Evaluating deep learning architectures for CO2 emissions forecasting: TCN, LSTM, and hybrid approaches with hyperparameter optimization
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.331523Keywords:
CO2 prediction, deep learning, random search, Bayesian optimization, hyperparameter, accuracyAbstract
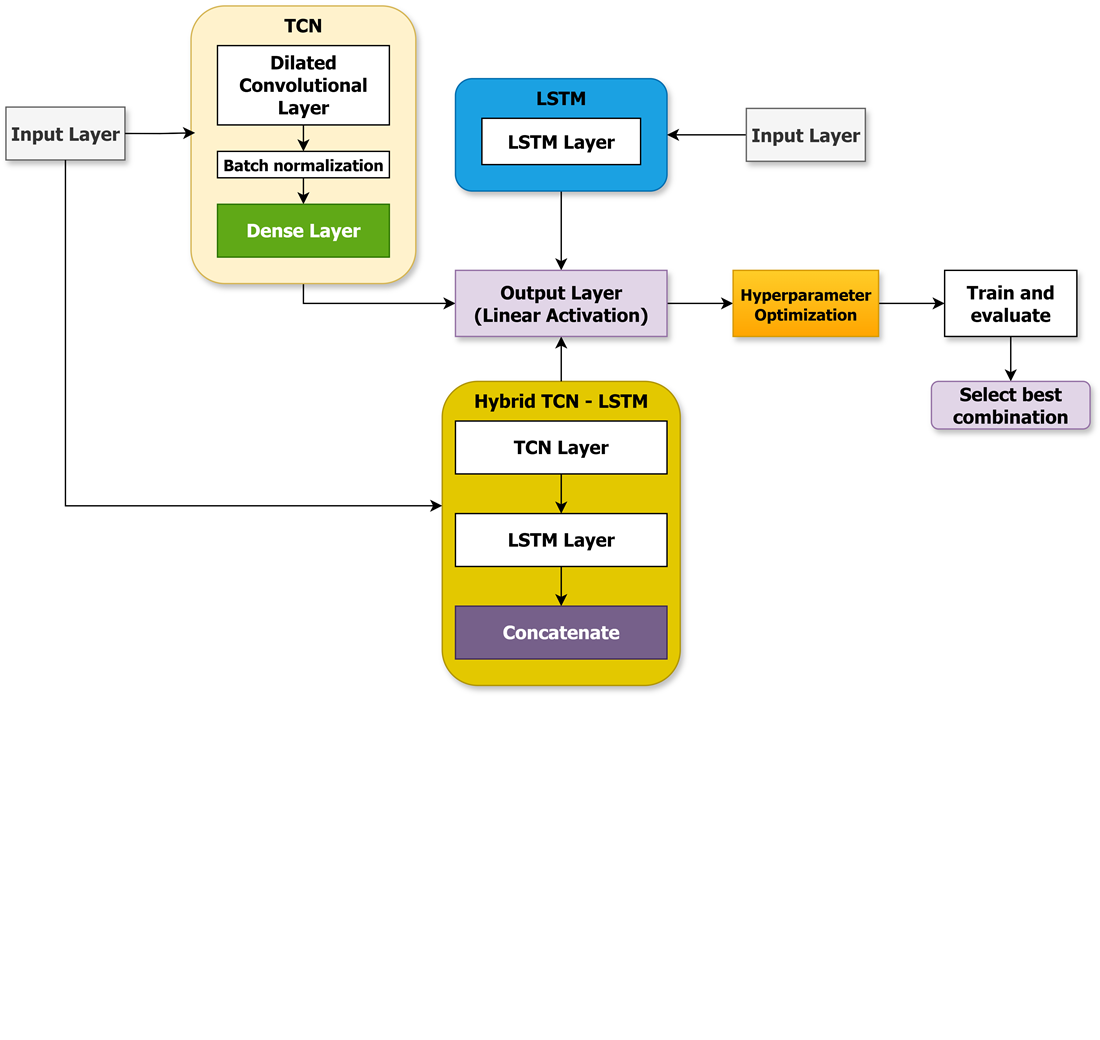
The object of the study is CO2 emission prediction using deep learning models. The problem lies in developing accurate models capable of handling temporal dependencies and periodic patterns in CO2 data. To address this, three deep learning models – temporal convolutional network (TCN), long short-term memory (LSTM), and a hybrid TCN-LSTM are evaluated. These models are optimized using random search and Bayesian optimization. Results indicate that the Hybrid TCN-LSTM model, optimized via random search, performs best, achieving MAE: 1.0269, R2: 0.9305, and MAPE: 4.47%. TCN excels at capturing periodic patterns through dilated convolutions, while LSTM handles long-term dependencies. Their integration combines these strengths, improving accuracy. Optimal hyperparameters (learning rate: 0.000539, dropout rate: 0.5) enhance robustness. Random search outperforms Bayesian optimization in navigating complex search spaces and avoiding local optima. Key findings include the hybrid model's ability to address short-term periodicity and long-term trends, and Random Search’s reliability over Bayesian methods in this context. These insights advance time series forecasting methodologies and support robust predictive frameworks. Practically, they aid environmental policy, energy planning, and carbon trading by enabling data-driven decisions for emission reduction. However, implementation requires high-quality historical data and sufficient computational resources
References
- DeAngelo, J., Azevedo, I., Bistline, J., Clarke, L., Luderer, G., Byers, E., Davis, S. J. (2021). Energy systems in scenarios at net-zero CO2 emissions. Nature Communications, 12 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-26356-y
- Zhao, Y., Liu, L., Wang, A., Liu, M. (2023). A novel deep learning based forecasting model for carbon emissions trading: A comparative analysis of regional markets. Solar Energy, 262, 111863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2023.111863
- Wei, X., Xu, Y. (2023). Research on carbon emission prediction and economic policy based on TCN-LSTM combined with attention mechanism. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fevo.2023.1270248
- Chen, C., Guo, J., Zhang, L., Wu, X., Yang, Z. (2024). Robust multi-scale time series prediction for building carbon emissions with explainable deep learning. Energy and Buildings, 312, 114159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2024.114159
- Hanifi, S., Cammarono, A., Zare-Behtash, H. (2024). Advanced hyperparameter optimization of deep learning models for wind power prediction. Renewable Energy, 221, 119700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2023.119700
