Selection of gelling agents to achieve high homogeneity of a concentrated product from quince (Cydonia Oblonga) fruits using graph theory
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.344558Keywords:
sol, gel, thixotropy, syneresis, xerogel, colloid, graph, vertices, edge, incidence, adjacencyAbstract
This study investigates the quality of a concentrated quince fruit product. Given the widespread use of concentrated fruit products, particularly quince jelly, in various climatic zones, as well as their potential as a medicinal and dietary product, assessing product quality using mathematical methods, particularly graph theory, is of interest in processing technology.
Quince fruits, with their rich chemical composition, stand out among other fruits with their pleasant aroma. These volatile components migrate into the finished product, even after the raw materials are processed. Quince jelly is obtained by concentrating the juice, resulting in the formation of a colloidal system. However, manufacturing the product using gel technology, or more accurately, sol-gel technology, is determined by the added ingredients and environmental parameters. The advantage of this technology is that the resulting product has a more homogeneous appearance and a pleasant taste. The viscosity of the resulting product varies little across grades, averaging 2.17∙104 mPa∙s, and its Valent strength is 400. In terms of material flows, the consumption per ton of finished product was 1,328 kg.
The structure of fruit jelly is formed by the addition of gelling agents to the juice. Therefore, this product is not considered the result of a strict sol-gel processing method, where the transition from sol to gel structure occurs through chemical reactions. In fruit jelly, the ingredients themselves create a three-dimensional network structure, but not a solid crystalline one. This network structure is formed by hydrolysis of pectin substances and the polycondensation of polygalacturonic acids, resulting in the formation of salt bridges.
References
- Ameen, S., Shaheer Akhtar, M., Jiménez-Suárez, A., Seisdedos, G. (Eds.) (2024). Nanotechnology and Nanomaterials Annual Volume 2024. Intechopen. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.115572
- Abdurakhmanov, E., Abdurakhmanov, I. Er., Begimkulov, J. N., Ismoilov, E. K., Kholmurzaev, F. F. (2023). Analytical chemistry zol-gel is produced on the basis of processes ammonia uses nanomaterials creation of selective gas sensors. European Journal of Emerging Technology and Discoveries, 1 (9), 24–31. Available at: https://europeanscience.org/index.php/1/article/view/341
