Building a model of the flow in a nozzle-flapper valve of the HP-3 control pump to improve the stability of characteristics
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.329024Keywords:
nozzle-flapper, numerical modeling, stagnant zone, vortex flowAbstract
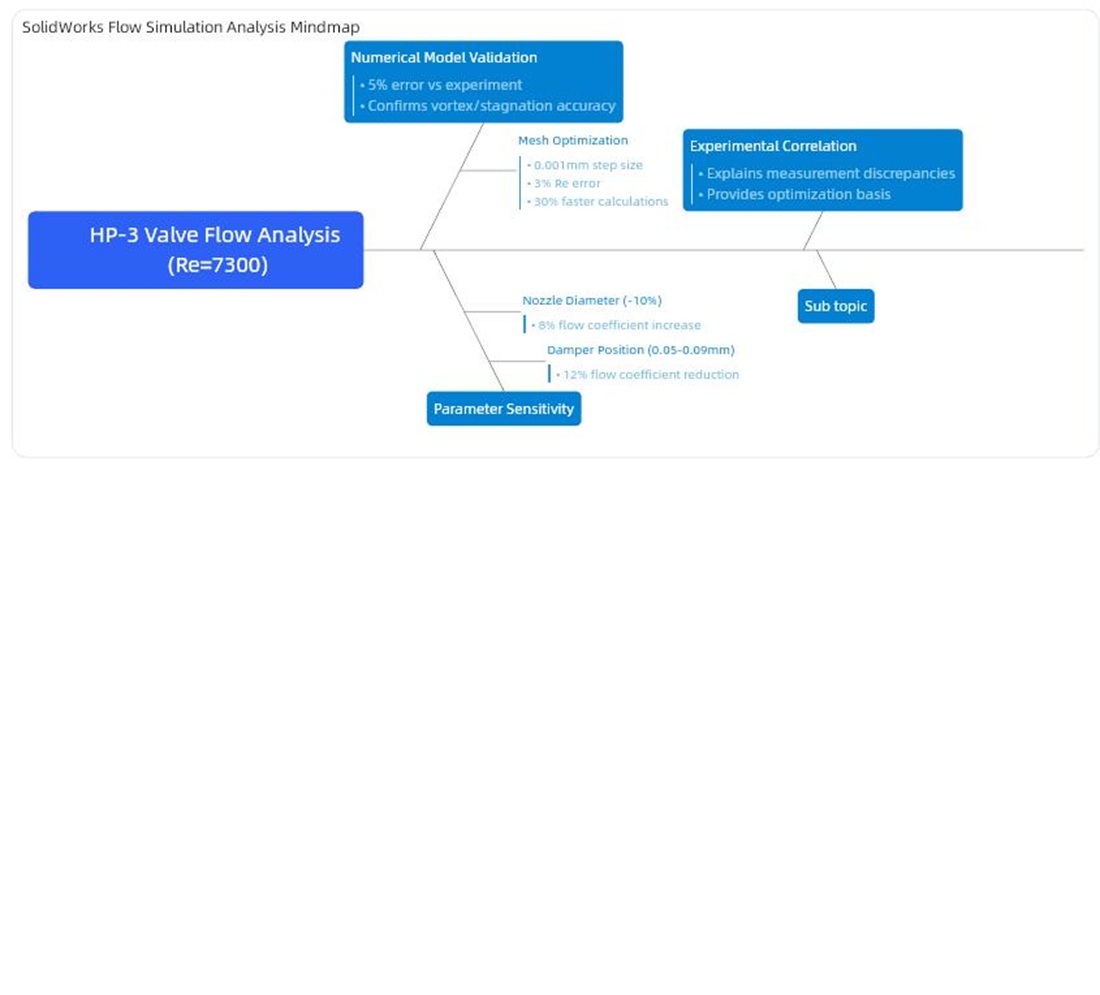
The object of this study is the flow of a viscous incompressible fluid in a nozzle-flapper valve used as part of the free turbine speed controller in the HP-3 pump-regulator of the TV3-117 turboprop helicopter engine. The task addressed relates to a need for detailed calculations of the fluid flow because of unsatisfactory operation of the valve under actual operating conditions. An additional difficulty was the contradictory data on the characteristics of such valves in the literature, which made it impossible to determine the flow characteristics and directions for improving the design.
This paper reports the results of numerical calculations of the flow in the valve performed in the SolidWorks Flow Simulation environment. A mathematical model is proposed that takes into account the influence of the design mesh on the accuracy and computational time volume, as well as ways to improve accuracy without a significant increase in resources. The model was verified by comparing it with the manufacturer’s experimental data. The results have made it possible to solve the problem through the detailed construction of the model taking into account the valve geometry and optimization of the computational mesh, which ensured a balance between accuracy and computational speed.
