Optimization of Fe-Cr-Mn alloy composition as implant material for mechanical properties and corrosion resistance
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.341820Keywords:
Fe-Cr-Mn alloys, implant materials, microstructure, mechanical properties, corrosion resistanceAbstract
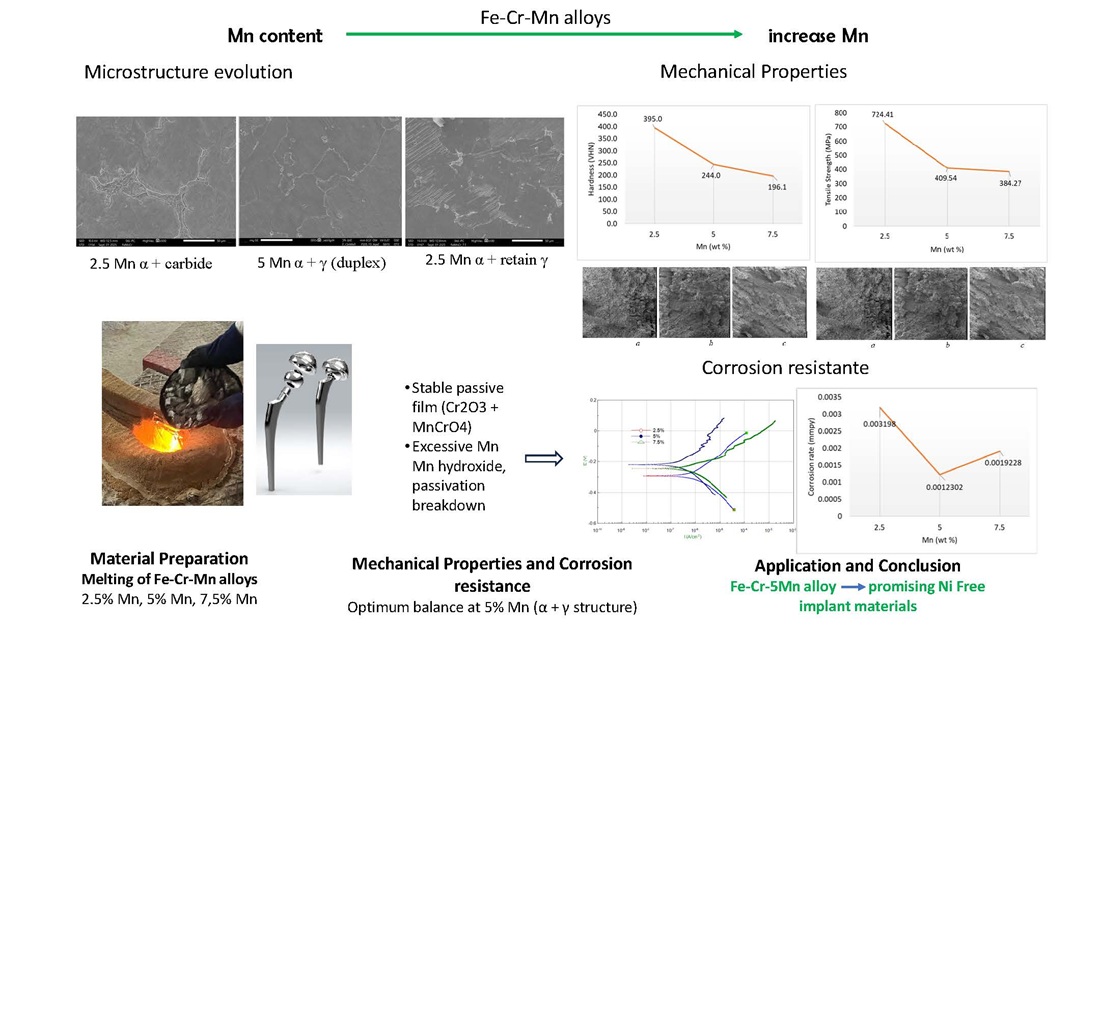
The object of this study is Fe-Cr-Mn stainless steel alloys containing 0.23–0.41 wt.% C and 17.59–18.36 wt.% Cr with varying Mn content. The development of nickel-free stainless steels addresses the drawbacks of conventional implant materials such as titanium alloys, Co-Cr alloys, and AISI 316L stainless steel, which often suffer from biocompatibility issues, toxicity, and mechanical incompatibility with bone. The Fe-Cr-Mn alloys were produced by high-frequency induction melting and subsequently tested for microstructure, mechanical, wear, and corrosion properties. SEM-EDS revealed a transition from ferritic structure (2.5% Mn) to duplex α+γ (5% Mn) and predominantly austenitic structure (7.5% Mn). Mechanical testing showed that hardness and tensile strength peaked at 2.5% Mn, while ductility and impact toughness improved with increasing Mn, reaching their highest values at 5% Mn. Wear resistance increased significantly at higher Mn levels due to the formation of stable tribo-oxides and the strengthening effect of the austenitic matrix. Electrochemical testing in 0.9% NaCl solution showed that Fe-18Cr-5Mn possessed the best corrosion resistance, attributed to the stability of its passive film, while excessive Mn (7.5%) caused passivation breakdown through Mn-hydroxide formation. Overall, Fe-18Cr-5Mn exhibited the best synergy between strength, toughness, wear resistance, and corrosion protection under physiological saline conditions, establishing it as a promising nickel-free stainless steel for next-generation biomedical implant materials
References
- Borgioli, F., Galvanetto, E., Bacci, T. (2021). Surface Modification of a Nickel-Free Austenitic Stainless Steel by Low-Temperature Nitriding. Metals, 11 (11), 1845. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11111845
- Pani, R., Behera, R. R., Roy, S. (2023). Corrosion Behaviour of Metallic Biomaterials in Physiological Environments. Handbook of Research on Corrosion Sciences and Engineering, 246–273. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-6684-7689-5.ch009
- Radice, S., Neto, M. Q., Fischer, A., Wimmer, M. A. (2021). Nickel‐free high‐nitrogen austenitic steel outperforms CoCrMo alloy regarding tribocorrosion in simulated inflammatory synovial fluids. Journal of Orthopaedic Research, 40 (6), 1397–1408. https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.25174
- Ansary, S., Mondal, S., Sekh, M., Haque, R., Haidar, S. (2022). Indigenous Production of Porous 316L through Powder Metallurgy and Investigation of their Mechanical Properties. Key Engineering Materials, 933, 32–41. https://doi.org/10.4028/p-2fqtl1
- Patnaik, L., Ranjan Maity, S., Kumar, S. (2020). Status of nickel free stainless steel in biomedical field: A review of last 10 years and what else can be done. Materials Today: Proceedings, 26, 638–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.12.205
- Xu, S., Gao, F., Han, J., Xiong, S., Duan, X., Zha, F., Yu, B. et al. (2022). Corrosion Behaviors of Fe-22Cr-16Mn-0.55N High-Nitrogen Austenitic Stainless Steel in 3.5% NaCl Solution. Coatings, 12 (11), 1769. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12111769
- Jiang, G., Wu, M., Yang, X., Wang, H., Zhu, Y. (2024). Effect of Mn addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of GX40CrNiSi25-12 austenitic heat resistant steel. China Foundry, 21 (3), 205–212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41230-024-3134-6
