Improving accuracy of the spectral-correlation direction finding and delay estimation using machine learning
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.327021Keywords:
spectral-correlation analysis, radio signal monitoring, signal parameter prediction, direction finding accuracyAbstract
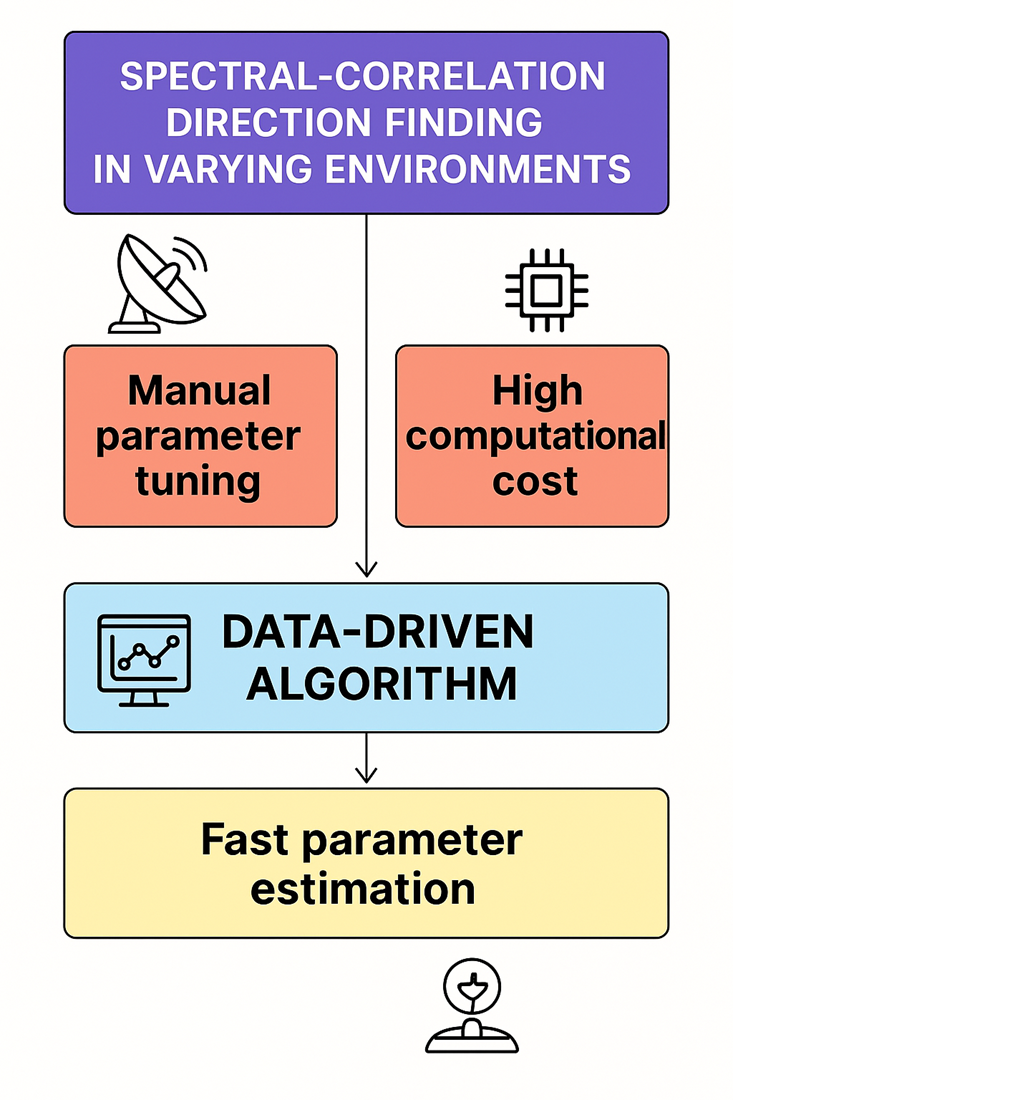
The object of the study is the process of radio signal delay and direction estimation using digital spectral-correlation analysis enhanced by machine learning. This process is essential for high-accuracy direction finding in electromagnetic monitoring systems. The problem addressed is the low adaptability and insufficient accuracy of traditional direction finding methods under variable signal conditions, especially due to manual parameter selection and the computational complexity of correlation processing.
