Fault detection of rotating machinery in the petrochemical industry using a deep learning based approach: TabNet – WGAN
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.332597Keywords:
rotating machinery, fault detection, deep learning, WGAN, TabNet, SHAP, predictive maintenanceAbstract
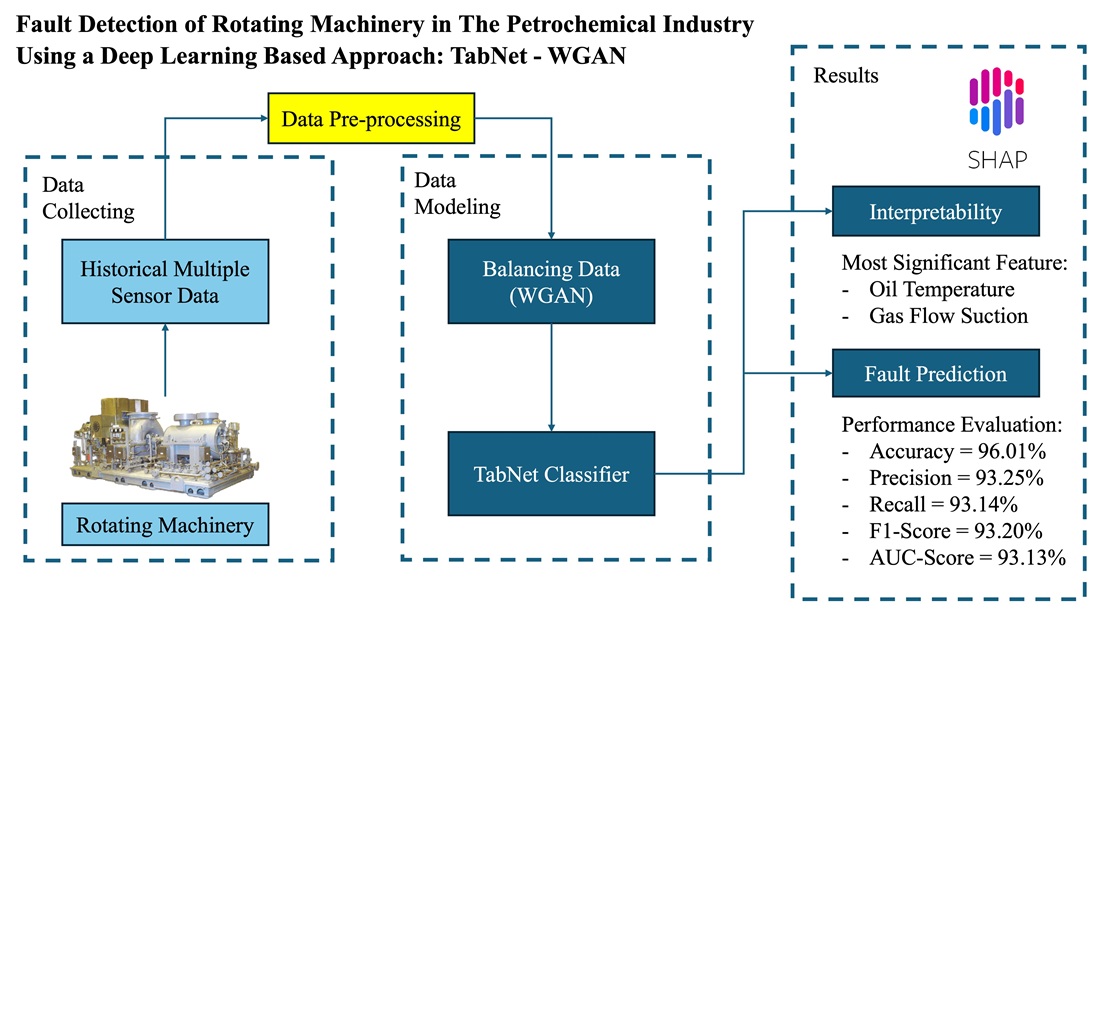
The object of the study is the fault detection process in critical rotating machinery, specifically steam turbines and compressors, operating within a petrochemical production environment. Traditional fault detection methods, though proven and cost-effective, struggle to address modern industrial challenges – such as the increasing complexity of sensor data, class imbalance in failure records, and the need for real-time interpretability. Recent advancements in deep learning offer promising solutions to these limitations. This study proposes an integrated framework that combines Wasserstein Generative Adversarial Network (WGAN) for data balancing and TabNet, an interpretable deep learning model optimized for tabular sensor data. The goal is to enhance the accuracy and interpretability of fault detection under imbalanced, high-dimensional industrial datasets. Using historical data from a petrochemical plant (2015–2024), the WGAN-TabNet model demonstrated superior performance compared to traditional classifiers (Logistic Regression, SVM, XGBoost), achieving an accuracy of 96.01%, precision of 93.25%, recall of 93.14%, F1-score of 93.20%, and AUC score of 93.13%. The interpretability provided by combination of TabNet and SHAP analysis further identified key operational variables influencing failure such as oil temperature and gas flow rate, offering actionable insights for predictive maintenance. The results underscore that integrating deep learning with robust data balancing significantly improves fault detection where traditional methods fall short, supporting practical implementation in modern predictive maintenance systems
References
- Mobley, R. K. (2002). An Introduction to Predictive Maintenance. Butterworth-Heinemann. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-7506-7531-4.x5000-3
- Borgnakke, C., Sonntag, R. E. (2013). Fundamentals of Thermodynamics. Wiley, 912.
