Enhancing industrial power systems: a case study on electrical savings improvement with microbial fuel cell
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.338866Keywords:
microbial fuel cells, industrial feeders, grid integration, energy savings, cost reductionAbstract
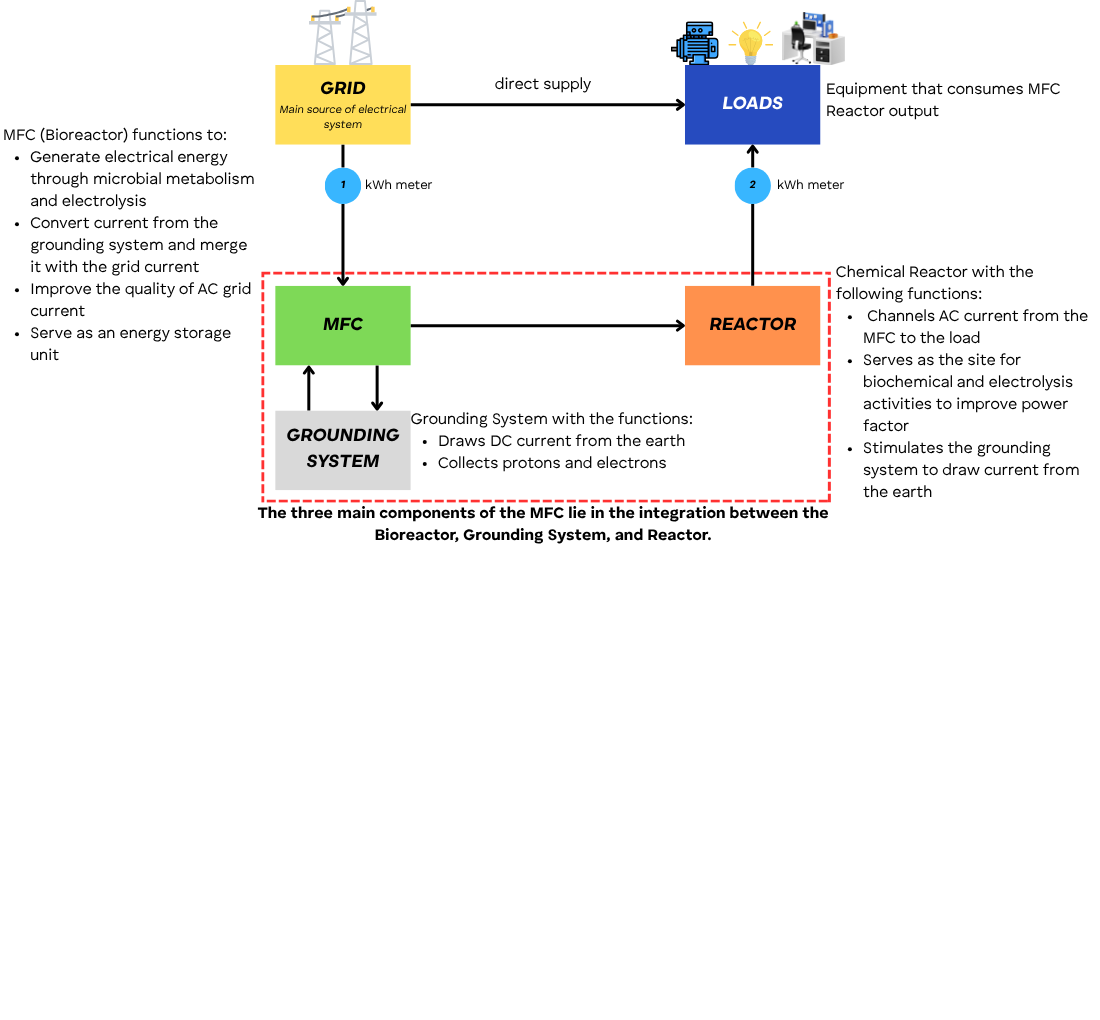
The object of the study is the industrial feeder system rated at 100 kVA and 150 kVA, which was integrated with an MFC system operating in parallel with the grid. This research explores the application of microbial fuel cells (MFCs) for industrial-scale power systems, focusing on their integration with medium-capacity feeders to reduce reliance on grid electricity. The central problem addressed is the scarcity of long-term, real-world demonstrations of MFCs operating in parallel with the public grid, particularly in feeders rated at 100 kVA and 150 kVA, where stable and reliable performance is critical. To overcome this gap, customized MFC panels were designed, equipped with a Delta PLC-based control system, and installed on two industrial feeders. Their operation was monitored continuously for nine months using PM-5350 power meters to capture load, grid, and MFC contributions. The results demonstrate that the MFCs consistently supplied a fraction of the feeder demand, reducing grid energy consumption by 9.68–18.48%, with an overall average saving of 12.38%. Corresponding reductions in electricity costs reached up to USD 1,034 per month. Differences in savings between the two feeders were explained by variations in load profiles, synchronization strategies, and microbial performance stability over time. A distinctive outcome of this study is the successful demonstration of reliable, long-horizon MFC operation under industrial conditions, enabled by protective interconnection schemes and automated control. The practical implications are significant: MFCs can be deployed on medium-scale feeders in manufacturing or processing industries to achieve measurable cost reductions while simultaneously contributing to renewable energy adoption and waste-to-energy initiatives. These findings strengthen the case for MFCs as a viable complement to conventional distributed generation technologies
References
- Hung, Y.-H., Liu, T.-Y., Chen, H.-Y. (2019). Renewable Coffee Waste-Derived Porous Carbons as Anode Materials for High-Performance Sustainable Microbial Fuel Cells. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 7 (20), 16991–16999. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b02405
- Kusmayadi, A., Leong, Y. K., Yen, H., Huang, C., Dong, C., Chang, J. (2020). Microalgae-microbial fuel cell (mMFC): an integrated process for electricity generation, wastewater treatment, CO2 sequestration and biomass production. International Journal of Energy Research, 44 (12), 9254–9265. https://doi.org/10.1002/er.5531
- Yalcinkaya, F., Torres-Mendieta, R., Hruza, J., Vávrová, A., Svobodová, L., Pietrelli, A., Ieropoulos, I. (2024). Nanofiber applications in microbial fuel cells for enhanced energy generation: a mini review. RSC Advances, 14 (13), 9122–9136. https://doi.org/10.1039/d4ra00674g
- Kordek-Khalil, K., Altiok, E., Salvian, A., Siekierka, A., Torres-Mendieta, R., Avignone-Rossa, C. et al. (2023). Nanocomposite use in MFCs: a state of the art review. Sustainable Energy & Fuels, 7 (24), 5608–5624. https://doi.org/10.1039/d3se00975k
- Chaijak, P., Thipraksa, J. (2022). Improved Performance of a Novel-Model Laccase Based Microbial Fuel Cell (LB-MFC) with Edible Mushroom as a Whole-Cell Biocatalyst. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 31 (5), 4481–4485. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/147196