The essence of the obtained results is a machine learning-based method for predicting radio signal parameters (delay and angle), which reduced the standard deviation of direction finding estimates to 0.08–0.026° and delay estimation error to 1.5–14.8 μs across a signal-to-noise ratio range of 9 to 37 dB. These results are supported by averaging over 1000 realizations using Monte Carlo simulation, confirming their stability under noise. Due to its distinctive features, the proposed solution addressed the problem by enabling automated selection of processing parameters through a trained neural network that adapts to nonlinear signal characteristics, minimizing the need for manual adjustment or exhaustive search.
These results are explained by the model’s ability to identify hidden dependencies between signal parameters and processing outcomes, enabling adaptive behavior and reduced deviations. Although no computational complexity assessment is provided, prediction-based parameter estimation is expected to improve processing speed in future implementations. The results can be applied in real-time electromagnetic monitoring, radio surveillance, and defense applications, especially under limited computing resources or varying noise conditions
References
- Rembovskij, A. M. (2015). Radio monitoring – tasks, methods, means. Moscow: Hot line. Telekom, 640.
- Tsyporenko, V., Tsyporenko, V., Andreiev, O., Sabibolda, A. (2021). Digital spectral correlation method for measuring radio signal reception delay and direction finding. Technical Engineering, 2 (88), 113–121. https://doi.org/10.26642/ten-2021-2(88)-113-121
- Elbir, A. M. (2017). Direction Finding in the Presence of Direction-Dependent Mutual Coupling. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 16, 1541–1544. https://doi.org/10.1109/lawp.2017.2647983
- Tsyporenko, V. V., Tsyporenko, V. G., Nikitczuk, T. M. (2019). Optimization of direct digital method of correlative-interferometric direction finding with reconstruction of spatial analytical signal. Radio Electronics, Computer Science, Control, 3, 15–24. https://doi.org/10.15588/1607-3274-2019-3-2
- Duplouy, J., Morlaas, C., Aubert, H., Potier, P., Pouliguen, P. (2019). Wideband Vector Antenna for Dual-Polarized and Three-Dimensional Direction-Finding Applications. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 18 (8), 1572–1575. https://doi.org/10.1109/lawp.2019.2923531
- Lee, J.-H., Kim, J.-K., Ryu, H.-K., Park, Y.-J. (2018). Multiple Array Spacings for an Interferometer Direction Finder With High Direction-Finding Accuracy in a Wide Range of Frequencies. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 17 (4), 563–566. https://doi.org/10.1109/lawp.2018.2803107
- Xie, X., Xu, Z. (2018). Direction Finding of BPSK Signals Using Time-Modulated Array. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 28 (7), 618–620. https://doi.org/10.1109/lmwc.2018.2834523
- Cai, J., Zhou, H., Huang, W., Wen, B. (2021). Ship Detection and Direction Finding Based on Time-Frequency Analysis for Compact HF Radar. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 18 (1), 72–76. https://doi.org/10.1109/lgrs.2020.2967387
- He, C., Liang, X., Li, Z., Geng, J., Jin, R. (2015). Direction Finding by Time-Modulated Array With Harmonic Characteristic Analysis. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 14, 642–645. https://doi.org/10.1109/lawp.2014.2373432
