Розробка комплексній системи двовісного сонячного трекінгу та моніторингу фотоелектричних перетворювачів
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.332548Ключові слова:
двоосьовий сонячний трекер, система online моніторингу, web-інтерфейс, фотоелектричні перетворювачі, чиста енергіяАнотація
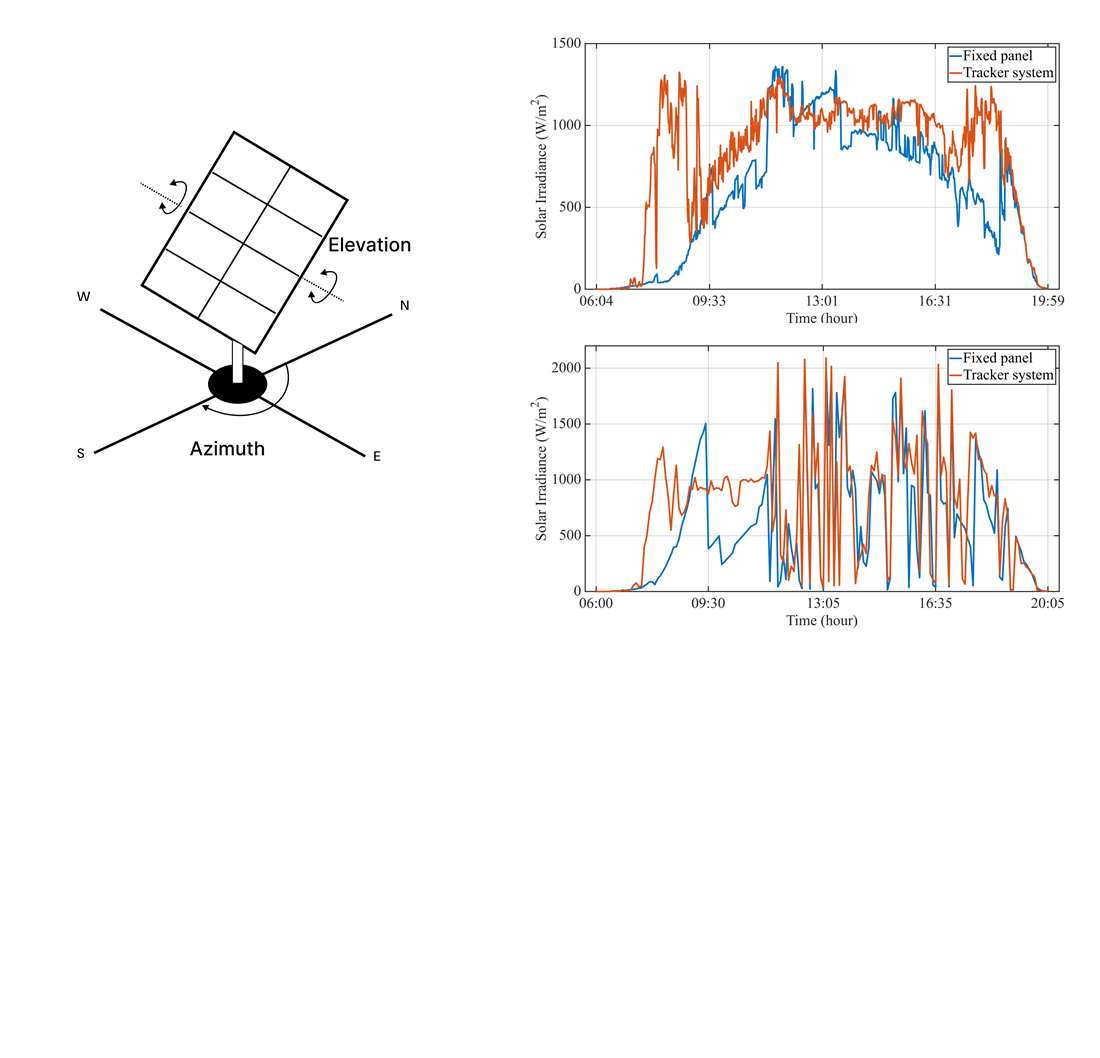
Об'єктом дослідження є двоосьові трекерні системи відстеження положення Сонця та моніторингу параметрів фотоелектричних панелей. Проблемою, що вирішувалася, є оптимізація позиціонування фотоелектричних панелей для підвищення їхньої ефективності та максимізації виробництва електроенергії, зокрема вибір оптимального алгоритму трекінгу з урахуванням вартості реалізації та терміну окупності в умовах змінних кліматичних факторів. Суть отриманих результатів полягає в розробці та впровадженні системи керування кутами нахилу та азимуту панелей згідно з обраним алгоритмом трекінгу та здійсненні онлайн-моніторингу ключових параметрів роботи фотоелектричного перетворювача і метеоданих. Завдяки точному розрахунку траєкторії Сонця та двоосьовому відстеженню зменшено кількість зайвих рухів, що сприяє зниженню енергоспоживання трекера та зменшенню зношування приводу, підвищуючи надійність системи та знижуючи експлуатаційні витрати. Ці результати пояснюються застосуванням двоосьових алгоритмів із точним розрахунком положення Сонця, а також реалізацією web-інтерфейсу та інтегрованої бази даних для накопичення статистичних даних про ефективність трекінгу. Система забезпечує збір і аналіз інформації в режимі реального часу та дозволяє змінювати алгоритм трекінгу і проводити дослідження його ефективності для певної локації чи кліматичної зони. Зручний web-інтерфейс дозволяє користувачам отримувати дані у вигляді графіків і та значень з сенсорів. На практиці розроблену систему можна використовувати для довгострокового моніторингу ефективності трекінгу, аналізу окупності інвестицій і планування експлуатаційних витрат. Експериментальні дослідження показали, що двоосьова трекерна система з алгоритмом точного розрахунку положення Сонця підвищує ефективність виробництва електроенергії у весняний сонячний день у західному регіоні України на понад 25 %
Посилання
- Dambhare, M. V., Butey, B., Moharil, S. V. (2021). Solar photovoltaic technology: A review of different types of solar cells and its future trends. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1913 (1), 012053. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1913/1/012053
- Ruvinskii, M. A., Kostyuk, O. B., Dzundza, B. S., Yaremiy, I. P., Mokhnatskyi, M. L., Yavorskyy, Ya. S. (2017). Kinetic Phenomena and Thermoelectric Properties of Polycrystalline Thin Films Based on PbSnAgTe Compounds. Journal of Nano- and Electronic Physics, 9 (5), 05004-1-05004–05006. https://doi.org/10.21272/jnep.9(5).05004
- Kostyuk, O. B., Dzundza, B. S., Yavorsky, Ya. S., Dashevsky, Z. M. (2021). Development of Thermal Detector Based on Flexible Film Thermoelectric Module. Physics and Chemistry of Solid State, 22 (1), 45–52. https://doi.org/10.15330/pcss.22.1.45-52
- Dashevsky, Z., Mamykin, S., Dzundza, B., Auslender, M., Shneck, R. Z. (2023). A Review of Nanocrystalline Film Thermoelectrics on Lead Chalcogenide Semiconductors: Progress and Application. Energies, 16 (9), 3774. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16093774
- Izam, N. S. M. N., Itam, Z., Sing, W. L., Syamsir, A. (2022). Sustainable Development Perspectives of Solar Energy Technologies with Focus on Solar Photovoltaic—A Review. Energies, 15 (8), 2790. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15082790