- Nayak, C., Anand, A., Kamboj, N., Kantonen, T., Kajander, K., Tupala, V. et al. (2024). Tribological behavior and biocompatibility of novel Nickel-Free stainless steel manufactured via laser powder bed fusion for biomedical applications. Materials & Design, 242, 113013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2024.113013
- Xu, N., Chen, G., Zhang, Q., Hu, H., Xu, G. (2025). Study on the Deformation Behavior and Mechanical Properties of Lightweight Economic Stainless Steels with Varying Al and Mn Contents. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 9 (7), 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9070206
- Patra, S., Agrawal, A., Mandal, A., Podder, A. S. (2021). Characteristics and Manufacturability of Duplex Stainless Steel: A Review. Transactions of the Indian Institute of Metals, 74 (5), 1089–1098. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-021-02278-7
- Li, Z., Luo, H., Hou, L., Zhao, Q., Wang, X., Chang, Y. (2025). Effect of Mn addition on the corrosion behavior of FeCrNiMn Si alloys in simulated seawater environment. Corrosion Science, 252, 112978. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2025.112978
- Hsu, K.-M., Chien, W.-L., Lin, C.-S. (2023). The improved stability and corrosion resistance of the passive film on Mn-containing FeCrNiCoMnx high entropy alloys by multiple pickling. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 962, 171141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.171141
- Wang, Z., Yan, Y., Wu, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhao, X., Su, Y., Qiao, L. (2023). Recent research progress on the passivation and selective oxidation for the 3d-transition-metal and refractory multi-principal element alloys. Npj Materials Degradation, 7 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41529-023-00410-0
- Kartikasari, R., Kadiman, S., Muhfidin, R., Aziz, I., Triyono, T. (2024). Development of Fe-Cr-C alloys with high Mn content for bone implant. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (12 (131)), 31–38. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.312442
- Kartikasari, R., Subardi, A., Muhfidin, R., Aziz, I., Effendy, M., Triyono, T., Diharjo, K. (2023). Development of Fe-13.8Cr-8.9Mn alloy for steel biomaterials. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6 (12 (126)), 6–15. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.293009
- Ladani, L., Palmieri, M. (2024). Review of the Use of Metals in Biomedical Applications: Biocompatibility, Additive Manufacturing Technologies, and Standards and Regulations. Metals, 14 (9), 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14091039
- Romanczuk-Ruszuk, E., Krawczyńska, A., Łukaszewicz, A., Józwik, J., Tofil, A., Oksiuta, Z. (2023). Bioactivity, Cytotoxicity, and Tribological Studies of Nickel-Free Austenitic Stainless Steel Obtained via Powder Metallurgy Route. Materials, 16 (24), 7637. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16247637
- Bosch, J., Martin, U., Aperador, W., Bastidas, J. M., Ress, J., Bastidas, D. M. (2021). Corrosion Behavior of High-Mn Austenitic Fe–Mn–Al–Cr–C Steels in NaCl and NaOH Solutions. Materials, 14 (2), 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14020425
- Jung, J., Ma, B. (2002). Pat. No. US8043446B2. High manganese duplex stainless steel having superior hot workabilities and method manufacturing thereof. Available at: https://patents.google.com/patent/US8043446B2/en
