Effect of the brass waste recycling process on mechanical properties with investment casting for gear materials
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.299764Keywords:
environmentally friendly, gear manufacture, investment casting, mechanical properties, brass recyclingAbstract
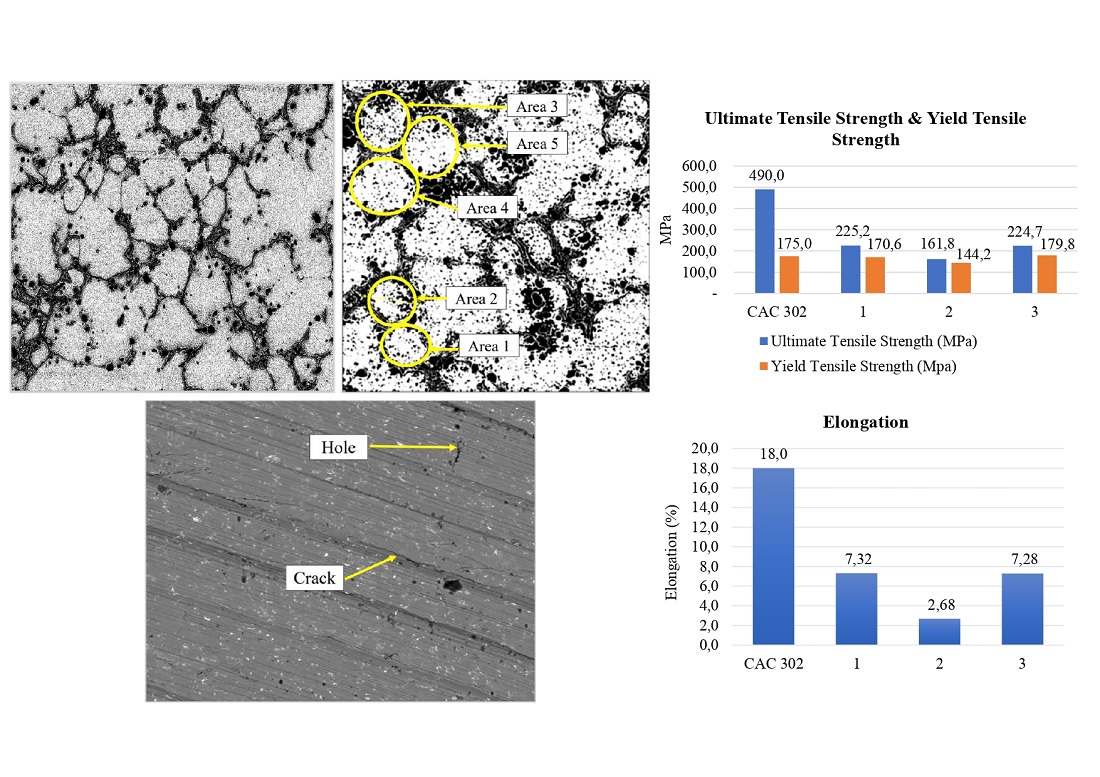
This study is an experimental research to analyze the characteristics and mechanical properties of the casting process of recycled brass alloy, which will be used as a material for gears. Currently, the remaining production and waste from brass alloys continue to increase. Another thing is the increase in the need for brass gears, so environmentally friendly material engineering is needed to provide good quality and efficient energy use, especially during the casting process. The casting process uses an electric furnace that melts brass alloys at 526 up to 900 °C within 1 hour and molds to make test specimens. The results of microstructural testing for grain size in recycled brass alloys range from 74.63 μm to 84.57 μm. The maximum tensile strength produced is up to 225.2 MPa, the maximum yield strength is up to 179.8 MPa, and the maximum elongation is up to 7.3 %. The roughness of recycled brass alloys has a maximum Ra value (average roughness) of up to 0.836 μm. Validation was carried out by comparing the mechanical properties of CAC 302 brass products and the study results. The data shows that recycled brass's maximum yield strength value is 179.8 MPa and CAC 302 brass material is 175 MPa, but for the ultimate tensile strength value, the value of recycled brass is far below CAC 302 products. These results can be a consideration for the industry to be able to use recycled brass alloys for gear products because the yield strength value is not far from CAC 302 brass products. The impact result of this study produces recycled brass alloys that are environmentally friendly, efficient in smelting energy consumption, and have good yield strength. The results of this research can benefit the manufacture of gear components made of brass alloys.
References
- X. Li, B. Ma, C. Wang, and Y. Chen, “Morphology evolution and agglomeration mechanism of Fe5Si3 precipitated phase after Fe–Si microalloying and its effect on the properties of brasses,” Mater. Charact., vol. 205, no. August, p. 113261, 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2023.113261.
- W. Liu et al., “Corrosion behavior of silica-alumina refractories for scrap brass smelter linings,” J. Clean. Prod., vol. 370, no. August, p. 133600, 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133600.
- X. Li, B. Ma, C. Wang, W. Liu, B. Zhang, and Y. Chen, “Action and segregation mechanism of Fe-rich phase in as-cast brass with different Fe contents,” J. Mol. Liq., vol. 371, p. 121161, 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2022.121161.
- P. Asadi, M. Akbari, A. Armani, M. R. M. Aliha, M. Peyghami, and T. Sadowski, “Recycling of brass chips by sustainable friction stir extrusion,” J. Clean. Prod., vol. 418, no. June, p. 138132, 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.138132.
- Z. Xia, X. Zhang, X. Huang, S. Yang, Y. Chen, and L. Ye, “Hydrometallurgical stepwise recovery of copper and zinc from smelting slag of waste brass in ammonium chloride solution,” Hydrometallurgy, vol. 197, no. August, p. 105475, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2020.105475.
