Determining epidemiological patterns in disease identification using mathematical models on machine learning based multilayer structures
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.310522Keywords:
SEIR mathematical models, clustering, epidemiology, multilayer networks, machine learningAbstract
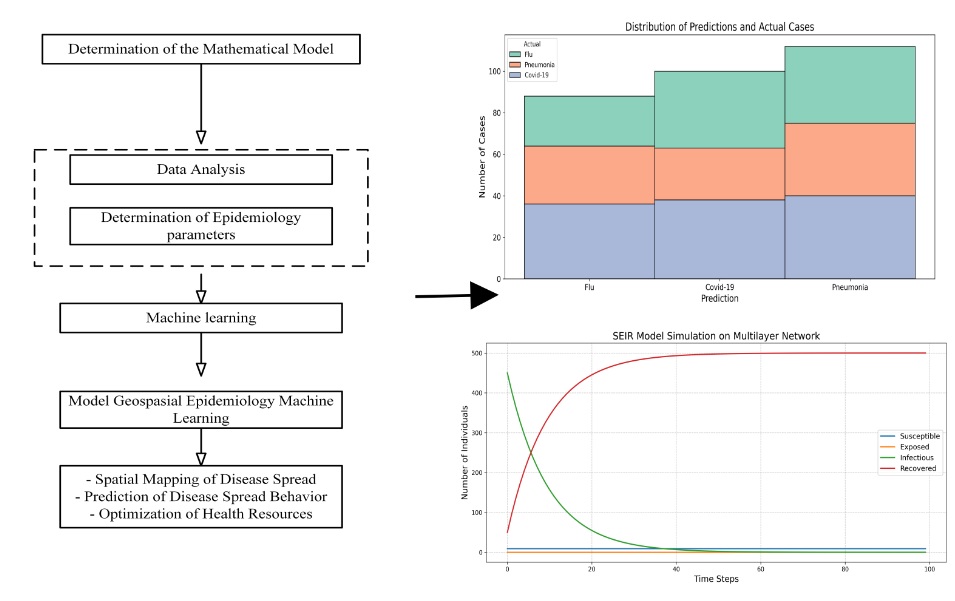
The object of the study is epidemiological grouping using the SEIR mathematical model on a machine learning-based multilayer network. The problems in this research are related to managing epidemiological data on a large scale to determine disease patterns and identification such as the number of recovered cases, number of infected cases and number of deaths and demographic factors. In the process, traditional methods make it difficult to carry out processes such as determining patterns and identifying diseases. So, it is necessary to use machine learning and the SEIR (Susceptible-Exposed-Infectious-Recovered) mathematical model which can be integrated with multilayer networks to increase accuracy and effectiveness in identifying diseases and determining patterns. The results obtained from this research are a model that can identify and determine patterns of disease spread in large-scale epidemiological data. In its application, the SEIR mathematical model combined into a social layer and an environmental layer in a multilayer network. This research is research with a level of novelty in the application of the SEIR mathematical model to multilayer networks and machine learning so that the model formed can be used to view the distribution of epidemiological data for disease-related information. Machine learning aims to process large-scale data in minimal time resulting in clustering and identification of diseases such as flu, Covid-19 and pneumonia. This research has an accuracy of 94 % using the MAPE evaluation technique. It is hoped that the resulting model can be used in the world of health for disease mapping in certain areas as a reference for mitigating the spread of disease
References
- Wu, F., Wu, T., Yuce, M. R. (2019). Design and Implementation of a Wearable Sensor Network System for IoT-Connected Safety and Health Applications. 2019 IEEE 5th World Forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT). https://doi.org/10.1109/wf-iot.2019.8767280
- Liu, J., Zhao, Z., Ji, J., Hu, M. (2020). Research and application of wireless sensor network technology in power transmission and distribution system. Intelligent and Converged Networks, 1 (2), 199–220. https://doi.org/10.23919/icn.2020.0016
- Swamy, S. N., Jadhav, D., Kulkarni, N. (2017). Security threats in the application layer in IOT applications. 2017 International Conference on I-SMAC (IoT in Social, Mobile, Analytics and Cloud) (I-SMAC). https://doi.org/10.1109/i-smac.2017.8058395
- Shivalingagowda, C., Ahmad, H., Jayasree, P. V. Y., Sah, D. K. (2021). Wireless Sensor Network Routing Protocols Using Machine Learning. Architectural Wireless Networks Solutions and Security Issues, 99–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-0386-0_7
- Khutsoane, O., Isong, B., Gasela, N., Abu-Mahfouz, A. M. (2020). WaterGrid-Sense: A LoRa-Based Sensor Node for Industrial IoT Applications. IEEE Sensors Journal, 20 (5), 2722–2729. https://doi.org/10.1109/jsen.2019.2951345
- Wang, A., Dara, R., Yousefinaghani, S., Maier, E., Sharif, S. (2023). A Review of Social Media Data Utilization for the Prediction of Disease Outbreaks and Understanding Public Perception. Big Data and Cognitive Computing, 7 (2), 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc7020072
- Hajiakhoond Bidoki, N., Mantzaris, A. V., Sukthankar, G. (2019). An LSTM Model for Predicting Cross-Platform Bursts of Social Media Activity. Information, 10 (12), 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/info10120394
- Ertam, F., Kilincer, I. F., Yaman, O., Sengur, A. (2020). A New IoT Application for Dynamic WiFi based Wireless Sensor Network. 2020 International Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEE). https://doi.org/10.1109/icee49691.2020.9249771
- Yahya, O. H., Alrikabi, H., Aljazaery, I. A. (2020). Reducing the Data Rate in Internet of Things Applications by Using Wireless Sensor Network. International Journal of Online and Biomedical Engineering (IJOE), 16 (03), 107–https://doi.org/10.3991/ijoe.v16i03.13021