- Renewable capacity statistics 2025 (2025). IRENA. Available at: https://www.irena.org/-/media/Files/IRENA/Agency/Publication/2025/Mar/IRENA_DAT_RE_Capacity_Statistics_2025.pdf
- Champion Photovoltaic Module Efficiency Chart. NREL. Available at: https://www.nrel.gov/pv/module-efficiency
- Barrios-Sánchez, J. M., Tlapanco-Ríos, E. I. (2025). Dual-Axis Solar Tracking System for Enhanced Photovoltaic Efficiency in Tropical Climates. Sustainability, 17 (3), 1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17031117
- Shang, H., Shen, W. (2023). Design and Implementation of a Dual-Axis Solar Tracking System. Energies, 16 (17), 6330. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16176330
- Hammoumi, A. E., Motahhir, S., Ghzizal, A. E., Chalh, A., Derouich, A. (2018). A simple and low‐cost active dual‐axis solar tracker. Energy Science & Engineering, 6 (5), 607–620. https://doi.org/10.1002/ese3.236
- Jamroen, C., Fongkerd, C., Krongpha, W., Komkum, P., Pirayawaraporn, A., Chindakham, N. (2021). A novel UV sensor-based dual-axis solar tracking system: Implementation and performance analysis. Applied Energy, 299, 117295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2021.117295
- Pratama, A. Y., Fauzy, A., Effendi, H. (2019). Performance Enhancement of Solar Panel Using Dual Axis Solar Tracker. 2019 International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Informatics (ICEEI), 444–447. https://doi.org/10.1109/iceei47359.2019.8988902
- Amadi, H. N., Gutierrez, S. (2019). Design and Performance Evaluation of a Dual-Axis Solar Tracking System for Rural Applications. European Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, 3 (1). https://doi.org/10.24018/ejece.2019.3.1.52
- Holota, V. I., Kogut, I., Druzhinin, A., Khoverko, Y. (2013). High Sensitive Active MOS Photo Detector on the Local 3D SOI-Structure. Advanced Materials Research, 854, 45–47. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.854.45
- Kogut, I. T., Holota, V. I., Druzhinin, A., Dovhij, V. V. (2016). The Device-Technological Simulation of Local 3D SOI-Structures. Journal of Nano Research, 39, 228–234. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/jnanor.39.228
- Sunrise/Sunset calculations. NOAA. Available at: https://gml.noaa.gov/grad/solcalc/solareqns.PDF
- Sun Angle Calculator. Available at: https://www.omnicalculator.com/physics/sun-angle
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2025 Vitalii Fedenko, Bogdan Dzundza, Myroslav Pavlyuk, Omelian Poplavskyi

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.
Ліцензійний договір – це документ, в якому автор гарантує, що володіє усіма авторськими правами на твір (рукопис, статтю, тощо).
Автори, підписуючи Ліцензійний договір з ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР», мають усі права на подальше використання свого твору за умови посилання на наше видання, в якому твір опублікований. Відповідно до умов Ліцензійного договору, Видавець ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР» не забирає ваші авторські права та отримує від авторів дозвіл на використання та розповсюдження публікації через світові наукові ресурси (власні електронні ресурси, наукометричні бази даних, репозитарії, бібліотеки тощо).
За відсутності підписаного Ліцензійного договору або за відсутністю вказаних в цьому договорі ідентифікаторів, що дають змогу ідентифікувати особу автора, редакція не має права працювати з рукописом.
Важливо пам’ятати, що існує і інший тип угоди між авторами та видавцями – коли авторські права передаються від авторів до видавця. В такому разі автори втрачають права власності на свій твір та не можуть його використовувати в будь-який спосіб.









