Devising a method for designing multicomponent diffusers of compressors in turbogenerators with hydrogen cooling
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.337285Keywords:
turbogenerator, compressor diffuser, multilayer seal, gas-dynamic calculations, circulating currentsAbstract
This study's object is the aerodynamic characteristics of the compressor diffusers in hydrogen-cooled turbogenerators.
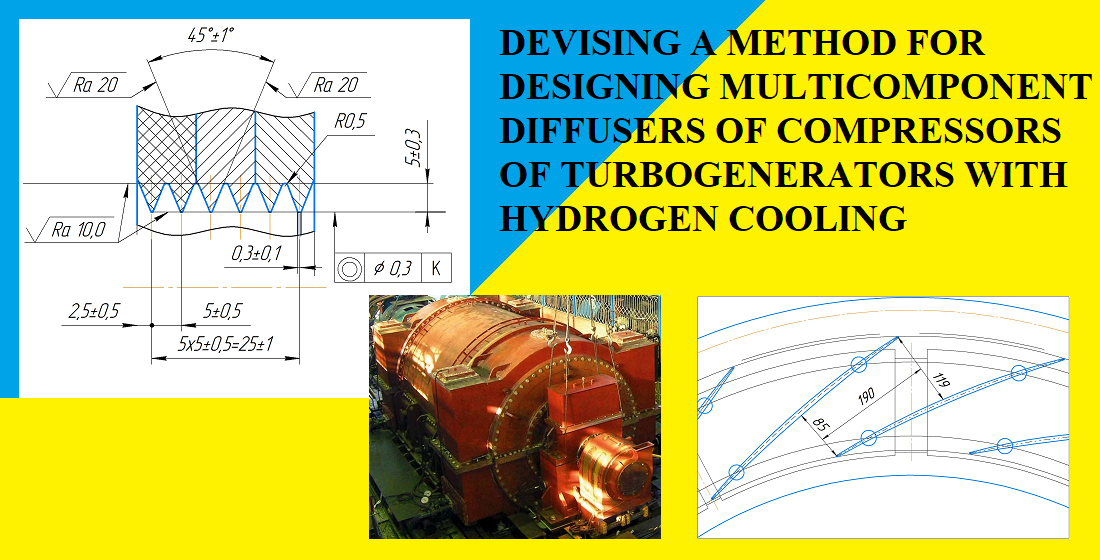
This paper reports a solution to the task of improving the efficiency of a cooling system discharge unit. This issue relates to enabling the necessary gas consumption while reducing the number of diffuser blades. The problem was solved by introducing a seal with improved technological control capabilities and step-by-step optimization of the diffuser flow part.
Another issue is the thermal loads on the power components of the diffuser unit due to the action of circulating currents and temperature gradients. The problem was solved by introducing dielectric and non-magnetic elements into the structure, by additional finning and multi-component design for the diffuser strength circuits.
The main result is the designed multi-component diffuser structure with a number of blades of 20 while enabling a head of Hst = 978 mm H2O. The adopted duct opening angle was 20°. Other necessary geometric parameters were determined. The introduction of a multilayer seal made it possible to reduce the gap between the impeller and the diffuser to 0.9 mm. The proposed design was tested on the bench at a manufacturing enterprise.
The results of the study are attributed to the use of non-magnetic and dielectric materials (AISI 321 steel and fiberglass), as well as the introduction of additional strength decoupling elements.
A special feature of the proposed method is the application of mathematical models based on the basic equations of gas dynamics, taking into account the composition principles of engineering alloys and synthetic materials. This could be achieved via a step-by-step optimization of the design.
