Improving the efficiency of evaporation plants that produce condensed milk by applying liquid-vapor jet units
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.339764Keywords:
evaporation unit, liquid-vapor jet unit, condensed milk, recompression, efficiency, thermal economicsAbstract
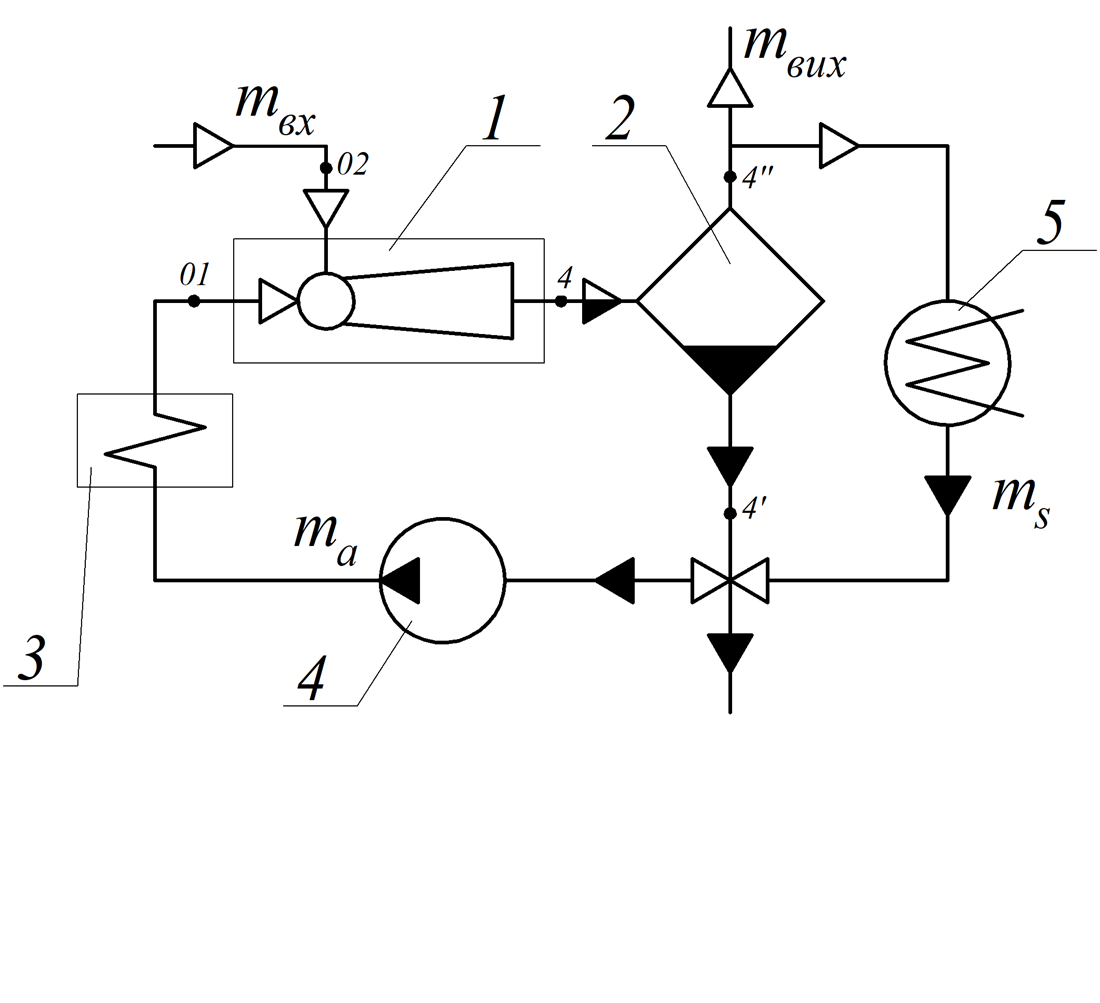
This study's object is the evaporation unit that produces condensed milk.
