stability of a laminar pipe flow subjected to a step-like increase in the flow rate. Physics of Fluids, 34 (6). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0090337
- Michioku, K. (2017). Three dimensional potential flow analysis on diversion and intake works from a straight channel. Journal of Japan Society of Civil Engineers, Ser. B1 (Hydraulic Engineering), 73 (3), 71–76. https://doi.org/10.2208/jscejhe.73.71
- Lebon, B., Peixinho, J., Ishizaka, S., Tasaka, Y. (2018). Subcritical transition to turbulence in a sudden circular pipe expansion. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 849, 340–354. https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2018.421
- Shajari, G., Abbasi, M., Jamei, M. K. (2020). Entrance length of oscillatory flows in parallel plate microchannels. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 235 (19), 3833–3843. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954406220968125
- Schlichting, H., Gersten, K. (2017). Boundary-Layer Theory. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-52919-5
- Tikhonov, A. N., Samarskii, A. A. (1999). Equations of Mathematical Physics. Moscow: Nauka, 799.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Arestak Sarukhanyan, Garnik Vermishyan, Hovhannes Kelejyan, Pargev Baljyan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.









