Ensuring sustainable use of generative artificial intelligence by enterprises based on resource consumption optimization
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.330586Keywords:
generative artificial intelligence, GPT-models, sustainable development, energy efficiency, ecological footprintAbstract
The object of this study is the impact of using generative artificial intelligence (AI) on the resource efficiency of enterprises in the context of sustainable development. The issue relates to the fact that despite the ability of generative AI to optimize management and production processes, its use is accompanied by an increase in electricity consumption (grid, mostly non-renewable) and water, which creates new environmental risks.
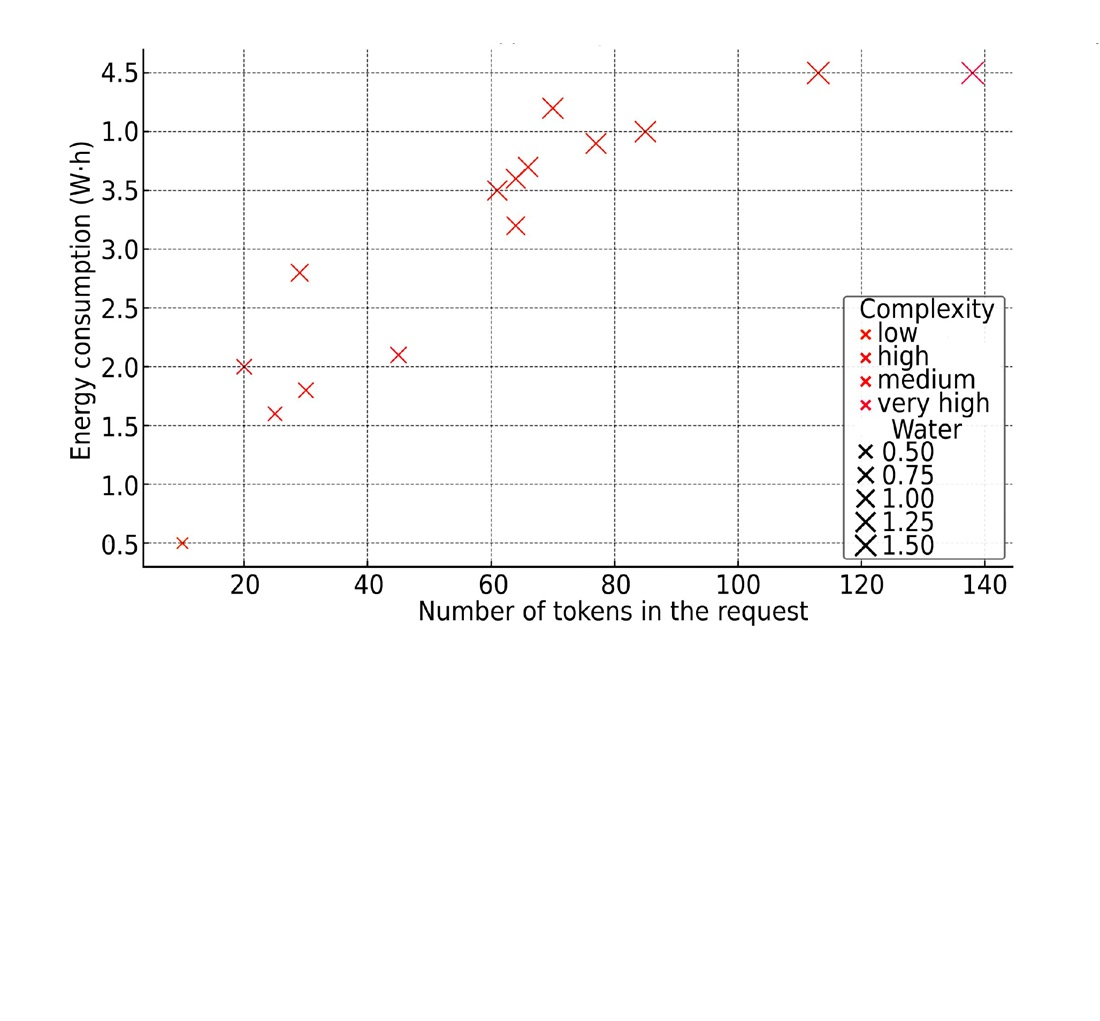
This paper systematizes existing methods for indirectly estimating energy and water consumption in the process of generative AI model functioning. Based on this, an approach to assessing the ecological footprint of generative AI has been devised, which takes into account four indicators such as query length, complexity, task type, and industry. A special feature of the proposed approach is a combination of quantitative analysis, regression modeling, and query classification to assess resource intensity.