The problem of low efficiency of evaporation units producing condensed milk has been solved by replacing steam jet ejectors with fundamentally new two-phase jet devices represented by liquid-vapor jet units. Their operational process is based on a jet thermocompression principle, which makes it possible to reduce the consumption of boiler steam, which is used in steam jet ejectors as a working jet of active flow. In liquid-vapor jet devices, boiler steam is used only to heat the working fluid of the active flow in a heat exchanger-heater. Given this, it is possible to reduce its consumption by 2.95 times and achieve the economic effect averaging USD 1,337.
Another advantage of liquid-vapor jet units is that the generation of working steam occurs in the supersonic part of the active flow nozzle. As a result, it is possible to improve the degree of increase in the pressure of the secondary flow and abandon its multi-stage compression as is implemented in steam jet ejectors. This further increases the efficiency of installations based on such units by 25–30% compared to steam jet ejectors.
And, most importantly, the use of liquid-vapor jet devices makes it possible to simplify the design of the evaporation unit and switch from a two-case to a single-case scheme. This provides a reduction in the cost of a product unit by an average of USD 450 per ton.
This paper reports the thermodynamical, exergy, and thermoeconomic analyses. As a result of the study, it was found that the modernization of evaporation units that produce condensed milk by using liquid-vapor jet unit makes it possible to improve the efficiency of such systems by 2.1 times on average
References
- Deeth, H. C., Lewis, M. J. (2017). High Temperature Processing of Milk and Milk Products. John Wiley & Sons. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118460467
- Hamzaoui, M., Nesreddine, H., Aidoun, Z., Balistrou, M. (2018). Experimental study of a low grade heat driven ejector cooling system using the working fluid R245fa. International Journal of Refrigeration, 86, 388–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrefrig.2017.11.018
- Śmierciew, K., Pawluczuk, A., Gagan, J., Butrymowicz, D. (2019). Thermodynamic analysis of two-phase injector for various working fluids. Applied Thermal Engineering, 157, 113713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2019.113713
- Prestes, A. A., Helm, C. V., Esmerino, E. A., Silva, R., Prudencio, E. S. (2022). Conventional and alternative concentration processes in milk manufacturing: a comparative study on dairy properties. Food Science and Technology, 42. https://doi.org/10.1590/fst.08822
- Yang, D., Leng, B., Li, T., Li, M. (2020). Energy Saving Research on Multi-effect Evaporation Crystallization Process of Bittern Based on MVR and TVR Heat Pump Technology. American Journal of Chemical Engineering, 8 (3), 54. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajche.20200803.11
- Croguennec, T., Jeantet, R., Schuck, P. (2016). From Milk to Dairy Products. Handbook of Food Science and Technology 3, 1–63. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119296225.ch1
- Besagni, G., Mereu, R., Inzoli, F. (2016). Ejector refrigeration: A comprehensive review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 53, 373–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.08.059
- Liang, L., Qi, C., Wang, X., Jin, Q., McClements, D. J. (2017). Influence of Homogenization and Thermal Processing on the Gastrointestinal Fate of Bovine Milk Fat: In Vitro Digestion Study. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 65 (50), 11109–11117. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b04721
- Dos Santos Morais, R., Louvet, N., Borges, F., Dumas, D., Cvetkovska-Ben Mohamed, L., Barrau, S. et al. (2021). Impact of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG on the Emulsion Stability of Raw Milk. Foods, 10 (5), 991. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10050991
- Besagni, G., Cristiani, N., Croci, L., Guédon, G. R., Inzoli, F. (2021). Multi-scale evaluation of ejector performances: The influence of refrigerants and ejector design. Applied Thermal Engineering, 186, 116502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2020.116502
- Riaz, F., Yam, F. Z., Qyyum, M. A., Shahzad, M. W., Farooq, M., Lee, P. S., Lee, M. (2021). Direct Analytical Modeling for Optimal, On-Design Performance of Ejector for Simulating Heat-Driven Systems. Energies, 14 (10), 2819. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14102819
