A hybrid multi-scale convolution neural network with attention and texture features for improved image classification
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.331524Keywords:
multi-scale kernel, attention mechanisms, CIFAR-10, GLCM, LBP, Gabor filtersAbstract
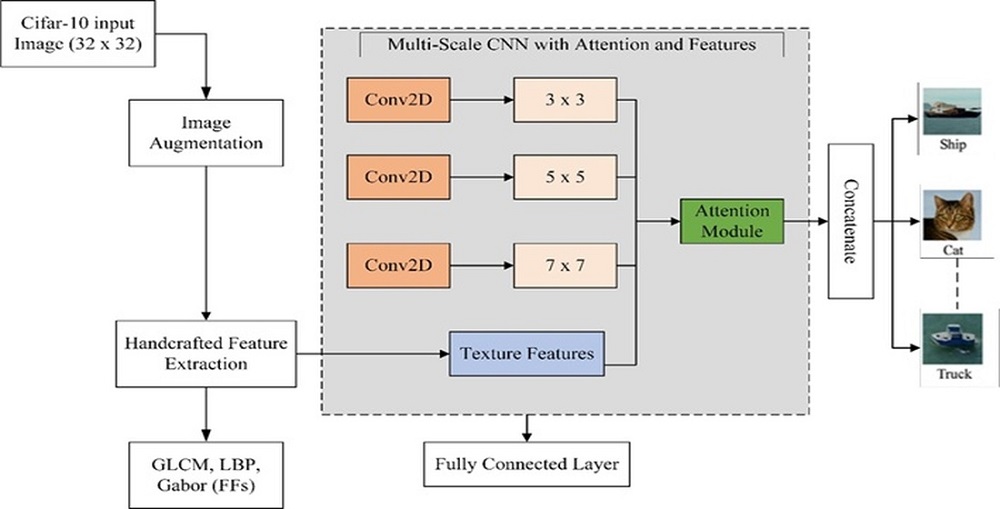
The object of this study is the classification of low-resolution and multi-class images, represented by the CIFAR-10 benchmark dataset. It is challenging to accurately classify low-resolution and multi-class images because traditional CNNs usually have trouble identifying both global and complex texture patterns. To address this issue, this study employs the CIFAR-10 dataset as a representative benchmark for real-world scenarios where image quality is limited, such as in low-cost medical imaging, remote sensing, and security surveillance systems. The limited discriminability of traditional CNNs in these situations is the primary issue addressed. The proposed method employs three parallel convolutional streams with distinct kernel sizes (3 × 3, 5 × 5, and 7 × 7) to capture hierarchical spatial patterns, followed by the integration of two attention mechanisms – squeeze-and-excitation and convolutional block attention module – that adaptively emphasize the most relevant spatial and channel-wise information. In addition, structural texture descriptors such as Gray-level co-occurrence matrix, local binary pattern, and Gabor filters are computed independently and later fused with the deep representations to enrich the feature space. Experiments were carried out on the CIFAR-10 dataset under varying levels of class complexity: 10, 5, and 3 categories. The results reveal that the hybrid approach significantly improves precision, recall, and F1-score across all scenarios, with the highest accuracy of 90.87% obtained when only three classes are involved. These improvements are explained by the complementary nature of deep and handcrafted features, which together enable the model to learn both global semantics and fine-grained local textures can achieve higher classification accuracy, improved reliability, and reduced misclassification errors, ultimately enhancing the effectiveness of applications ranging from medical decision support to intelligent surveillance.
