Удосконалення алгоритму Лейдена для виявлення інфлюенсерів
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.315180Ключові слова:
інфлюенсер, граф, розфарбування, Лувен, Лейден, оптимізація, центральність, спільнота, Garuda IndonesiaАнотація
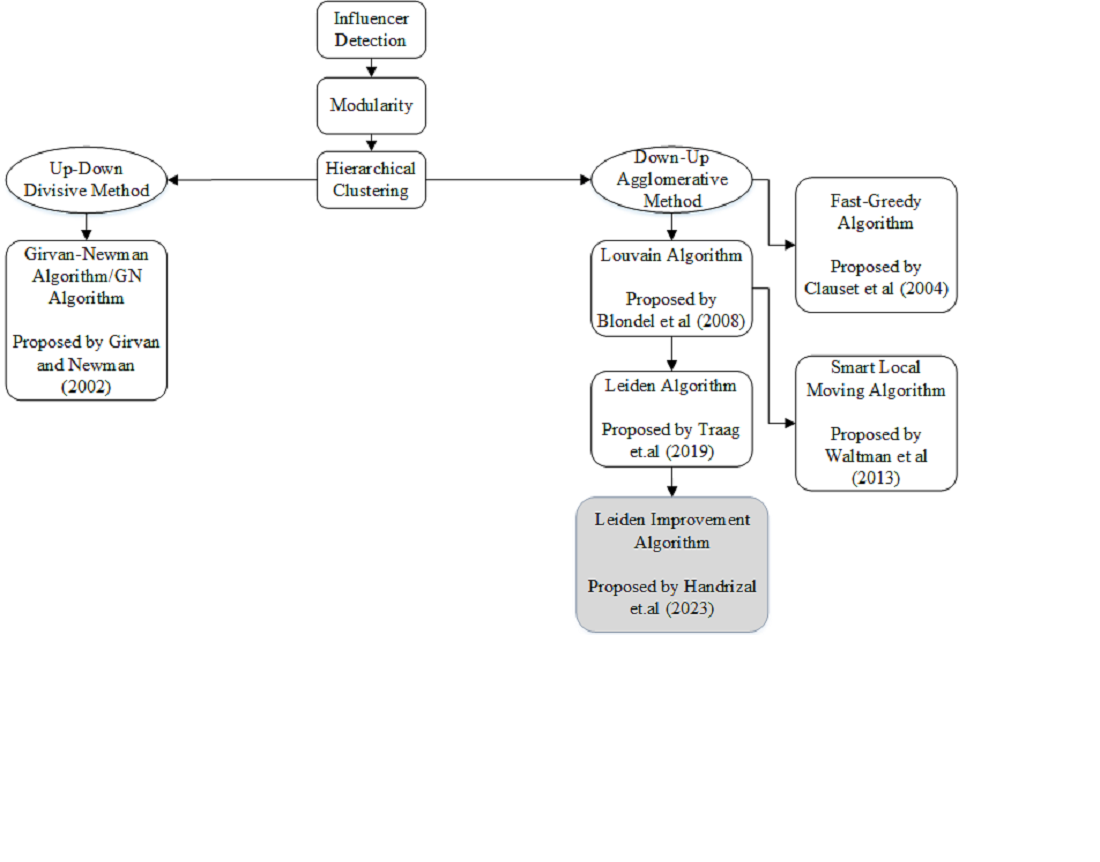
Інфлюенсер – це той, хто має здатність переконати велику кількість людей вжити певних дій, незалежно від місця та часу. Роль інфлюенсерів, особливо на платформах соціальних мереж, значно зросла. Одним з поширених інструментів, що використовується бізнесом сьогодні, є групування підписників. Однак цей інструмент обмежений виявленням інфлюенсерів лише на основі взаємної підписки, що підкреслює необхідність більш удосконаленого підходу до виявлення інфлюенсерів. У цьому дослідженні пропонується новий метод, що поєднує алгоритм розфарбування Лейдена з центральністю за ступенем для виявлення інфлюенсерів. Даний підхід використовує мережевий аналіз для визначення закономірностей та взаємозв'язків у великих наборах даних. Спершу алгоритм розфарбування Лейдена поділяє мережу на різні спільноти, які вважаються потенційними спільнотами інфлюенсерів. Потім центральність за ступенем підсилює цей процес за рахунок визначення тісно пов’язаних вузлів, що вказують на інфлюенсерів. Запропонований метод був перевірений на основі даних, отриманих з Twitter (X) з ключовим словом «GarudaIndonesia». Процес збору даних здійснювався за допомогою інструменту Tweet Harvest, у результаті чого отримано набір даних обсягом 22,623 рядки. Набір даних був перевірений за трьома сценаріями: перший з 1000 рядками, другий з 2000 рядками і третій з 5000 рядками. Запропонований метод порівнювався з методом розфарбування Лувена, що показало збільшення значення модульності алгоритму розфарбування Лейдена на 0,0240. Це збільшення демонструє здатність методу Лейдена досягти більш оптимального поділу мережі. Крім того, алгоритм розфарбування Лейдена скоротив час обробки на 14,85 секунди порівняно з методом Лувена, що підкреслює його більш високу продуктивність. Це особливо важливо у випадках застосування, що вимагають швидких результатів, зокрема в аналізі великих обсягів даних. Врешті, алгоритм Лейдена дозволив скоротити кількість спільнот на 1149, створивши більш просту та організовану структуру спільнот, що полегшує та підвищує ефективність аналізу
Посилання
- Chen, C.-W., Nguyen, D. T. T., Chih, M., Chen, P.-Y. (2024). Fostering YouTube followers’ stickiness through social contagion: The role of digital influencer’ characteristics and followers’ compensation psychology. Computers in Human Behavior, 158, 108304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2024.108304
- Laor, T. (2024). Do micro-celebrities preserve social roles? Differences between secular and religious female Instagram lifestyle influencers. Technology in Society, 78, 102642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2024.102642
- Kurniasari, F., Prihanto, J. N., Andre, N. (2023). Identifying determinant factors influencing user’s behavioral intention to use Traveloka Paylater. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2 (13 (122)), 52–61. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.275735
- Deng, F., Tuo, M., Chen, S., Zhang, Z. (2024). Born for marketing? The effects of virtual versus human influencers on brand endorsement effectiveness: The role of advertising recognition. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 80, 103904. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2024.103904
- Wang, Z.-Y., Zhang, C.-P., Othman Yahya, R. (2024). High-quality community detection in complex networks based on node influence analysis. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 182, 114849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2024.114849
