Optimization of border gateway routing protocol with Lagrange multiplier and gradient descent integration for network
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.326561Keywords:
BGP, connection stability, routing, machine learning, Lagrange multiplier, gradient descentAbstract
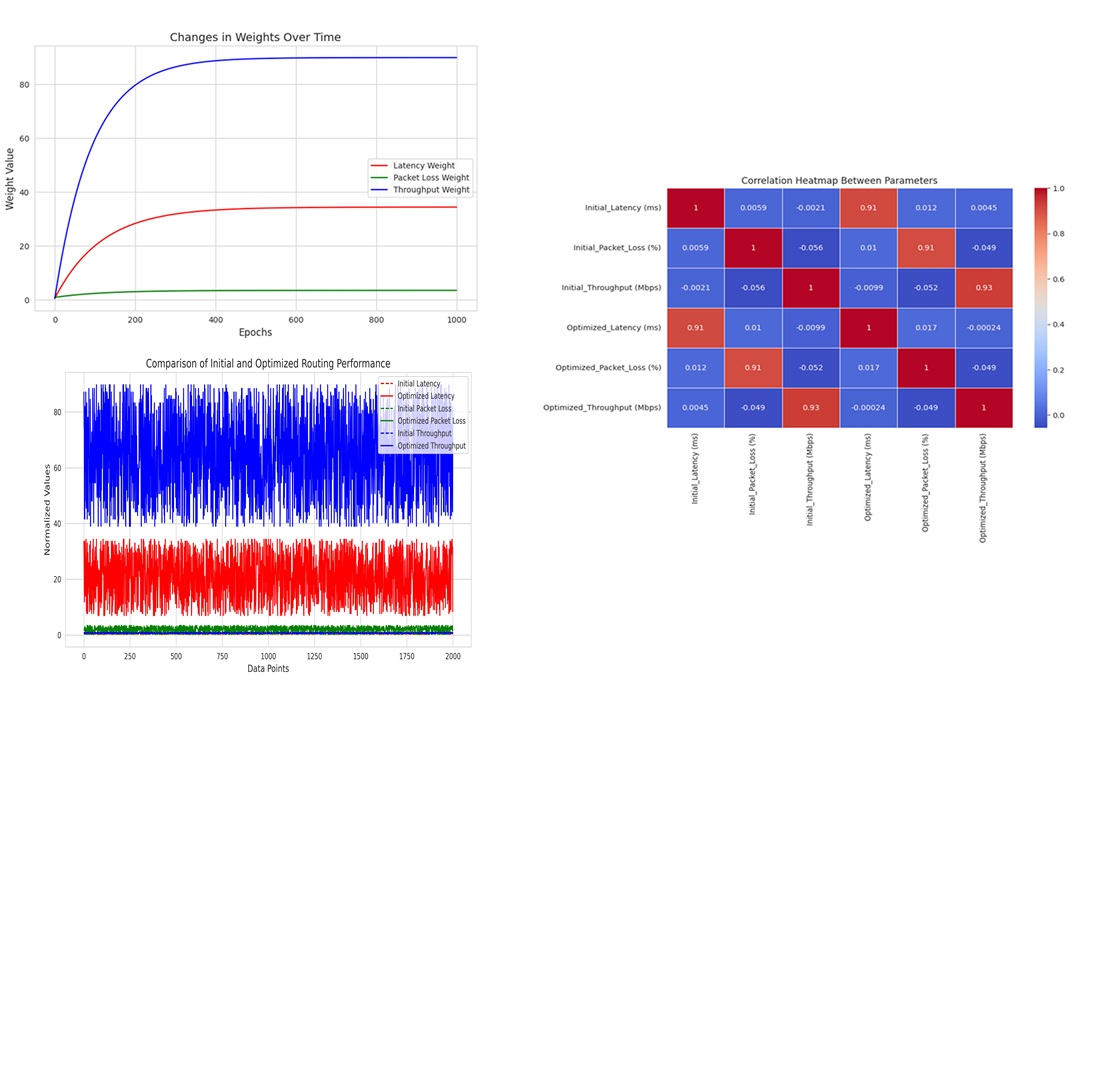
This study has a research object, namely data transmission lines. In this study, there are problems that must be solved related to the optimization of network transmission routes that are dynamic and adaptive to changes in real-time conditions, including latency factors, connection stability, and algorithm integration that can accommodate large-scale network needs efficiently in terms of transmission. The results obtained from this study are in the form of a model that can identify route management and optimize the border gateway protocol. The results of the study show that the application of this method can optimize the transmission path by considering network constraints and real-time condition dynamics. This study has an interpretation that the proposed model is proven to be effective in improving network performance, with increased efficiency, reduced constraints, and the ability to adapt to changes in network conditions. This is evidenced by the accuracy in the form of quantitative effectiveness by producing 95 % accuracy with the Reinforcement Learning model, able to significantly increase efficiency and accuracy compared to traditional methods in BGP routing optimization. The characteristics contained in this study include the ability to manage and identify transmission routes to improve network efficiency, reduce latency, increase throughput, minimize the number of hops in managing BGP transmission routes. There are limitations related to input data processing that require deeper annotation. This study contributes to BGP route optimization with machine learning algorithms that can be applied in complex and dynamic networks
References
- Shahid, K., Ahmad, S. N., Rizvi, S. T. H. (2024). Optimizing Network Performance: A Comparative Analysis of EIGRP, OSPF, and BGP in IPv6-Based Load-Sharing and Link-Failover Systems. Future Internet, 16 (9), 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi16090339
- Mastilak, L., Helebrandt, P., Galinski, M., Kotuliak, I. (2022). Secure Inter-Domain Routing Based on Blockchain: A Comprehensive Survey. Sensors, 22 (4), 1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22041437
- Scott, B. A., Johnstone, M. N., Szewczyk, P. (2024). A Survey of Advanced Border Gateway Protocol Attack Detection Techniques. Sensors, 24 (19), 6414. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24196414
- Djenna, A., Harous, S., Saidouni, D. E. (2021). Internet of Things Meet Internet of Threats: New Concern Cyber Security Issues of Critical Cyber Infrastructure. Applied Sciences, 11 (10), 4580. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104580
- Romo-Chavero, M. A., Cantoral-Ceballos, J. A., Pérez-Díaz, J. A., Martinez-Cagnazzo, C. (2024). Median Absolute Deviation for BGP Anomaly Detection. Future Internet, 16 (5), 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi16050146
- Gupta, C., Johri, I., Srinivasan, K., Hu, Y.-C., Qaisar, S. M., Huang, K.-Y. (2022). A Systematic Review on Machine Learning and Deep Learning Models for Electronic Information Security in Mobile Networks. Sensors, 22 (5), 2017. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22052017
- Rahmani, A. M., Gia, T. N., Negash, B., Anzanpour, A., Azimi, I., Jiang, M., Liljeberg, P. (2018). Exploiting smart e-Health gateways at the edge of healthcare Internet-of-Things: A fog computing approach. Future Generation Computer Systems, 78, 641–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2017.02.014
