Оптимізація процесу флотоекстракції барвників
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.327556Ключові слова:
флотоекстракція, очищення стічних вод, кореляційний аналіз, математична модель процесу флотоекстракціїАнотація
Об’єктом дослідження виступає процес флотоекстракційного очищення стічних вод, забруднених барвниками. Синтетичні барвники є токсичними, канцерогенними та мутагенними, викликають серйозні проблеми зі здоров'ям людей, не піддаються біологічному розкладу.
Таким чином, існує гостра необхідність у розробці економічно ефективних та екологічно безпечних підходів до очищення стічних вод, що містять барвники, перед їх скиданням у навколишнє середовище.
Запропонована технологія флотоекстракції, яка поєднує переваги іонної флотації та рідинної екстракції.
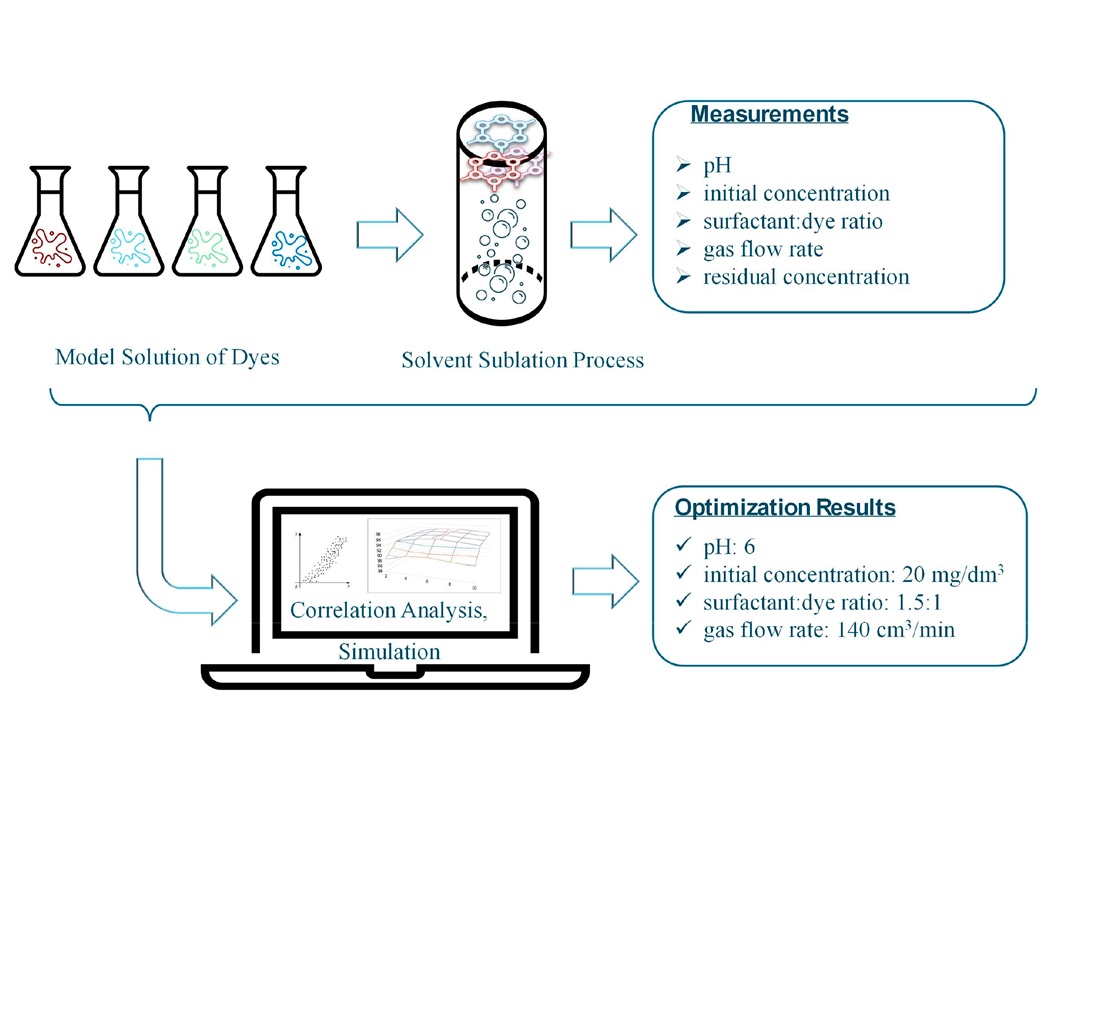
Було досліджено вплив параметрів процесу на ефективність флотоекстракційного очищення стічних вод від синтетичних барвників для забезпечення максимальної ефективності (мінімальних значень залишкових концентрацій полютантів).