- Goto, Y., Yoshida, N. (2019). Scaling up Microbial Fuel Cells for Treating Swine Wastewater. Water, 11 (9), 1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091803
- Jabbar, N., Alardhi, S., Al-Jadir, T., Abed Dhahad, H. (2023). Contaminants Removal from Real Refinery Wastewater Associated with Energy Generation in Microbial Fuel Cell. Journal of Ecological Engineering, 24 (1), 107–114. https://doi.org/10.12911/22998993/156081
- Mukherjee, A., Patel, R., Zaveri, P., Shah, M. T., Munshi, N. S. (2022). Microbial fuel cell performance for aromatic hydrocarbon bioremediation and common effluent treatment plant wastewater treatment with bioelectricity generation through series-parallel connection. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 75 (4), 785–795. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.13612
- Singh, S., Suresh, S. (2020). A novel microbial fuel cell technology for energy generation and comparison of power densities for different electrodes using nanotechnology. Rasayan Journal of Chemistry, 13 (01), 672–675. https://doi.org/10.31788/rjc.2020.1315556
- Muazu, R. I., Sadhukhan, J., Venkata Mohan, S., Gadkari, S. (2023). Hexavalent chromium waste removal via bioelectrochemical systems – a life cycle assessment perspective. Environmental Science: Water Research & Technology, 9 (10), 2487–2500. https://doi.org/10.1039/d3ew00344b
- Naseer, M. N., Zaidi, A. A., Dutta, K., Jaafar, J., Wahab, Y. A., Cai, Y. (2023). A Novel Computational Platform for Steady-State and Dynamic Simulation of Dual-Chambered Microbial Fuel Cell. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 170 (9), 094504. https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/acf882
- Xu, L., Zhao, Y., Doherty, L., Hu, Y., Hao, X. (2015). The integrated processes for wastewater treatment based on the principle of microbial fuel cells: A review. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 46 (1), 60–91. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2015.1061884
- Li, Y., Wu, Y., Puranik, S., Lei, Y., Vadas, T., Li, B. (2014). Metals as electron acceptors in single-chamber microbial fuel cells. Journal of Power Sources, 269, 430–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.06.117
- Li, W.-W., Yu, H.-Q. (2013). Utilization of Microbe-Derived Electricity for Practical Application. Environmental Science & Technology, 48 (1), 17–18. https://doi.org/10.1021/es405023b
- Obileke, K., Onyeaka, H., Meyer, E. L., Nwokolo, N. (2021). Microbial fuel cells, a renewable energy technology for bio-electricity generation: A mini-review. Electrochemistry Communications, 125, 107003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2021.107003
- Prathiba, S., Kumar, P. S., Vo, D.-V. N. (2022). RETRACTED: Recent advancements in microbial fuel cells: A review on its electron transfer mechanisms, microbial community, types of substrates and design for bio-electrochemical treatment. Chemosphere, 286, 131856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131856
- Ramya, M., Senthil Kumar, P. (2022). A review on recent advancements in bioenergy production using microbial fuel cells. Chemosphere, 288, 132512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132512
- Patwardhan, S. B., Savla, N., Pandit, S., Gupta, P. K., Mathuriya, A. S., Lahiri, D. et al. (2021). Microbial Fuel Cell United with Other Existing Technologies for Enhanced Power Generation and Efficient Wastewater Treatment. Applied Sciences, 11 (22), 10777. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210777