An empirical study has shown that high-volume queries (analytical and creative) generate significantly higher resource consumption (2.1–2.3 Wh of electricity and more than 0.8 liters of water) while factual queries create a minimal load (< 0.12 Wh). This difference is explained by the complexity of information processing and the involvement of significant computing power in cloud data centers.
To evaluate the feasibility of AI implementation, a sustainability index has been proposed to assess the balance between the efficiency achieved and resources spent. The proposed approach could be used by enterprises under conditions of limited access to energy and water resources, in particular during post-war recovery and implementation of the principles of sustainable development
References
- Fang, B., Yu, J., Chen, Z., Osman, A. I., Farghali, M., Ihara, I. et al. (2023). Artificial intelligence for waste management in smart cities: a review. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 21 (4), 1959–1989. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-023-01604-3
- Priore, P., Gómez, A., Pino, R., Rosillo, R. (2014). Dynamic scheduling of manufacturing systems using machine learning: An updated review. Artificial Intelligence for Engineering Design, Analysis and Manufacturing, 28 (1), 83–97. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0890060413000516
- Li, S., Yu, T., Cao, X., Pei, Z., Yi, W., Chen, Y., Lv, R. (2021). Machine learning‐based scheduling: a bibliometric perspective. IET Collaborative Intelligent Manufacturing, 3 (2), 131–146. https://doi.org/10.1049/cim2.12004
- Wen, X., Shen, Q., Wang, S., Zhang, H. (2024). Leveraging AI and Machine Learning Models for Enhanced Efficiency in Renewable Energy Systems. Applied and Computational Engineering, 96 (1), 107–112. https://doi.org/10.54254/2755-2721/96/20241416
- Kuzior, A., Sira, M., Brożek, P. (2023). Use of Artificial Intelligence in Terms of Open Innovation Process and Management. Sustainability, 15 (9), 7205. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097205
- Huang, M.-H., Rust, R. T. (2020). A strategic framework for artificial intelligence in marketing. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 49 (1), 30–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-020-00749-9
- Lu, M. (2025). Ranked: The Top 25 Countries With the Most Data Centers. Visual Capitalist. Available at: https://www.visualcapitalist.com/ranked-the-top-25-countries-with-the-most-data-centers/?utm_source=
- Kiev Data Centers. DataCenter Map. Available at: https://www.datacentermap.com/ukraine/kiev/?utm_source=
- Wang, Q., Zhang, F., Li, R. (2024). Artificial intelligence and sustainable development during urbanization: Perspectives on AI R&D innovation, AI infrastructure, and AI market advantage. Sustainable Development, 33 (1), 1136–1156. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.3150
- Vinuesa, R., Azizpour, H., Leite, I., Balaam, M., Dignum, V., Domisch, S. et al. (2020). The role of artificial intelligence in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals. Nature Communications, 11 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-14108-y
- Olatunde, T., Okwandu, A., Akande, D., Sikhakhane, Z. (2024). Reviewing the role of artificial intelligence in energy efficiency optimization. Engineering Science & Technology Journal, 5 (4), 1243–1256. https://doi.org/10.51594/estj.v5i4.1015
- Tabbakh, A., Al Amin, L., Islam, M., Mahmud, G. M. I., Chowdhury, I. K., Mukta, M. S. H. (2024). Towards sustainable AI: a comprehensive framework for Green AI. Discover Sustainability, 5 (1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43621-024-00641-4
- Zavrazhnyi, K. Yu. (2023). Vykorystannia shtuchnoho intelektu ta vplyv tsyfrovizatsiyi na stalyi rozvytok korporatyvnoho biznesu. Akademichni viziyi, 26. Available at: https://academy-vision.org/index.php/av/article/view/754
- Sukhodolia, O. M. (2022). Shtuchnyi intelekt v enerhetytsi. Kyiv: NISD, 49. https://doi.org/10.53679/NISS-analytrep.2022.09
- Mashkov, O., Abidov, S., Ivashchenko, T., Ovodenko, T., Pechenyi, V. (2023). Prospects and problems of creating intelligent support systems for environmental decision-making. Ecological Sciences, 1, 168–174. https://doi.org/10.32846/2306-9716/2023.eco.1-46.28