Експериментально отримано залежності ефективності очищення для чотирьох барвників від обраних параметрів: рН, вихідна концентрація полютанту, витрата газу та співвідношення ПАР: полютант.
На основі виконаних досліджень, використовуючи математичний апарат системи STАR, побудовано математичну регресійну модель 2-го порядку. Похибка апроксимації становить 0,834; отже, запропонована модель з достатнім ступенем точності описує експериментальні дані.
Розв’язок сформульованої задачі оптимізації виконано за допомогою програми «ОPTІMІZ-M» і визначено оптимальні умови проведення процесу, за яких досягається максимальне видалення барвників (97,20 %):
– рН: 6.
– вихідна концентрація полютанту: 20 мг/ дм3.
– співвідношення ПАР:полютант: 1,5:1.
– витрата газу: 140 см3/хв.
Оптимізація флотоекстракційного очищення забезпечує високу якість очищення стічних вод за мінімальних витрат, зменшення викидів барвників у навколишнє середовище, що потенційно підвищить конкурентоспроможність підприємств на ринку
Посилання
- Kumari, S., Singh, R., Jahangeer, J., Garg, M. C. (2024). Innovative Strategies for Dye Removal from Textile Wastewater: A Comprehensive Review of Treatment Approaches and Challenges. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 235 (11). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-024-07532-4
- Ahsan, A., Jamil, F., Rashad, M. A., Hussain, M., Inayat, A., Akhter, P. et al. (2023). Wastewater from the textile industry: Review of the technologies for wastewater treatment and reuse. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 40 (9), 2060–2081. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-023-1475-2
- Yadav, S., Pipil, H., Chawla, H., Taneja, S., Kumar, S., Haritash, A. K. (2022). Textile Industry Wastewater Treatment Using Eco-Friendly Techniques. Proceedings of International Conference on Innovative Technologies for Clean and Sustainable Development (ICITCSD – 2021), 63–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-93936-6_6
- Periyasamy, A. P. (2024). Recent Advances in the Remediation of Textile-Dye-Containing Wastewater: Prioritizing Human Health and Sustainable Wastewater Treatment. Sustainability, 16 (2), 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020495
- Hynes, N. R. J., Kumar, J. S., Kamyab, H., Sujana, J. A. J., Al-Khashman, O. A., Kuslu, Y. et al. (2020). Modern enabling techniques and adsorbents based dye removal with sustainability concerns in textile industrial sector -A comprehensive review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 272, 122636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122636
- Shindhal, T., Rakholiya, P., Varjani, S., Pandey, A., Ngo, H. H., Guo, W. et al. (2020). A critical review on advances in the practices and perspectives for the treatment of dye industry wastewater. Bioengineered, 12 (1), 70–87. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2020.1863034
- Ndagano, U. N., Cahill, L., Smullen, C., Gaughran, J., Kelleher, S. M. (2025). The Current State-of-the-Art of the Processes Involved in the Chemical Recycling of Textile Waste. Molecules, 30 (2), 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30020299
- Alsukaibi, A. K. D. (2022). Various Approaches for the Detoxification of Toxic Dyes in Wastewater. Processes, 10 (10), 1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10101968
- Kumar, V., Anwar, S., Prabhu, S. V. (2024). A Discussion On Physiochemical And Biomediated Removal Approaches Of Dyes From Textile Effluents: A Review. IJCRT. 12 (2), 62–75. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/378481295
- Gupta, K. N., Kumar, R., Thakur, A. K., Khan, N. A. (2023). Treatment of Dyeing Wastewater Using Foam Separation: Optimization Studies. Water, 15 (12), 2236. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15122236
- Fei, X., Li, W., Zhu, S., Liu, L., Yang, Y. (2017). Simultaneous treatment of dye wastewater and surfactant wastewater by foam separation: Experimental and mesoscopic simulation study. Separation Science and Technology, 53 (10), 1604–1610. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2017.1406951
- Bi, P., Dong, H., Dong, J. (2010). The recent progress of solvent sublation. Journal of Chromatography A, 1217 (16), 2716–2725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2009.11.020
- Lu, Y., Wang, Y., Zhu, X. (2001). The removal of bromophenol blue from water by solvent sublation. Separation Science and Technology, 36 (16), 3763–3776. https://doi.org/10.1081/ss-100108361
- Lu, Y., Zhu, X., Peng, Y. (2003). The Removal of Methyl Violet from Water by Solvent Sublation. Separation Science and Technology, 38 (6), 1385–1398. https://doi.org/10.1081/ss-120018815
- Lu, Y., Liu, J., Tang, J., Wei, B., Liu, J. (2005). The Removal of Indigo Carmine from Water by Solvent Sublation. Separation Science and Technology, 40 (5), 1115–1127. https://doi.org/10.1081/ss-200048175