- Thapa, B. S., Pandit, S., Patwardhan, S. B., Tripathi, S., Mathuriya, A. S., Gupta, P. K. et al. (2022). Application of Microbial Fuel Cell (MFC) for Pharmaceutical Wastewater Treatment: An Overview and Future Perspectives. Sustainability, 14 (14), 8379. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148379
- Freis, S. M., Alexander, J. D., Anderson, J. E., Corley, R. P., De La Vega, A. I., Gustavson, D. E. et al. (2024). Associations between executive functions assessed in different contexts in a genetically informative sample. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 153 (1), 70–85. https://doi.org/10.1037/xge0001471
- Pandit, S., Savla, N., Sonawane, J. M., Sani, A. M., Gupta, P. K., Mathuriya, A. S. et al. (2021). Agricultural Waste and Wastewater as Feedstock for Bioelectricity Generation Using Microbial Fuel Cells: Recent Advances. Fermentation, 7 (3), 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation7030169
- Xing, H., Stuart, C., Spence, S., Chen, H. (2021). Fuel Cell Power Systems for Maritime Applications: Progress and Perspectives. Sustainability, 13 (3), 1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031213
- Niju, S., Priyadharshini, K. (2023). A review on microbial fuel cell technology for Brewery industry wastewater treatment – From fundamentals to pilot scale studies. Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy, 42 (6). https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.14191
- Abir Hossain, A.-M., Masud, N., Yasin, M. S., Ali, M. (2020). Analysis of the Performance of Microbial Fuel Cell as a Potential Energy Storage Device. Proceedings of International Exchange and Innovation Conference on Engineering & Sciences (IEICES), 6, 149–155. https://doi.org/10.5109/4102481
- Jatoi, A. S., Baloch, A. G., Jadhav, A., Nizamuddin, S., Aziz, S., Soomro, S. A. et al. (2019). Improving fermentation industry sludge treatment as well as energy production with constructed dual chamber microbial fuel cell. SN Applied Sciences, 2 (1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-1826-0
- Breheny, M., Bowman, K., Farahmand, N., Gomaa, O., Keshavarz, T., Kyazze, G. (2019). Biocatalytic electrode improvement strategies in microbial fuel cell systems. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 94 (7), 2081–2091. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.5916
- Demir, Ö., Gümüş, E. (2023). Effects of pre‐treated sludge on sludge stabilization and electricity generation in microbial fuel cell. Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy, 42 (5). https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.14119
- Din, M. I., Ahmed, M., Ahmad, M., Iqbal, M., Ahmad, Z., Hussain, Z. et al. (2023). Investigating the Activity of Carbon Fiber Electrode for Electricity Generation from Waste Potatoes in a Single-Chambered Microbial Fuel Cell. Journal of Chemistry, 2023, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/8520657
- Saleh, M., Yalvaç, M., Halef, L., Hekim, M. Ş., Arslan, H. (2020). Bulgur industry wastewater treatment by microbial fuel cell – exploratory study. Turkish Journal of Engineering, 4 (4), 203–208. https://doi.org/10.31127/tuje.646603
- Chaijak, P., Michu, P. (2022). Modified Water Hyacinth Biochar as a Low-Cost Supercapacitor Electrode for Electricity Generation From Pharmaceutical Wastewater. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 31 (6), 5471–5475. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/150463
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Levin Halim, Nico Saputro, Jenny N M Tan-Soetedjo, Anastasia Prima Kristijarti

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