- Yin, H., Yin, Y., Li, H., Zhu, J., Xian, Z., Tang, Y. et al. (2025). Carbon emissions trading price forecasting based on temporal-spatial multidimensional collaborative attention network and segment imbalance regression. Applied Energy, 377, 124357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2024.124357
- Gong, M., Zhang, Y., Li, J., Chen, L. (2024). Dynamic spatial–temporal model for carbon emission forecasting. Journal of Cleaner Production, 463, 142581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.142581
- Chen, J., Cui, Y., Zhang, X., Yang, J., Zhou, M. (2024). Temporal Convolutional Network for Carbon Tax Projection: A Data-Driven Approach. Applied Sciences, 14 (20), 9213. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14209213
- Rafi, M. A., Rodrigues, G. N., Mir, M. N. H., Bhuiyan, M. S. M., Mridha, M. F., Islam, M. R., Watanobe, Y. (2025). A Hybrid Temporal Convolutional Network and Transformer Model for Accurate and Scalable Sales Forecasting. IEEE Open Journal of the Computer Society, 6, 380–391. https://doi.org/10.1109/ojcs.2025.3538579
- Liu, X., Yang, L., Du, J., Zhang, H., Hu, J., Chen, A., Lv, W. (2024). Carbon and air pollutant emissions forecast of China’s cement industry from 2021 to 2035. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 204, 107498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2024.107498
- Shaikh, A. K., Nazir, A., Khalique, N., Shah, A. S., Adhikari, N. (2023). A new approach to seasonal energy consumption forecasting using temporal convolutional networks. Results in Engineering, 19, 101296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rineng.2023.101296
- Li, Q., Ren, X., Zhang, F., Gao, L., Hao, B. (2024). A novel ultra-short-term wind power forecasting method based on TCN and Informer models. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 120, 109632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2024.109632
- Liu, S., Xu, T., Du, X., Zhang, Y., Wu, J. (2024). A hybrid deep learning model based on parallel architecture TCN-LSTM with Savitzky-Golay filter for wind power prediction. Energy Conversion and Management, 302, 118122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2024.118122
- Tahir, M. F., Yousaf, M. Z., Tzes, A., El Moursi, M. S., El-Fouly, T. H. M. (2024). Enhanced solar photovoltaic power prediction using diverse machine learning algorithms with hyperparameter optimization. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 200, 114581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2024.114581
- Mahmoud, A., Mohammed, A. (2024). Leveraging Hybrid Deep Learning Models for Enhanced Multivariate Time Series Forecasting. Neural Processing Letters, 56 (5). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-024-11656-3
- Ritchie, H., Rosado, P., Roser, M. (2023). CO2 and Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Our World in Data. https://ourworldindata.org/co2-and-greenhouse-gas-emissions
- Barzani, A. R., Pahlavani, P., Ghorbanzadeh, O., Gholamnia, K., Ghamisi, P. (2024). Evaluating the Impact of Recursive Feature Elimination on Machine Learning Models for Predicting Forest Fire-Prone Zones. Fire, 7 (12), 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire7120440