The proposed structure could be implemented when designing and modernizing hydrogen-cooled turbogenerators
References
- Biswal, G. R., Dewal, M. L., Maheshwari, R. P. (2012). A comprehensive scheme for cooling of large generators using hydrogen cooling systems. 2012 IEEE 8th International Colloquium on Signal Processing and Its Applications, 105–109. https://doi.org/10.1109/cspa.2012.6194700
- Pulagam, M. K. R., Rout, S. K., Muduli, K. K., Syed, S. A., Barik, D., Hussein, A. K. (2024). Internal Finned Heat Exchangers: Thermal and Hydraulic Performance Review. International Journal of Heat and Technology, 42 (2), 583–592. https://doi.org/10.18280/ijht.420225
- Venkatesh, B., Kiran, A., Khan, M., Rahmani, M. K. I., Upadhyay, L., Babu, J. C., Narayana, T. L. (2024). Performance optimization for an optimal operating condition for a shell and heat exchanger using a multi-objective genetic algorithm approach. PLOS ONE, 19 (6), e0304097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0304097
- Balitskii, A. I., Syrotyuk, A. M., Havrilyuk, M. R., Balitska, V. O., Kolesnikov, V. O., Ivaskevych, L. M. (2023). Hydrogen Cooling of Turbo Aggregates and the Problem of Rotor Shafts Materials Degradation Evaluation. Energies, 16 (23), 7851. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16237851
- Balitskii, A. I., Kvasnytska, Y. H., Ivaskevych, L. M., Kvasnytska, K. H., Balitskii, O. A., Shalevska, I. A. et al. (2023). Hydrogen and Corrosion Resistance of Nickel Superalloys for Gas Turbines, Engines Cooled Blades. Energies, 16 (3), 1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16031154
- Dong, J., Song, B., Yuan, X., Jin, W., Wang, J. (2024). Research on aerodynamic performance of centrifugal compressors for hydrogen-mixed natural gas. PLOS ONE, 19 (10), e0312829. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0312829
- Zhang, Y., Xu, S., Wan, Y. (2020). Performance improvement of centrifugal compressors for fuel cell vehicles using the aerodynamic optimization and data mining methods. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 45 (19), 11276–11286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.02.026
- SanAndres, U., Almandoz, G., Poza, J., Ugalde, G. (2014). Design of Cooling Systems Using Computational Fluid Dynamics and Analytical Thermal Models. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 61 (8), 4383–4391. https://doi.org/10.1109/tie.2013.2286081
- Dang, D.-D., Pham, X.-T., Labbe, P., Torriano, F., Morissette, J.-F., Hudon, C. (2018). CFD analysis of turbulent convective heat transfer in a hydro-generator rotor-stator system. Applied Thermal Engineering, 130, 17–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.11.034
- Korovkin, N. V., Verkhovtsev, D., Gulay, S. (2021). Rotor Air-Cooling Efficiency of Powerful Turbogenerator. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 36 (3), 1983–1990. https://doi.org/10.1109/tec.2020.3045063
- Peng, Q., Bao, R., Li, J., Ren, J., Tang, J., Li, J. et al. (2024). Centrifugal compressor performance prediction and dynamic simulation of natural gas hydrogen blended. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 52, 872–893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2023.10.023
- Taher, M., Evans, F. (2021). Centrifugal Compressor Polytropic Performance – Improved Rapid Calculation Results – Cubic Polynomial Methods. International Journal of Turbomachinery, Propulsion and Power, 6 (2), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtpp6020015
- Taher, M., Evans, B. (2020). Using a Cubic Polynomial Temperature-Entropy Constant Efficiency Path for Centrifugal Compressor Polytropic Performance Evaluation. http://dx.doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.23470.54083/1
- Evans, B. F., Huble, S. (2017). Centrifugal Compressor Performance: Making Enlightened Analysis Decisions. In Proceedings of the 46th Turbomachinery Symposium. Available at: https://oaktrust.library.tamu.edu/server/api/core/bitstreams/24440913-33e7-4938-9fcf-c6aa37860751/content
- Zhou, G.-H., Han, L., Fan, Z.-N., Zhang, H.-B., Dong, X.-C., Wang, J. et al. (2018). Ventilation Cooling Design for a Novel 350-MW Air-Cooled Turbo Generator. IEEE Access, 6, 62184–62192. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2018.2875757
- Tang, Q., Wu, H., Li, J., Lou, H., Yang, C. (2022). Performance Optimization of Centrifugal Compressors Based on Throughflow Model. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 47 (12), 16439–16450. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-06736-2
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Oleksii Tretiak, Stanislav Kravchenko, Bogdan Shestak, Denys Shpitalnyi, Mariia Arefieva, Iryna Tretiak, Serhii Serhiienko, Anton Kovryga

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