- Morisada, M., Miwa, Y., Dahana, W. D. (2019). Identifying valuable customer segments in online fashion markets: An implication for customer tier programs. Electronic Commerce Research and Applications, 33, 100822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elerap.2018.100822
- Abdelkader, O. A. (2023). ChatGPT’s influence on customer experience in digital marketing: Investigating the moderating roles. Heliyon, 9 (8), e18770. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18770
- Tataryntseva, Y., Pushkar, O., Druhova, O., Osypova, S., Makarenko, A., Mordovtsev, O. (2022). Economic evaluation of digital marketing management at the enterprise. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2 (13 (116)), 24–30. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2022.254485
- Armutcu, B., Tan, A., Amponsah, M., Parida, S., Ramkissoon, H. (2023). Tourist behaviour: The role of digital marketing and social media. Acta Psychologica, 240, 104025. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actpsy.2023.104025
- Vasylyshyna, L., Yahelska, K., Aldankova, H., Liashuk, K. (2024). Development of marketing research technologies as the basis of a socially responsible marketing strategy. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (13 (131)), 76–85. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.312227
- Novytska, I., Chychkalo-Kondratska, I., Chyzhevska, M., Sydorenko-Melnyk, H., Tуtarenko, L. (2021). Digital Marketing in the System of Promotion of Organic Products. WSEAS TRANSACTIONS ON BUSINESS AND ECONOMICS, 18, 524–530. https://doi.org/10.37394/23207.2021.18.53
- Vrontis, D., Makrides, A., Christofi, M., Thrassou, A. (2021). Social media influencer marketing: A systematic review, integrative framework and future research agenda. International Journal of Consumer Studies, 45 (4), 617–644. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijcs.12647
- Peter, M. K., Dalla Vecchia, M. (2020). The Digital Marketing Toolkit: A Literature Review for the Identification of Digital Marketing Channels and Platforms. New Trends in Business Information Systems and Technology, 251–265. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-48332-6_17
- Veleva, S. S., Tsvetanova, A. I. (2020). Characteristics of the digital marketing advantages and disadvantages. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 940 (1), 012065. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/940/1/012065
- Khanom, M. T. (2023). Using social media marketing in the digital era: A necessity or a choice. International Journal of Research in Business and Social Science (2147- 4478), 12 (3), 88–98. https://doi.org/10.20525/ijrbs.v12i3.2507
- Cai, Y., Wang, H., Ye, H., Jin, Y., Gao, W. (2023). Depression detection on online social network with multivariate time series feature of user depressive symptoms. Expert Systems with Applications, 217, 119538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2023.119538
- Abdelhamid, S., Aly, M., Katz, A. (2020). Harvesting tweets for a better understanding of Engineering Students’ First-Year Experiences. 2020 First-Year Engineering Experience Proceedings. https://doi.org/10.18260/1-2--35771
- Blondel, V. D., Guillaume, J.-L., Lambiotte, R., Lefebvre, E. (2008). Fast unfolding of communities in large networks. Journal of Statistical Mechanics: Theory and Experiment, 2008 (10), P10008. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-5468/2008/10/p10008
- Traag, V. A., Waltman, L., van Eck, N. J. (2019). From Louvain to Leiden: guaranteeing well-connected communities. Scientific Reports, 9 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-41695-z
- De Meo, P., Ferrara, E., Fiumara, G., Provetti, A. (2011). Generalized Louvain method for community detection in large networks. 2011 11th International Conference on Intelligent Systems Design and Applications, 88–93. https://doi.org/10.1109/isda.2011.6121636