- Mejjaouli, S., Babiceanu, R. F. (2015). RFID-wireless sensor networks integration: Decision models and optimization of logistics systems operations. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 35, 234–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmsy.2015.02.005
- You, G., Zhu, Y. (2020). Structure and Key Technologies of Wireless Sensor Network. 2020 Cross Strait Radio Science & Wireless Technology Conference (CSRSWTC). https://doi.org/10.1109/csrswtc50769.2020.9372727
- Taherdoost, H. (2023). Enhancing Social Media Platforms with Machine Learning Algorithms and Neural Networks. Algorithms, 16 (6), 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/a16060271
- Gutierrez-Osorio, C., González, F. A., Pedraza, C. A. (2022). Deep Learning Ensemble Model for the Prediction of Traffic Accidents Using Social Media Data. Computers, 11 (9), 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers11090126
- Huang, J.-Y., Lee, W.-P., Lee, K.-D. (2022). Predicting Adverse Drug Reactions from Social Media Posts: Data Balance, Feature Selection and Deep Learning. Healthcare, 10 (4), 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10040618
- Regulski, K., Opaliński, A., Swadźba, J., Sitkowski, P., Wąsowicz, P., Kwietniewska-Śmietana, A. (2024). Machine Learning Prediction Techniques in the Optimization of Diagnostic Laboratories’ Network Operations. Applied Sciences, 14 (6), 2429. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14062429
- Ghostine, R., Gharamti, M., Hassrouny, S., Hoteit, I. (2021). An Extended SEIR Model with Vaccination for Forecasting the COVID-19 Pandemic in Saudi Arabia Using an Ensemble Kalman Filter. Mathematics, 9 (6), 636. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9060636
- Aljohani, A. (2023). Predictive Analytics and Machine Learning for Real-Time Supply Chain Risk Mitigation and Agility. Sustainability, 15 (20), 15088. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152015088
- Sánchez Lasheras, F. (2021). Predicting the Future-Big Data and Machine Learning. Energies, 14 (23), 8041. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14238041
- He, Z., Yu, J., Gu, T., Yang, D. (2024). Query execution time estimation in graph databases based on graph neural networks. Journal of King Saud University - Computer and Information Sciences, 36 (4), 102018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2024.102018
- Zhu, L., Zhang, H., Bai, L. (2024). Hierarchical pattern-based complex query of temporal knowledge graph. Knowledge-Based Systems, 284, 111301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2023.111301
- Saleem, F., AL-Ghamdi, A. S. A.-M., Alassafi, M. O., AlGhamdi, S. A. (2022). Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Mathematical Models to Analyze Forecasting and Epidemiology of COVID-19: A Systematic Literature Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19 (9), 5099. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19095099
- Gopal, K., Lee, L. S., Seow, H.-V. (2021). Parameter Estimation of Compartmental Epidemiological Model Using Harmony Search Algorithm and Its Variants. Applied Sciences, 11 (3), 1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11031138
- Xu, Z., Qian, M. (2023). Predicting Popularity of Viral Content in Social Media through a Temporal-Spatial Cascade Convolutional Learning Framework. Mathematics, 11 (14), 3059. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11143059
- Abu-Salih, B., Al-Tawil, M., Aljarah, I., Faris, H., Wongthongtham, P., Chan, K. Y., Beheshti, A. (2021). Relational Learning Analysis of Social Politics using Knowledge Graph Embedding. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 35 (4), 1497–1536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10618-021-00760-w
- Malozyomov, B. V., Martyushev, N. V., Sorokova, S. N., Efremenkov, E. A., Valuev, D. V., Qi, M. (2024). Analysis of a Predictive Mathematical Model of Weather Changes Based on Neural Networks. Mathematics, 12 (3), 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12030480
- Shafqat, W., Byun, Y.-C. (2019). Topic Predictions and Optimized Recommendation Mechanism Based on Integrated Topic Modeling and Deep Neural Networks in Crowdfunding Platforms. Applied Sciences, 9 (24), 5496. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9245496
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Riah Ukur Ginting, Muhammad Zarlis, Poltak Sihombing, Syahril Efendi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