- Mahmoudian, J., Mazzelli, F., Milazzo, A., Malpress, R., Buttsworth, D. R. (2021). Experiments on water vapour condensation within supersonic nozzle flow generated by an impulse tunnel. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 134, 103473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmultiphaseflow.2020.103473
- Grazzini, G., Milazzo, A., Mazzelli, F. (2018). Ejectors for Efficient Refrigeration. Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-75244-0
- Milazzo, A., Rocchetti, A. (2015). Modelling of ejector chillers with steam and other working fluids. International Journal of Refrigeration, 57, 277–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrefrig.2015.05.015
- Sarevski, V. N., Sarevski, M. N. (2012). Characteristics Of R718 Thermocompression Refrigerating / Heat Pump Systems With Two-Phase Ejectors. International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference. Available at: https://docs.lib.purdue.edu/iracc/1214/
- Assari, M. R., Tabrizi, H. B., Beik, A. J. G., Shamesri, K. (2022). Numerical Study of Water-air Ejector using Mixture and Two-phase Models. International Journal of Engineering, 35 (2), 307–318. https://doi.org/10.5829/ije.2022.35.02b.06
- Topal, H. İ., Tol, H. İ., Kopaç, M., Arabkoohsar, A. (2022). Energy, exergy and economic investigation of operating temperature impacts on district heating systems: Transition from high to low-temperature networks. Energy, 251, 123845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2022.123845
- Khoshgoftar Manesh, M. H., Onishi, V. C. (2021). Energy, Exergy, and Thermo-Economic Analysis of Renewable Energy-Driven Polygeneration Systems for Sustainable Desalination. Processes, 9 (2), 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9020210
- Sharapov, S., Yevtushenko, S., Panchenko, V., Kozin, V., Ivchenko, O. (2022). Improving the efficiency of condensation installations of steam turbines by applying liquid-vapor ejector. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (8 (118)), 44–51. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.263331
- Sharapov, S., Krmela, J., Husiev, D., Verbytskiy, A., Bocko, J. (2024). Heat Utilization in Boiler Plants by Using Liquid-Vapor Jet Apparatus. Journal of Engineering Sciences, 11 (2), G1–G8. https://doi.org/10.21272/jes.2024.11(2).g1
- Sharapov, S., Mižáková, J., Husiev, D., Panchenko, V., Ivanov, V., Pavlenko, I., Židek, K. (2022). Vapor Overproduction Condition Monitoring in a Liquid–Vapor Ejector. Processes, 10 (11), 2383. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10112383
- Bergantini Botamede, B., Oliveira Salviano, L. (2023). Thermodynamic analysis of concentrated solar energy layouts integrated with combined power system. Applied Thermal Engineering, 229, 120618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2023.120618
- Szablowski, L., Morosuk, T. (2022). Advanced Exergy Analysis of Adiabatic Underwater Compressed Air Energy Storage System. Entropy, 25 (1), 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25010077
- Szablowski, L., Krawczyk, P., Wolowicz, M. (2021). Exergy Analysis of Adiabatic Liquid Air Energy Storage (A-LAES) System Based on Linde–Hampson Cycle. Energies, 14 (4), 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14040945
- Tashtoush, B., Songa, I., Morosuk, T. (2022). Exergoeconomic Analysis of a Variable Area Solar Ejector Refrigeration System under Hot Climatic Conditions. Energies, 15 (24), 9540. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15249540
- Elmorsy, L., Morosuk, T., Tsatsaronis, G. (2022). Comparative exergoeconomic evaluation of integrated solar combined-cycle (ISCC) configurations. Renewable Energy, 185, 680–691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2021.12.108
- Tashtoush, B., Morosuk, T., Chudasama, J. (2020). Exergy and Exergoeconomic Analysis of a Cogeneration Hybrid Solar Organic Rankine Cycle with Ejector. Entropy, 22 (6), 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22060702
- Elmorsy, L., Morosuk, T., Tsatsaronis, G. (2020). Exergy-Based Analysis and Optimization of an Integrated Solar Combined-Cycle Power Plant. Entropy, 22 (6), 655. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22060655
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Serhii Sharapov, Sviatoslav Yevtushenko, Anton Verbytskiy, Maksym Skydanenko, Serhii Khovanskyi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