- Zhang, J., Fei, J., Song, X., Feng, J. (2021). An Improved Louvain Algorithm for Community Detection. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2021, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/1485592
- Zhang, W. (2022). Improving commuting zones using the Louvain community detection algorithm. Economics Letters, 219, 110827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econlet.2022.110827
- Gilad, G., Sharan, R. (2023). From Leiden to Tel-Aviv University (TAU): exploring clustering solutions via a genetic algorithm. PNAS Nexus, 2 (6). https://doi.org/10.1093/pnasnexus/pgad180
- Bhowmick, A. K., Meneni, K., Danisch, M., Guillaume, J.-L., Mitra, B. (2020). LouvainNE. Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining. https://doi.org/10.1145/3336191.3371800
- Roghani, H., Bouyer, A. (2023). A Fast Local Balanced Label Diffusion Algorithm for Community Detection in Social Networks. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 35 (6), 5472–5484. https://doi.org/10.1109/tkde.2022.3162161
- Gupta, S. K., Singh, Dr. D. P. (2023). CBLA: A Clique Based Louvain Algorithm for Detecting Overlapping Community. Procedia Computer Science, 218, 2201–2209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2023.01.196
- Singh, D., Garg, R. (2022). NI-Louvain: A novel algorithm to detect overlapping communities with influence analysis. Journal of King Saud University - Computer and Information Sciences, 34 (9), 7765–7774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2021.07.006
- Hairol Anuar, S. H., Abas, Z. A., Yunos, N. M., Mohd Zaki, N. H., Hashim, N. A., Mokhtar, M. F. et al. (2021). Comparison between Louvain and Leiden Algorithm for Network Structure: A Review. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2129 (1), 012028. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/2129/1/012028
- Mardiansyah, H., Suwilo, S., Nababan, E. B., Efendi, S. (2023). Community Clustering on Fraud Transactions Applied the Louvain-Coloring Algorithm. International Journal of Electronics and Telecommunications, 593–598. https://doi.org/10.24425/ijet.2023.146512
- Sahu, S., Kothapalli, K., Banerjee, D. S. (2024). Fast Leiden Algorithm for Community Detection in Shared Memory Setting. Proceedings of the 53rd International Conference on Parallel Processing, 11–20. https://doi.org/10.1145/3673038.3673146
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2025 Handrizal Handrizal, Poltak Sihombing, Erna Budhiarti Nababan, Mohammad Andri Budiman

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.
Ліцензійний договір – це документ, в якому автор гарантує, що володіє усіма авторськими правами на твір (рукопис, статтю, тощо).
Автори, підписуючи Ліцензійний договір з ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР», мають усі права на подальше використання свого твору за умови посилання на наше видання, в якому твір опублікований. Відповідно до умов Ліцензійного договору, Видавець ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР» не забирає ваші авторські права та отримує від авторів дозвіл на використання та розповсюдження публікації через світові наукові ресурси (власні електронні ресурси, наукометричні бази даних, репозитарії, бібліотеки тощо).
За відсутності підписаного Ліцензійного договору або за відсутністю вказаних в цьому договорі ідентифікаторів, що дають змогу ідентифікувати особу автора, редакція не має права працювати з рукописом.
Важливо пам’ятати, що існує і інший тип угоди між авторами та видавцями – коли авторські права передаються від авторів до видавця. В такому разі автори втрачають права власності на свій твір та не можуть його використовувати в будь-який спосіб.