- P. Stavroulakis, A. I. Toulfatzis, G. A. Pantazopoulos, and A. S. Paipetis, “Machinable Leaded and Eco-Friendly Brass Alloys for High Performance Manufacturing Processes: A Critical Review,” Metals (Basel)., vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 1–31, 2022, doi: 10.3390/met12020246.
- A. Rohrmoser and M. Merklein, “Influence of Metal Flank Hardness of Machined and Cold Forged Gears on Wear within a Metal-Polyamide Gear Pair and Targeted Process Adaptation,” J. Mater. Eng. Perform., vol. 32, no. 4, pp. 1984–2006, 2023, doi: 10.1007/s11665-022-07251-z.
- K. D. Mohapatra, M. P. Satpathy, and S. K. Sahoo, “Comparison of optimization techniques for MRR and surface roughness in wire EDM process for gear cutting,” Int. J. Ind. Eng. Comput., vol. 8, no. 2, pp. 251–262, 2016, doi: 10.5267/j.ijiec.2016.9.002.
- A. Rohrmoser and M. Merklein, “Influence of Metal Flank Hardness of Machined and Cold Forged Gears on Wear within a Metal-Polyamide Gear Pair and Targeted Process Adaptation,” J. Mater. Eng. Perform., vol. 32, no. 4, pp. 1984–2006, 2023, doi: 10.1007/s11665-022-07251-z.
- Y. F. Du, B. Han, and H. Li, “Experimental and Numberical Simulation of Sma-Friction Damper Based on Gear Mechanism,” Gongcheng Lixue/Engineering Mech., vol. 39, no. 12, pp. 190–201, 2022, doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2021.07.0564.
- S. K. Chaubey, N. K. Jain, and K. Gupta, “A comprehensive investigation on development of lightweight aluminium miniature gears by thermoelectric erosion machining process,” Micromachines, vol. 12, no. 10, 2021, doi: 10.3390/mi12101230.
- R. Nur, M. Muas, Apollo, and S. Risal, “Effect of Current and Wire Speed on Surface Roughness in the manufacturing of Straight Gear using Wire-cut EDM Process,” IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng., vol. 619, no. 1, 2019, doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/619/1/012002.
- S. Memar, M. Azadi, and H. abdoos, “An evaluation on microstructure, wear, and compression behavior of Al2O3 /brass matrix nanocomposites fabricated by stir casting method,” Mater. Today Commun., vol. 34, no. December 2022, p. 105130, 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.105130.
- C. Li, T. Zhang, Y. Liu, and J. Liu, “Effect of process parameters on surface quality and bonding quality of brass cladding copper stranded wire prepared by continuous pouring process for clad,” J. Mater. Res. Technol., vol. 26, pp. 8025–8035, 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2023.09.140.
- L. [Amaral 2018] Amaral, R. Quinta, T. E. Silva, R. M. B. Soares, S. D. Castellanos, and A. M. P. de Jesus, “Effect of lead on the machinability of brass alloys using polycrystalline diamond cutting tools,” J. Strain Anal. Eng. Des., vol. 53, no. 8, pp. 602–615, 2018, doi: 10.1177/0309324718796384.
- A. Vazdirvanidis, A. Rikos, A. I. Toulfatzis, and G. A. Pantazopoulos, “Electron Backscatter Diffraction (EBSD) Analysis of Machinable Lead-Free Brass Alloys: Connecting Texture with Fracture,” Metals (Basel)., vol. 12, no. 4, 2022, doi: 10.3390/met12040569.
- C. Yang et al., “High-strength and free-cutting silicon brasses designed via the zinc equivalent rule,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A, vol. 723, no. December 2017, pp. 296–305, 2018, doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2018.03.055.
- R. Li, Z. Xiao, Z. Li, X. Meng, and X. Wang, “Work Hardening Behavior and Microstructure Evolution of a Cu-Ti-Cr-Mg Alloy during Room Temperature and Cryogenic Rolling,” Materials (Basel)., vol. 16, no. 1, 2023, doi: 10.3390/ma16010424.
- Ö. [Semih 2023] Semih and A. Recep, “Investigation of microstructure, machinability, and mechanical properties of new-generation hybrid lead-free brass alloys,” High Temp. Mater. Process., vol. 42, no. 1, 2023, doi: 10.1515/htmp-2022-0263.
- M. E. Moussa, M. Amin, and K. M. Ibrahim, “Effect of Ultrasonic Vibration Treatment on Microstructure, Tensile Properties, Hardness and Wear Behaviour of Brass Alloy,” International Journal of Metalcasting, vol. 17, no. 1. pp. 305–313, 2023. doi: 10.1007/s40962-021-00748-8.
- J. Choucri et al., “Corrosion behavior and susceptibility to stress corrosion cracking of leaded and lead-free brasses in simulated drinking water,” Materials (Basel)., vol. 15, no. 1, 2022, doi: 10.3390/ma15010144.
- C. Li, T. Zhang, Y. Liu, and J. Liu, “Effect of process parameters on surface quality and bonding quality of brass cladding copper stranded wire prepared by continuous pouring process for clad,” J. Mater. Res. Technol., vol. 26, pp. 8025–8035, 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2023.09.140.
- TAE SUNG Industrial, “High Strength Brass Casting - Tae-Sung-Specification.pdf.pdf.” p. 1, 2024.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Erwin Erwin, Didik Sugiyanto, Danny Faturahman, Yefri Chan, Husen Asbanu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