- Udendhran, R., Sasikala, R., Nishanthi, R., Vasanthi, J. (2023). Smart Energy Consumption Control in Commercial Buildings Using Machine Learning and IOT. E3S Web of Conferences, 387, 02003. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202338702003
- Hamid, M., Ganne, A. (2023). Artificial intelligence in energy markets and power systems. International Research Journal of Modernization in Engineering Technology and Science, 5 (4). https://doi.org/10.56726/irjmets35943
- Burki, A. K., Ahamed Mafaz, M. N., Ahmad, Z., Zulfaka, A., Bin Isa, M. Y. (2024). Artificial Intelligence and Environmental Sustainability: Insights from PLS-SEM on Resource Efficiency and Carbon Emission Reduction. OPSearch: American Journal of Open Research, 3 (10), 277–288. https://doi.org/10.58811/opsearch.v3i10.141
- Lin, B., Zhu, Y. (2024). Latent Information in the Evolving Energy Structure. Journal of Global Information Management, 32 (1), 1–21. https://doi.org/10.4018/jgim.358476
- Liu, L., Yang, K., Fujii, H., Liu, J. (2021). Artificial intelligence and energy intensity in China’s industrial sector: Effect and transmission channel. Economic Analysis and Policy, 70, 276–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eap.2021.03.002
- Strubell, E., Ganesh, A., McCallum, A. (2019). Energy and Policy Considerations for Deep Learning in NLP. Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/p19-1355
- Li, P., Yang, J., Islam, M. A., Ren, S. (2023). Making AI Less "Thirsty": Uncovering and Addressing the Secret Water Footprint of AI Models. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2304.03271
- Castaño, J., Martínez-Fernández, S., Franch, X., Bogner, J. (2023). Exploring the Carbon Footprint of Hugging Face’s ML Models: A Repository Mining Study. 2023 ACM/IEEE International Symposium on Empirical Software Engineering and Measurement (ESEM), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1109/esem56168.2023.10304801
- Verdecchia, R., Cruz, L., Sallou, J., Lin, M., Wickenden, J., Hotellier, E. (2022). Data-Centric Green AI An Exploratory Empirical Study. 2022 International Conference on ICT for Sustainability (ICT4S), 35–45. https://doi.org/10.1109/ict4s55073.2022.00015
- Ghadi, Y. Y., Mazhar, T., Shah, S. F. A., Haq, I., Ahmad, W., Ouahada, K., Hamam, H. (2023). Integration of federated learning with IoT for smart cities applications, challenges, and solutions. PeerJ Computer Science, 9, e1657. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj-cs.1657
- Zastosuvannia shtuchnoho intelektu: sfery, pryklady, perevahy ta trudnoshchi (2024). Sigma Software University. Available at: https://university.sigma.software/where-is-artificial-intelligence-used/
- Pidhaina, Ye. (2024). Amazon, Uber, Spotify, JP Morgan, Netflix, Tesla toshcho: uspishni ta provalni keisy zaluchennia shtuchnoho intelektu. Mind. Available at: https://mind.ua/publications/20275247-amazon-uber-spotify-jp-morgan-netflix-tesla-toshcho-uspishni-ta-provalni-kejsi-zaluchennya-shtuchnogo
- Kuzomko, V., Buranhulova, V., Buranhulova, V. (2021). Possibilities of using artificial intelligence in the activities of modern enterprises. Economy and Society, 32. https://doi.org/10.32782/2524-0072/2021-32-67
- Lacoste, A., Luccioni, A. S., Schmidt, V., Dandres, T. (2019). Quantifying the Carbon Emissions of Machine Learning. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1910.09700
- ML CO2 Impact. Available at: https://mlco2.github.io/impact/#home
- García-Martín, E., Rodrigues, C. F., Riley, G., Grahn, H. (2019). Estimation of energy consumption in machine learning. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 134, 75–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpdc.2019.07.007
- Krystalakos, O., Nalmpantis, C., Vrakas, D. (2018). Sliding Window Approach for Online Energy Disaggregation Using Artificial Neural Networks. Proceedings of the 10th Hellenic Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1145/3200947.3201011
- Desislavov, R., Martínez-Plumed, F., Hernández-Orallo, J. (2023). Trends in AI inference energy consumption: Beyond the performance-vs-parameter laws of deep learning. Sustainable Computing: Informatics and Systems, 38, 100857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suscom.2023.100857
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Dmytro Antoniuk, Oleksandr Koliada

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.