- Nabizadeh, M., Nasirian, F., Li, X., Saraswat, Y., Waheibi, R., Hsiao, L. C., Bi, D. et al. (2024). Network physics of attractive colloidal gels: Resilience, rigidity, and phase diagram. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 121 (3). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2316394121
- Niu, Y., Fan, Y., Zhang, J. (2025). Progress and Challenge in the Risk Management of Food Additives. Journal of Food Protection, 88 (10), 100607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfp.2025.100607
- Mazur, L. M., Popova, I. V., Simurova, N. V., Sliva, Yu. V. (2014). Fiziko-himicheskie processy geleobrazovaniya pektinov v pishevyh tehnologiyah. Sahar, 1, 1–5. Available at: https://dspace.nuft.edu.ua/server/api/core/bitstreams/f403b104-d84d-4147-88a6-1716c8336bb5/content
- Wan-Mohtar, W. A. A. Q. I., Abdul Halim-Lim, S., Pillai Balamurugan, J., Mohd Saad, M. Z., Azizan, N. A. Z., Jamaludin, A. A., Ilham, Z. (2021). Effect of Sugar-Pectin-Citric Acid Pre-Commercialization Formulation on the Physicochemical, Sensory, and Shelf-Life Properties of Musa cavendish Banana Jam. Sains Malaysiana, 50 (5), 1329–1342. https://doi.org/10.17576/jsm-2021-5005-13
- Kastner, H., Kern, K., Wilde, R., Berthold, A., Einhorn-Stoll, U., Drusch, S. (2014). Structure formation in sugar containing pectin gels – Influence of tartaric acid content (pH) and cooling rate on the gelation of high-methoxylated pectin. Food Chemistry, 144, 44–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.06.127
- da Costa Amaral, S., Roux, D., Caton, F., Rinaudo, M., Barbieri, S. F., Meira Silveira, J. L. (2021). Extraction, characterization and gelling ability of pectins from Araçá (Psidium cattleianum Sabine) fruits. Food Hydrocolloids, 121, 106845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.106845
- Barros, F. C. N., da Silva, D. C., Sombra, V. G., Maciel, J. S., Feitosa, J. P. A., Freitas, A. L. P., de Paula, R. C. M. (2013). Structural characterization of polysaccharide obtained from red seaweed Gracilaria caudata (J Agardh). Carbohydrate Polymers, 92 (1), 598–603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.09.009
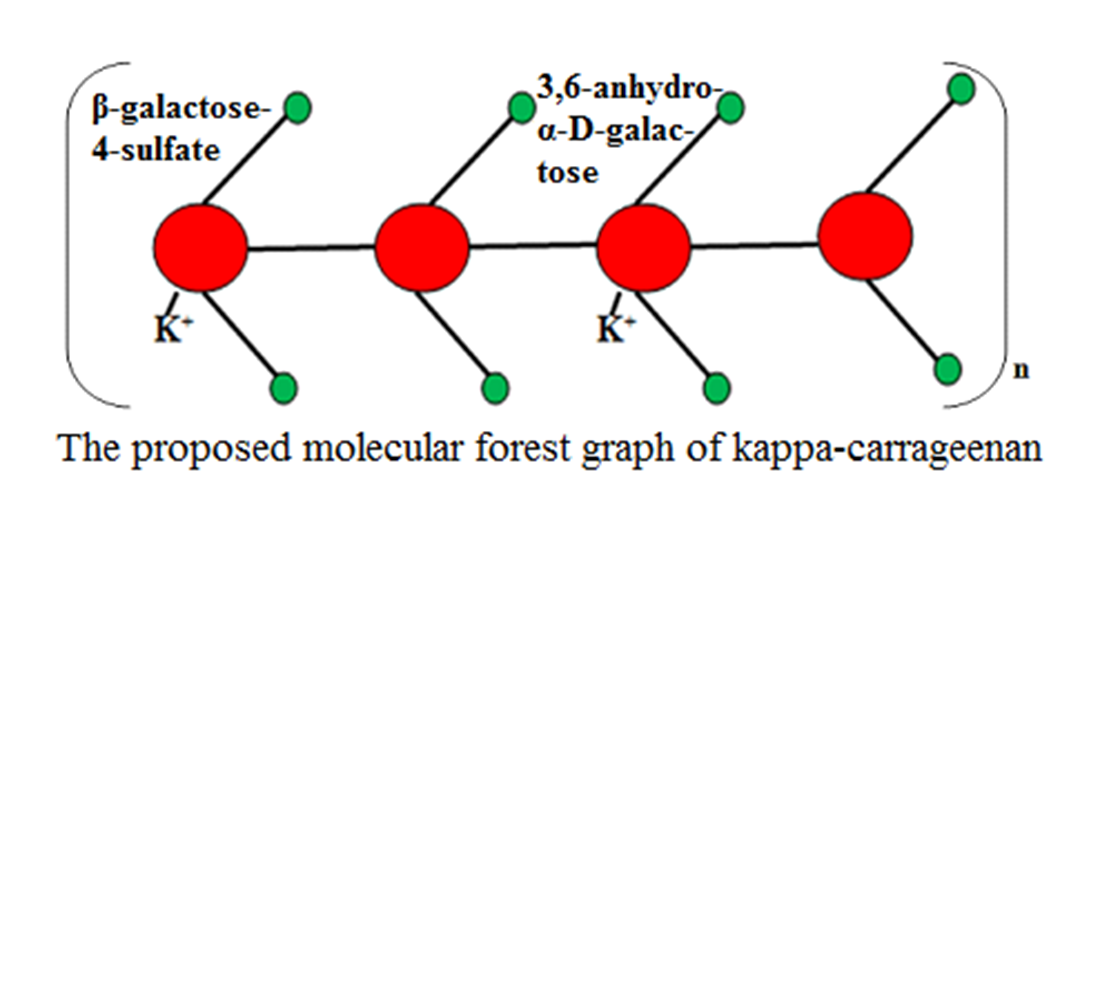
- Ciancia, M., Matulewicz, M. C., Tuvikene, R. (2020). Structural Diversity in Galactans From Red Seaweeds and Its Influence on Rheological Properties. Frontiers in Plant Science, 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.559986
- Gubsky, S. M., Muzyka, S. M., Foshan, A. L., Evlash, V. V., Kalugin, O. N. (2018). Reologic properties of aqueous solutions of agar and gelatine for confectionery. Kharkiv University Bulletin. Chemical Series, 31, 64–78. https://doi.org/10.26565/2220-637x-2018-31-06