The results are attributed to the application of state-of-the-art hydrodynamic calculation software, precise mesh tuning, as well as proper validation of the model to reflect the actual physical processes in the valve. The model built makes it possible to study the flow in the valve and could be used to analyze the impact of manufacturing defects. The model is suitable for parametric studies and modification of valves in helicopter engines of the TV3-117 type or similar systems. The model could also be adapted for other systems requiring flow analysis in similar valves
References
- SOLIDWORKS Installation and Administration. Available at: https://help.solidworks.com/2022/english/Installation/install_guide/c_install_admin_overview.htm
- Tabe Jamaat, A. G., Hattori, B. Y. (2022). Development of subgrid-scale model for LES of Burgers turbulence with large filter size. Physics of Fluids, 34 (4). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0087761
- Lytviak, O., Komar, S., Derevyanko, O., Durieiev, V. (2021). Devising quality control criteria for manufacturing control valves of the type «nozzle-flap». Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (1 (109)), 27–34. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2021.224918
- Lytviak, O., Loginov, V., Komar, S., Martseniuk, Y. (2021). Self-Oscillations of The Free Turbine Speed in Testing Turboshaft Engine with Hydraulic Dynamometer. Aerospace, 8 (4), 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace8040114
- Liu, Y., Ren, Y., Zhang, M., Wei, K., Hao, L. (2022). Solenoid valves quality improvement based on Six Sigma management. International Journal of Lean Six Sigma, 14 (1), 72–93. https://doi.org/10.1108/ijlss-08-2021-0140
- Jafari, B., Mashadi, B. (2022). Valve control of a hydraulically interconnected suspension system to improve vehicle handling qualities. Vehicle System Dynamics, 61 (4), 1011–1027. https://doi.org/10.1080/00423114.2022.2056490
- Fedorovich, O., Lutai, L., Trishch, R., Zabolotnyi, О., Khomiak, E., Nikitin, A. (2024). Models for Reducing the Duration and Cost of the Aviation Equipment Diagnostics Process Using the Decomposition of the Component Architecture of a Complex Product. Information Technology for Education, Science, and Technics, 108–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-71801-4_9
- Cheng, Y., Tang, Y., Wu, J., Jin, H., Shen, L. (2024). Numerical Simulation Study on Hydraulic Characteristics and Wear of Eccentric Semi-Ball Valve under Sediment Laden Water Flow. Sustainability, 16 (17), 7266. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16177266
- Lopes, R., Eça, L., Vaz, G. (2020). On the Numerical Behavior of RANS-Based Transition Models. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 142 (5). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4045576
- Laima, S., Zhou, X., Jin, X., Gao, D., Li, H. (2023). DeepTRNet: Time-resolved reconstruction of flow around a circular cylinder via spatiotemporal deep neural networks. Physics of Fluids, 35 (1). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0129049
- Kim, M., Park, J., Choi, H. (2024). Large eddy simulation of flow over a circular cylinder with a neural-network-based subgrid-scale model. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 984. https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2024.154
- SolidWorks Flow Simulation. Available at: https://www.goengineer.com/solidworks/simulation/solidworks-flow-simulation-cfd
- Popa, C. (2023). An aplication for the selection and sizing of control valve for control loop. Romanian Journal of Petroleum & Gas Technology, 4 (75) (2), 109–116. https://doi.org/10.51865/jpgt.2023.02.11
- Kim, J., Kim, H., Kim, J., Lee, C. (2022). Deep reinforcement learning for large-eddy simulation modeling in wall-bounded turbulence. Physics of Fluids, 34 (10). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0106940
- Trishch, R., Cherniak, O., Zdenek, D., Petraskevicius, V. (2024). Assessment of the occupational health and safety management system by qualimetric methods. Engineering Management in Production and Services, 16 (2), 118–127. https://doi.org/10.2478/emj-2024-0017
- Cherniak, O., Trishch, R., Ginevičius, R., Nechuiviter, O., Burdeina, V. (2024). Methodology for Assessing the Processes of the Occupational Safety Management System Using Functional Dependencies. Integrated Computer Technologies in Mechanical Engineering - 2023, 3–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-60549-9_1
- Khomiak, E., Burdeina, V., Cherniak, O., Olesia, N., Bubela, T. (2024). Improving the Method of Quality Control of the Fuel Element Shell in Order to Improve the Safety of a Nuclear Reactor. Integrated Computer Technologies in Mechanical Engineering - 2023, 351–360. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-61415-6_30
- Khomiak, E., Trishch, R., Zabolotnyi, O., Cherniak, О., Lutai, L., Katrich, O. (2024). Automated Mode of Improvement of the Quality Control System for Nuclear Reactor Fuel Element Shell Tightness. Information Technology for Education, Science, and Technics, 79–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-71801-4_7
- Wu, Q., Chen, Z., Xu, H., Cai, Y. (2024). A novel wall model for large-eddy simulation of the flow around a circular cylinder. Physics of Fluids, 36 (6). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0209462
- Nisters, C., Bauer, F., Brocker, M. (2020). Condition monitoring systems for hydraulic accumulators – improvements in efficiency, productivity and quality. Volume 2 - Conference, 195–203. https://doi.org/10.25368/2020.83
- Tong, Z., Xin, J., Song, J., Cao, X. E. (2023). A graphics-accelerated deep neural network approach for turbomachinery flows based on large eddy simulation. Physics of Fluids, 35 (9). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0160968
- Abekawa, A., Minamoto, Y., Osawa, K., Shimamoto, H., Tanahashi, M. (2023). Exploration of robust machine learning strategy for subgrid scale stress modeling. Physics of Fluids, 35 (1). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0134471
- Dong, X., Hong, H., Deng, X., Zhong, W., Hu, G. (2023). Surrogate model-based deep reinforcement learning for experimental study of active flow control of circular cylinder. Physics of Fluids, 35 (10). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0170316
- Zhan, Q., Bai, C., Ge, Y., Sun, X. (2023). Flow time history representation and reconstruction based on machine learning. Physics of Fluids, 35 (8). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0160296
- Wang, Y.-Z., Hua, Y., Aubry, N., Chen, Z.-H., Wu, W.-T., Cui, J. (2022). Accelerating and improving deep reinforcement learning-based active flow control: Transfer training of policy network. Physics of Fluids, 34 (7). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0099699
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Oleksandr Lytviak, Roman Trishch, Eduard Khomiak, Serhii Kochuk, Svitlana Khomenko, Ihor Tiupa

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