- Giampaolo, T. (2010). Compressor Handbook: Principles and Practice. The Fairmont Press, 376.
- Mobley, R. K. (2001). Plant Engineer’s Handbook. Butterworth-Heinemann.
- Moubray, J. (1997). Reliability-Centered Maintenance. Butterworth-Heinemann.
- Nunes, P., Santos, J., Rocha, E. (2023). Challenges in predictive maintenance – A review. CIRP Journal of Manufacturing Science and Technology, 40, 53–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirpj.2022.11.004
- Zhou, H., Pan, H., Zheng, K., Wu, Z., Xiang, Q. (2025). A novel oversampling method based on Wasserstein CGAN for imbalanced classification. Cybersecurity, 8 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42400-024-00290-0
- Jardine, A. K. S., Lin, D., Banjevic, D. (2006). A review on machinery diagnostics and prognostics implementing condition-based maintenance. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 20 (7), 1483–1510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2005.09.012
- Zhang, W., Yang, D., Wang, H. (2019). Data-Driven Methods for Predictive Maintenance of Industrial Equipment: A Survey. IEEE Systems Journal, 13 (3), 2213–2227. https://doi.org/10.1109/jsyst.2019.2905565
- Goodfellow, I., Bengio, Y., Courville, A. (2016). Deep Learning. The MIT Press, 800.
- Liu, R., Yang, B., Zio, E., Chen, X. (2018). Artificial intelligence for fault diagnosis of rotating machinery: A review. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 108, 33–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.02.016
- Chen, T., Guestrin, C. (2016). XGBoost. Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, 785–794. https://doi.org/10.1145/2939672.2939785
- Tarekegn, A. N., Giacobini, M., Michalak, K. (2021). A review of methods for imbalanced multi-label classification. Pattern Recognition, 118, 107965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2021.107965
- Chawla, N. V., Bowyer, K. W., Hall, L. O., Kegelmeyer, W. P. (2002). SMOTE: Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 16, 321–357. https://doi.org/10.1613/jair.953
- Blagus, R., Lusa, L. (2013). SMOTE for high-dimensional class-imbalanced data. BMC Bioinformatics, 14 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-106
- Goodfellow, I., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B., Warde-Farley, D., Ozair, S. et al. (2014). Generative Adversarial Networks. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS). arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1406.2661
- Arjovsky, M., Chintala, S., Bottou, L. (2017). Wasserstein GAN. International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1701.07875
- Arik, S. Ö., Pfister, T. (2021). TabNet: Attentive interpretable tabular learning. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1908.07442
- Fares, I. A., Abd Elaziz, M. (2025). Explainable TabNet Transformer-based on Google Vizier Optimizer for Anomaly Intrusion Detection System. Knowledge-Based Systems, 316, 113351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2025.113351
- Fan, J., Yuan, X., Miao, Z., Sun, Z., Mei, X., Zhou, F. (2022). Full Attention Wasserstein GAN With Gradient Normalization for Fault Diagnosis Under Imbalanced Data. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 71, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1109/tim.2022.3190525
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Muhammad Ikhsan Anshori, Arian Dhini

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