- Lu, Y., Wei, B., Wang, Y., Li, J. (2007). Studies on the Removal of Bromocresol Green from Water by Solvent Sublation. Separation Science and Technology, 42 (8), 1901–1911. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496390601174398
- Li, N., Zhang, Y., Gao, M., Yan, C., Wei, Y. (2024). Progress in the technology of solvent flotation. Journal of Chromatography B, 1249, 124370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2024.124370
- Obushenko, T., Tolstopalova, N., Kulesha, O., Astrelin, I. (2016). Thermodynamic Studies of Bromphenol Blue Removal from Water Using Solvent Sublation. Chemistry & Chemical Technology, 10 (4), 515–518. https://doi.org/10.23939/chcht10.04.515
- Obushenko, T., Sanginova, O., Tolstopalova, N., Chyrieva, M. (2022). Modeling of solvent sublation process and identification of parameters affecting the removal of Ni(II), Cu(II) and Fe(III) ions. Voprosy Khimii i Khimicheskoi Tekhnologii, 4, 49–55. https://doi.org/10.32434/0321-4095-2022-143-4-49-55
- Metody prykladnoi matematyky dlia vyrishennia inzhenernykh zadach khimichnoi tekhnolohiyi. Rozrakhunkova robota (2023). Kyiv: KPI im. Ihoria Sikorskoho, 115. Available at: https://ela.kpi.ua/handle/123456789/57131
- Osnovy teoriyi planuvannia eksperymentu: Rozdil dystsypliny «Metodyka ta orhanizatsiya naukovykh doslidzhen». Kyiv: KPI im. Ihoria Sikorskoho, 41. Available at: https://ela.kpi.ua/handle/123456789/62842
- Obushenko, T., Sanginova, O., Tolstopalova, N., Reminna, K. (2019). Simulation of solvent sublation process to forecast the amount of removed dyes. Water and Water Purification Technologies. Scientific And Technical News, 1 (24), 25–33. https://doi.org/10.20535/2218-93002412019172906
- Sanhinova, O. V., Bondarenko, S. H. (2021). Avtorske pravo No. 105383. Kompiuterna prohrama «OPTIMIZ-M». Available at: https://sis.nipo.gov.ua/uk/search/detail/1618634
- Shaheen, R., Hanif, M. A. (2024). High speed removal of toxic acid red dye using photocatalytic-hybrid composite material. Desalination and Water Treatment, 317, 100153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dwt.2024.100153
- Alkoshab, M. Q., Al-Amrani, W. A., Drmosh, Q. A., Onaizi, S. A. (2024). Zeolitic imidazolate framework-8/layered triple hydr(oxide) composite for boosting the adsorptive removal of acid red 1 dye from wastewater. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 699, 134637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2024.134637
- Oladoye, P. O., Ajiboye, T. O., Omotola, E. O., Oyewola, O. J. (2022). Methylene blue dye: Toxicity and potential elimination technology from wastewater. Results in Engineering, 16, 100678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rineng.2022.100678
- Raashid, M., Kazmi, M., Ikhlaq, A., Sulaiman, M., Akram, A., Afaf, A., Shafaqat, S. et al. (2024). Removal of acid red dye 1 from textile wastewater by heterogenous photocatalytic ozonation employing titanium dioxide and iron zeolite. Discover Chemical Engineering, 4 (1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43938-024-00059-4
- Yaqub, A., Zahid, M., Un Nisa, M., Iqbal, T., Hussain Shah, K., Samad Shah, N., Draz, M. U. (2024). Sustainable removal of methylene blue dye from textile effluents by magnetized Tea waste and Peanut shells. Chemical Engineering Science, 299, 120498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2024.120498
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2025 Tetiana Obushenko, Olga Sanginova, Nataliia Tolstopalova, Serhii Bondarenko, Daria Zahurska

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.
Ліцензійний договір – це документ, в якому автор гарантує, що володіє усіма авторськими правами на твір (рукопис, статтю, тощо).
Автори, підписуючи Ліцензійний договір з ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР», мають усі права на подальше використання свого твору за умови посилання на наше видання, в якому твір опублікований. Відповідно до умов Ліцензійного договору, Видавець ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР» не забирає ваші авторські права та отримує від авторів дозвіл на використання та розповсюдження публікації через світові наукові ресурси (власні електронні ресурси, наукометричні бази даних, репозитарії, бібліотеки тощо).
За відсутності підписаного Ліцензійного договору або за відсутністю вказаних в цьому договорі ідентифікаторів, що дають змогу ідентифікувати особу автора, редакція не має права працювати з рукописом.
Важливо пам’ятати, що існує і інший тип угоди між авторами та видавцями – коли авторські права передаються від авторів до видавця. В такому разі автори втрачають права власності на свій твір та не можуть його використовувати в будь-який спосіб.