- Wang, M., Qin, F. (2024). A TCN-Linear Hybrid Model for Chaotic Time Series Forecasting. Entropy, 26 (6), 467. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26060467
- Yao, J., Cai, Z., Qian, Z., Yang, B. (2023). A noval approach based on TCN-LSTM network for predicting waterlogging depth with waterlogging monitoring station. PLOS ONE, 18 (10), e0286821. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0286821
- Dong, J., Liu, X., Su, R., Xu, H., Yu, T. (2025). TCN-Transformer Deep Network with Random Forest for Prediction of the Chemical Synthetic Ammonia Process. ACS Omega, 10 (2), 2269–2279. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.4c09634
- Kong, F., Song, J., Yang, Z. (2022). A novel short-term carbon emission prediction model based on secondary decomposition method and long short-term memory network. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29 (43), 64983–64998. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20393-w
- Xie, T., Huang, Z., Tan, T., Chen, Y. (2024). Forecasting China’s agricultural carbon emissions: A comparative study based on deep learning models. Ecological Informatics, 82, 102661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoinf.2024.102661
- Bi, J., Zhang, X., Yuan, H., Zhang, J., Zhou, M. (2022). A Hybrid Prediction Method for Realistic Network Traffic With Temporal Convolutional Network and LSTM. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 19 (3), 1869–1879. https://doi.org/10.1109/tase.2021.3077537
- Ankalaki, S., Thippeswamy, M. N. (2023). A novel optimized parametric hyperbolic tangent swish activation function for 1D-CNN: application of sensor-based human activity recognition and anomaly detection. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 83 (22), 61789–61819. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-15766-3
- Sunkari, S., Sangam, A., P., V. S., M., S., Raman, R., Rajalakshmi, R., S., T. (2024). A refined ResNet18 architecture with Swish activation function for Diabetic Retinopathy classification. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 88, 105630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2023.105630
- Harumy, T. H. F., Zarlis, M., Lydia, M. S., Efendi, S. (2023). A novel approach to the development of neural network architecture based on metaheuristic protis approach. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (4 (124)), 46–59. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.281986
- Harumy, T. H. F., Br Ginting, D. S., Manik, F. Y., Alkhowarizmi, A. (2024). Developing an early detection model for skin diseases using a hybrid deep neural network to enhance health independence in coastal communities. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (9 (132)), 71–85. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.313983
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Roni Yunis, Tengku Henny Febriana Harumy, Syahril Efendi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