- Bui, T. N. T. V. (2019). Structure, Rheological Properties and Connectivity of Gels Formed by Carrageenan Extracted from Different Red Algae Species. Organic chemistry. Le Mans Université. Available at: https://theses.hal.science/tel-02077051/file/2019LEMA1007.pdf
- Kravchenko, A. O., Anastyuk, S. D., Glazunov, V. P., Sokolova, E. V., Isakov, V. V., Yermak, I. M. (2020). Structural characteristics of carrageenans of red alga Mastocarpus pacificus from sea of Japan. Carbohydrate Polymers, 229, 115518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115518
- Wei, Y., Lin, S., Lin, W., Nie, Y., Zou, X., Zheng, Y. et al. (2025). The Impact of κ‐Carrageenan on the Textural, Microstructural, and Molecular Properties of Heat‐Induced Egg White Protein Gel. Food Science & Nutrition, 13 (8). https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.70541
- Zhang, X., Yousaf, S., Naeem, A., Tawfiq, F. M., Aslam, A. (2024). Analyzing topological descriptors of guar gum and its derivatives for predicting physical properties in carbohydrates. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 253, 105203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemolab.2024.105203
- Qurratulain, M., Asha, S. B., Waseem, A. H. (2024). A Review of Graph Theory and Its Applications Across Various Disciplines. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET), 11 (03). Available at: https://www.irjet.net/archives/V11/i3/IRJET-V11I325.pdf
- Huang, R., Naeem, M., Siddiqui, M. K., Rauf, A., Rashid, M. U., Ali, M. A. (2024). Statistical analysis of topological indices in linear phenylenes for predicting physicochemical properties using algorithms. Scientific Reports, 14 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-70187-y
- Liu, S., Huang, S., Li, L. (2016). Thermoreversible gelation and viscoelasticity of κ-carrageenan hydrogels. Journal of Rheology, 60 (2), 203–214. https://doi.org/10.1122/1.4938525
- Zabashta, Y. F., Kovalchuk, V. I., Svechnikova, O. S,. Vergun, L. Y., Bulavin, L. A. (2024). The sol-gel transition in hydrogels as the first-order phase transition. Ukrainian Journal Of Physics, 69 (6), 409–416. https://doi.org/10.15407/ujpe69.6.409
- Ghosh, D., Győri, E., Paulos, A., Salia, N., Zamora, O. (2020). The maximum Wiener index of maximal planar graphs. Journal of Combinatorial Optimization, 40 (4), 1121–1135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-020-00655-4
- Min, W., Liu, C., Xu, L., Jiang, S. (2022). Applications of knowledge graphs for food science and industry. Patterns, 3 (5), 100484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patter.2022.100484
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Melahet Ismayilova, Mushfiq Khalilov, Mehriban Maharramova, Maryam Mammadaliyeva, Elza Omarova, Ahad Nabiyev, Afet Gasimova

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