- Yu, K. P., Jiang, H., Xu, X. Y., Huang, M. X. (2024). Design of corrosion-resistant alloys for preventing oxidation-induced nanoscale Cr-depletion by inclusion engineering. Materials & Design, 244, 113146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2024.113146
- Eliaz, N. (2019). Corrosion of Metallic Biomaterials: A Review. Materials, 12 (3), 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030407
- Rybalchenko, O., Anisimova, N., Martynenko, N., Rybalchenko, G., Belyakov, A., Shchetinin, I. et al. (2023). Biocompatibility and Degradation of Fe-Mn-5Si Alloy after Equal-Channel Angular Pressing: In Vitro and In Vivo Study. Applied Sciences, 13 (17), 9628. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13179628
- Ribeiro, J. J. K., Turin, A. R., Nuñez de la Rosa, Y. E., Quadros, P. V. C. A., Calabokis, O. P., Lepienski, C. M. et al. (2023). Mechanical Characterization at Nanoscale of Austenite, Ferrite, and Sigma Phases via Hardness Measurement and Fretting Wear Behavior of a Duplex Stainless Steel. Metals, 13 (5), 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13050864
- Omiogbemi, I. M.-B., Yawas, D. S., Das, A., Afolayan, M. O., Dauda, E. T., Kumar, R. et al. (2022). Mechanical properties and corrosion behaviour of duplex stainless steel weldment using novel electrodes. Scientific Reports, 12 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-26974-6
- Liu, S., Ge, Y., Liu, H., Liu, J., Feng, Y., Chen, C., Zhang, F. (2022). Tensile Properties and Microstructure Evolutions of Low-Density Duplex Fe–12Mn–7Al–0.2C–0.6Si Steel. Materials, 15 (7), 2498. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15072498
- Yan, X., Wu, Y., Zhang, M., Liu, S., Sun, L., Feng, Y. (2022). Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Ferrite–Austenite Duplex Fe-Mn-Al-(Cu)-C Steel under Different Annealing Temperatures. Materials, 15 (22), 8271. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15228271
- Zhang, C., Bao, X., Hao, M., Chen, W., Zhang, D., Wang, D. et al. (2022). Hierarchical nano-martensite-engineered a low-cost ultra-strong and ductile titanium alloy. Nature Communications, 13 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-33710-1
- Du, C., Wang, X. (2025). Intergranular precipitation evolution and its effect on the impact toughness of Super304H austenitic stainless steel weld metal during long-term aging at 650 °C. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 36, 7304–7317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2025.04.312
- Misra, R. D. K. (2023). A perspective in the understanding of strength–toughness combination during processing of engineering ferrous alloys. Materials Technology, 38 (1). https://doi.org/10.1080/10667857.2023.2278000
- He, J., Lv, J., Song, Z., Wang, C., Feng, H., Wu, X. et al. (2023). Maintaining Excellent Mechanical Properties via Additive Manufacturing of Low-N 25Cr-Type Duplex Stainless Steel. Materials, 16 (22), 7125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16227125
- Maier, A., Rühr, M., Stephan, M., Frankl, S., Roth, S., Schmidt, M. (2023). Tailoring material properties of duplex stainless steel by DED-LB/M and in situ alloying with elemental powders. Journal of Laser Applications, 35 (4). https://doi.org/10.2351/7.0001119
- Ma, H., Zhao, Y., Feng, Y., Yu, Z., Sun, J., Song, H. et al. (2024). Effect of Mn content on corrosion and mechanical behaviors of Fe-based medium entropy alloy. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 30, 5632–5651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2024.04.246
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Ratna Kartikasari, Sugiarto Kadiman, Rivan Muhfidin, Ihwanul Aziz

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