- Rosado-Sanz, J., Jarabo-Amores, M. P., De la Mata-Moya, D., Rey-Maestre, N. (2022). Adaptive Beamforming Approaches to Improve Passive Radar Performance in Sea and Wind Farms’ Clutter. Sensors, 22 (18), 6865. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22186865
- Smailov, N., Tsyporenko, V., Sabibolda, A., Tsyporenko, V., Kabdoldina, A., Zhekambayeva, M. et al. (2023). Improving the accuracy of a digital spectral correlation-interferometric method of direction finding with analytical signal reconstruction for processing an incomplete spectrum of the signal. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (9 (125)), 14–25. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.288397
- Sabibolda, A., Tsyporenko, V., Smailov, N., Tsyporenko, V., Abdykadyrov, A. (2024). Estimation of the Time Efficiency of a Radio Direction Finder Operating on the Basis of a Searchless Spectral Method of Dispersion-Correlation Radio Direction Finding. Advances in Asian Mechanism and Machine Science, 62–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-67569-0_8
- Kuttybayeva, A., Sabibolda, A., Kengesbayeva, S., Baigulbayeva, M., Amir, A., Sekenov, B. (2024). Investigation of a Fiber Optic Laser Sensor with Grating Resonator Using Mirrors. 2024 Conference of Young Researchers in Electrical and Electronic Engineering (ElCon), 709–711. https://doi.org/10.1109/elcon61730.2024.10468264
- Smailov, N., Tsyporenko, V., Sabibolda, A., Tsyporenko, V., Abdykadyrov, A., Kabdoldina, A. et al. (2024). Usprawnienie cyfrowego korelacyjno-interferometrycznego ustalania kierunku za pomocą przestrzennego sygnału analitycznego. Informatyka, Automatyka, Pomiary w Gospodarce i Ochronie Środowiska, 14 (3), 43–48. https://doi.org/10.35784/iapgos.6177
- Abdykadyrov, A., Smailov, N., Sabibolda, A., Tolen, G., Dosbayev, Z., Ualiyev, Z., Kadyrova, R. (2024). Optimization of distributed acoustic sensors based on fiber optic technologies. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (5 (131)), 50–59. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.313455
- Marxuly, S., Abdykadyrov, A., Chezhimbayeva, K., Smailov, N. (2024). Study of the ozone control process using electronic sensors. Informatyka Automatyka Pomiary W Gospodarce I Ochronie Środowiska, 14 (4), 38–45. https://doi.org/10.35784/iapgos.6051
- Podchashynskyi, Y., Luhovykh, O., Tsyporenko, V., Tsyporenko, V. (2021). Devising a method for measuring the motion parameters of industrial equipment in the quarry using adaptive parameters of a video sequence. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (9 (114)), 32–46. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2021.248624
- Zahoruiko, L., Martianova, T., Al-Hiari, M., Polovenko, L., Kovalchuk, M., Merinova, S. et al. (2024). Model matematyczny i struktura sieci neuronowej do wykrywania cyberataków na systemy teleinformatyczne i komunikacyjne. Informatyka, Automatyka, Pomiary w Gospodarce i Ochronie Środowiska, 14 (3), 49–55. https://doi.org/10.35784/iapgos.6155
- Mummaneni, S., Dodda, P., Ginjupalli, N. D. (2024). Inspirowane kojotami podejście do przewidywania tocznia rumieniowatego układowego z wykorzystaniem sieci neuronowych. Informatyka, Automatyka, Pomiary w Gospodarce i Ochronie Środowiska, 14 (2), 22–27. https://doi.org/10.35784/iapgos.6077
- Rayavarapu, S. M., Tammineni, S. P., Gottapu, S. R., & Singam, A. (2024). Przegląd generatywnych sieci przeciwstawnych dla zastosowań bezpieczeństwa. Informatyka, Automatyka, Pomiary w Gospodarce i Ochronie Środowiska, 14 (2), 66–70. https://doi.org/10.35784/iapgos.5778