- Wu, Y., Wu, Y., Guerrero, J. M., Vasquez, J. C. (2021). A comprehensive overview of framework for developing sustainable energy internet: From things-based energy network to services-based management system. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 150, 111409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2021.111409
- Zhao, X., Band, S. S., Elnaffar, S., Sookhak, M., Mosavi, A., Salwana, E. (2021). The Implementation of Border Gateway Protocol Using Software-Defined Networks: A Systematic Literature Review. IEEE Access, 9, 112596–112606. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2021.3103241
- Weitz, K., Woos, D., Torlak, E., Ernst, M. D., Krishnamurthy, A., Tatlock, Z. (2016). Scalable verification of border gateway protocol configurations with an SMT solver. Proceedings of the 2016 ACM SIGPLAN International Conference on Object-Oriented Programming, Systems, Languages, and Applications, 765–780. https://doi.org/10.1145/2983990.2984012
- Sharma, S., Kang, D. H., Montes de Oca, J. R., Mudgal, A. (2021). Machine learning methods for commercial vehicle wait time prediction at a border crossing. Research in Transportation Economics, 89, 101034. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.retrec.2021.101034
- Koyuncu, H., Tomar, G. S., Sharma, D. (2020). A New Energy Efficient Multitier Deterministic Energy-Efficient Clustering Routing Protocol for Wireless Sensor Networks. Symmetry, 12 (5), 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12050837
- Shah, P., Kasbe, T. (2021). A review on specification evaluation of broadcasting routing protocols in VANET. Computer Science Review, 41, 100418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cosrev.2021.100418
- Krisnawijaya, N. N. K., Paramartha, C. R. A. (2016). Penerapan jaringan multihoming pada jaringan komputer fakultas hukum. ILMU KOMPUTER, 9 (1), 23–31.
- Zhou, Q., Pezaros, D. (2020). A Prediction-Based Model for Consistent Adaptive Routing in Back-Bone Networks at Extreme Situations. Electronics, 9 (12), 2146. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9122146
- Dai, B., Cao, Y., Wu, Z., Dai, Z., Yao, R., Xu, Y. (2021). Routing optimization meets Machine Intelligence: A perspective for the future network. Neurocomputing, 459, 44–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2021.06.093
- Song, Y., Liu, Z., Li, K., He, X., Zhu, W. (2024). Research on High-Efficiency Routing Protocols for HWSNs Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning. Electronics, 13 (23), 4746. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13234746
- Dafhalla, A. K. Y., Elobaid, M. E., Tayfour Ahmed, A. E., Filali, A., SidAhmed, N. M. O., Attia, T. A. et al. (2025). Computer-Aided Efficient Routing and Reliable Protocol Optimization for Autonomous Vehicle Communication Networks. Computers, 14 (1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14010013
- Cosovic, M., Obradovic, S., Junuz, E. (2018). Deep Learning for Detection of BGP Anomalies. Time Series Analysis and Forecasting, 95–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-96944-2_7
- Jabbar, W. A., Ismail, M., Nordin, R., Arif, S. (2016). Power-efficient routing schemes for MANETs: a survey and open issues. Wireless Networks, 23 (6), 1917–1952. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-016-1263-6
- Fronza, I., Sillitti, A., Succi, G., Terho, M., Vlasenko, J. (2013). Failure prediction based on log files using Random Indexing and Support Vector Machines. Journal of Systems and Software, 86 (1), 2–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2012.06.025
- Avgerinou, M., Bertoldi, P., Castellazzi, L. (2017). Trends in Data Centre Energy Consumption under the European Code of Conduct for Data Centre Energy Efficiency. Energies, 10 (10), 1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10101470
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Ferry Fachrizal, Al-khowarizmi Al-khowarizmi, Okvi Nugroho

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