References
- Talebi, K., Torabi, Z., Daneshpour, N. (2024). Ensemble models based on CNN and LSTM for dropout prediction in MOOC. Expert Systems with Applications, 235, 121187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2023.121187
- Harumy, T. H. F., Zarlis, M., Lydia, M. S., Efendi, S. (2023). A novel approach to the development of neural network architecture based on metaheuristic protis approach. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (4 (124)), 46–59. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.281986
- Rao, K. N., Khalaf, O. I., Krishnasree, V., Kumar, A. S., Alsekait, D. M., Priyanka, S. S. et al. (2024). An efficient brain tumor detection and classification using pre-trained convolutional neural network models. Heliyon, 10 (17), e36773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36773
- Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G. E. (2017). ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Communications of the ACM, 60 (6), 84–90. https://doi.org/10.1145/3065386
- Wei, D., Zhou, B., Torrabla, A., Freeman, W. (2015). Understanding Intra-Class Knowledge Inside CNN. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1507.02379
- Zhou, F., Wang, J. (2024). Heartbeat classification method combining multi-branch convolutional neural networks and transformer. IScience, 27 (3), 109307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2024.109307
- Harumy, T. H. F., Br Ginting, D. S., Manik, F. Y., Alkhowarizmi, A. (2024). Developing an early detection model for skin diseases using a hybrid deep neural network to enhance health independence in coastal communities. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (9 (132)), 71–85. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.313983
- Zeng, G., He, Y., Yu, Z., Yang, X., Yang, R., Zhang, L. (2015). Preparation of novel high copper ions removal membranes by embedding organosilane-functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotube. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 91 (8), 2322–2330. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.4820
- Sengupta, A., Ye, Y., Wang, R., Liu, C., Roy, K. (2019). Going Deeper in Spiking Neural Networks: VGG and Residual Architectures. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.00095
- Tan, M., Le, Q. V. (2019). EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks Mingxing. International Conference on Machine Learning. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1905.11946
- Hu, J., Shen, L., Sun, G. (2018). Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2018.00745
- Woo, S., Park, J., Lee, J.-Y., Kweon, I. S. (2018). CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. Computer Vision – ECCV 2018, 3–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_1
- Chen, S.-H., Wu, Y.-L., Pan, C.-Y., Lian, L.-Y., Su, Q.-C. (2023). Breast ultrasound image classification and physiological assessment based on GoogLeNet. Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences, 16 (3), 100628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2023.100628
- Zhang, C., Pan, X., Li, H., Gardiner, A., Sargent, I., Hare, J., Atkinson, P. M. (2018). A hybrid MLP-CNN classifier for very fine resolution remotely sensed image classification. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 140, 133–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2017.07.014
- Shafiq, M. A., Wang, Z., Amin, A., Hegazy, T., Deriche, M., AlRegib, G. (2015). Detection of Salt-dome Boundary Surfaces in Migrated Seismic Volumes Using Gradient of Textures. SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2015, 1811–1815. https://doi.org/10.1190/segam2015-5927230.1
- Ojala, T., Pietikäinen, M., Harwood, D. (1996). A comparative study of texture measures with classification based on featured distributions. Pattern Recognition, 29 (1), 51–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-3203(95)00067-4
- Althnian, A., Aloboud, N., Alkharashi, N., Alduwaish, F., Alrshoud, M., Kurdi, H. (2020). Face Gender Recognition in the Wild: An Extensive Performance Comparison of Deep-Learned, Hand-Crafted, and Fused Features with Deep and Traditional Models. Applied Sciences, 11 (1), 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11010089
- Guo, J., Yuan, H., Shi, B., Zheng, X., Zhang, Z., Li, H., Sato, Y. (2024). A novel breast cancer image classification model based on multiscale texture feature analysis and dynamic learning. Scientific Reports, 14 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-57891-5
- Liao, N., Guan, J. (2024). Multi-scale Convolutional Feature Fusion Network Based on Attention Mechanism for IoT Traffic Classification. International Journal of Computational Intelligence Systems, 17 (1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44196-024-00421-y
- Yazdan, S. A., Ahmad, R., Iqbal, N., Rizwan, A., Khan, A. N., Kim, D.-H. (2022). An Efficient Multi-Scale Convolutional Neural Network Based Multi-Class Brain MRI Classification for SaMD. Tomography, 8 (4), 1905–1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8040161
- Ishengoma, F. S., Lyimo, N. N. (2024). Ensemble model for grape leaf disease detection using CNN feature extractors and random forest classifier. Heliyon, 10 (12), e33377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33377
- Xu, Z., Guo, X., Wang, J. (2024). Enhancing skin lesion segmentation with a fusion of convolutional neural networks and transformer models. Heliyon, 10 (10), e31395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31395
- Liu, X., Hu, L., Tie, L., Jun, L., Wang, X., Liu, X. (2024). Integration of Convolutional Neural Network and Vision Transformer for gesture recognition using sEMG. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 98, 106686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2024.106686
- Zhang, L., Zeng, W., Zhou, P., Deng, X., Wu, J., Wen, H. (2025). A fast and lightweight train image fault detection model based on convolutional neural networks. Image and Vision Computing, 154, 105380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imavis.2024.105380
- Krizhevsky, A. (2009). Learning Multiple Layers of Features from Tiny Images. University of Toronto. Available at: https://www.cs.utoronto.ca/~kriz/learning-features-2009-TR.pdf
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Irpan Adiputra Pardosi, Tengku Henny Febriana Harumy, Syahril Efendi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