- Stelmakh, N., Mandrovska, S., Galagan, R. (2024). Zastosowanie sieci neuronowych resnet-152 do analizy obrazów z uav do wykrywania pożaru. Informatyka, Automatyka, Pomiary w Gospodarce i Ochronie Środowiska, 14 (2), 77–82. https://doi.org/10.35784/iapgos.5862
- Lyfar, V., Lyfar, O., Zynchenko, V. (2024). Metody inteligentnej analizy danych z wykorzystaniem sieci neuronowych w diagnozie. Informatyka, Automatyka, Pomiary w Gospodarce i Ochronie Środowiska, 14 (2), 109–112. https://doi.org/10.35784/iapgos.5746
- Limtrakul, S., Wetweerapong, J. (2023). An enhanced differential evolution algorithm with adaptive weight bounds for efficient training of neural networks. Informatyka, Automatyka, Pomiary w Gospodarce i Ochronie Środowiska, 13 (1), 4–13. https://doi.org/10.35784/iapgos.3366
- Bilynsky, Y., Nikolskyy, A., Revenok, V., Pogorilyi, V., Smailova, S., Voloshina, O., Kumargazhanova, S. (2023). Convolutional neural networks for early computer diagnosis of child dysplasia. Informatyka, Automatyka, Pomiary w Gospodarce i Ochronie Środowiska, 13 (2), 56–63. https://doi.org/10.35784/iapgos.3499
- Michalska-Ciekańska, M. (2022). Głębokie sieci neuronowe dla diagnostyki zmian skórnych. Informatyka, Automatyka, Pomiary w Gospodarce i Ochronie Środowiska, 12 (3), 50–53. https://doi.org/10.35784/iapgos.3042
- Gęca, J. (2020). Performance comparison of machine learning algorithms for predictive maintenance. Informatyka, Automatyka, Pomiary w Gospodarce i Ochronie Środowiska, 10 (3), 32–35. https://doi.org/10.35784/iapgos.1834
- Smailov, N., Batyrgaliyev, A., Akhmediyarova, A., Seilova, N., Koshkinbayeva, M., Baigulbayeva, M. et al. (2020). Approaches to Evaluating the Quality of Masking Noise Interference. International Journal of Electronics and Telecommunications, 67 (01), 59–64. https://doi.org/10.24425/ijet.2021.135944
- Li, R., Zhao, L., Liu, C., Bi, M. (2022). Strongest Angle-of-Arrival Estimation for Hybrid Millimeter Wave Architecture with 1-Bit A/D Equipped at Transceivers. Sensors, 22 (9), 3140. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22093140
- Wang, J., Wang, P., Zhang, R., Wu, W. (2022). SDFnT-Based Parameter Estimation for OFDM Radar Systems with Intercarrier Interference. Sensors, 23 (1), 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010147
- Ren, B., Wang, T. (2022). Space-Time Adaptive Processing Based on Modified Sparse Learning via Iterative Minimization for Conformal Array Radar. Sensors, 22 (18), 6917. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22186917
- Jwo, D.-J., Cho, T.-S., Demssie, B. A. (2025). Dynamic Modeling and Its Impact on Estimation Accuracy for GPS Navigation Filters. Sensors, 25 (3), 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25030972
- Smailov, N., Uralova, F., Kadyrova, R., Magazov, R., Sabibolda, A. (2025). Optymalizacja metod uczenia maszynowego do deanonimizacji w sieciach społecznościowych. Informatyka, Automatyka, Pomiary w Gospodarce i Ochronie Środowiska, 15 (1), 101–104. https://doi.org/10.35784/iapgos.7098
- Wang, H., Yu, Z., Wen, F. (2024). Computationally Efficient Direction Finding for Conformal MIMO Radar. Sensors, 24 (18), 6065. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24186065
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Nurzhigit Smailov, Vitaliy Tsyporenko, Zhomart Ualiyev, Аіnur Issova, Zhandos Dosbayev, Yerlan Tashtay, Maigul Zhekambayeva, Temirlan Alimbekov, Rashida Kadyrova, Akezhan Sabibolda

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








