Розробка інтелектуальної системи розвитку соціальної стійкості міста
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.317717Ключові слова:
інтелектуальні системи, моделювання, розумні міста, соціально-економічний аналіз, машинне навчанняАнотація
В статті розглядається комплексний підхід до використання інтелектуальних систем у контексті розумних міст, який спрямований на підвищення їх соціальної стійкості в умовах зростаючої урбанізації та глобалізації.
Міста стикаються з викликами, пов’язаними з необхідністю оптимізації управління міськими ресурсами та покращенням якості життя мешканців, що вимагає інноваційних підходів до планування та використання передових технологій.
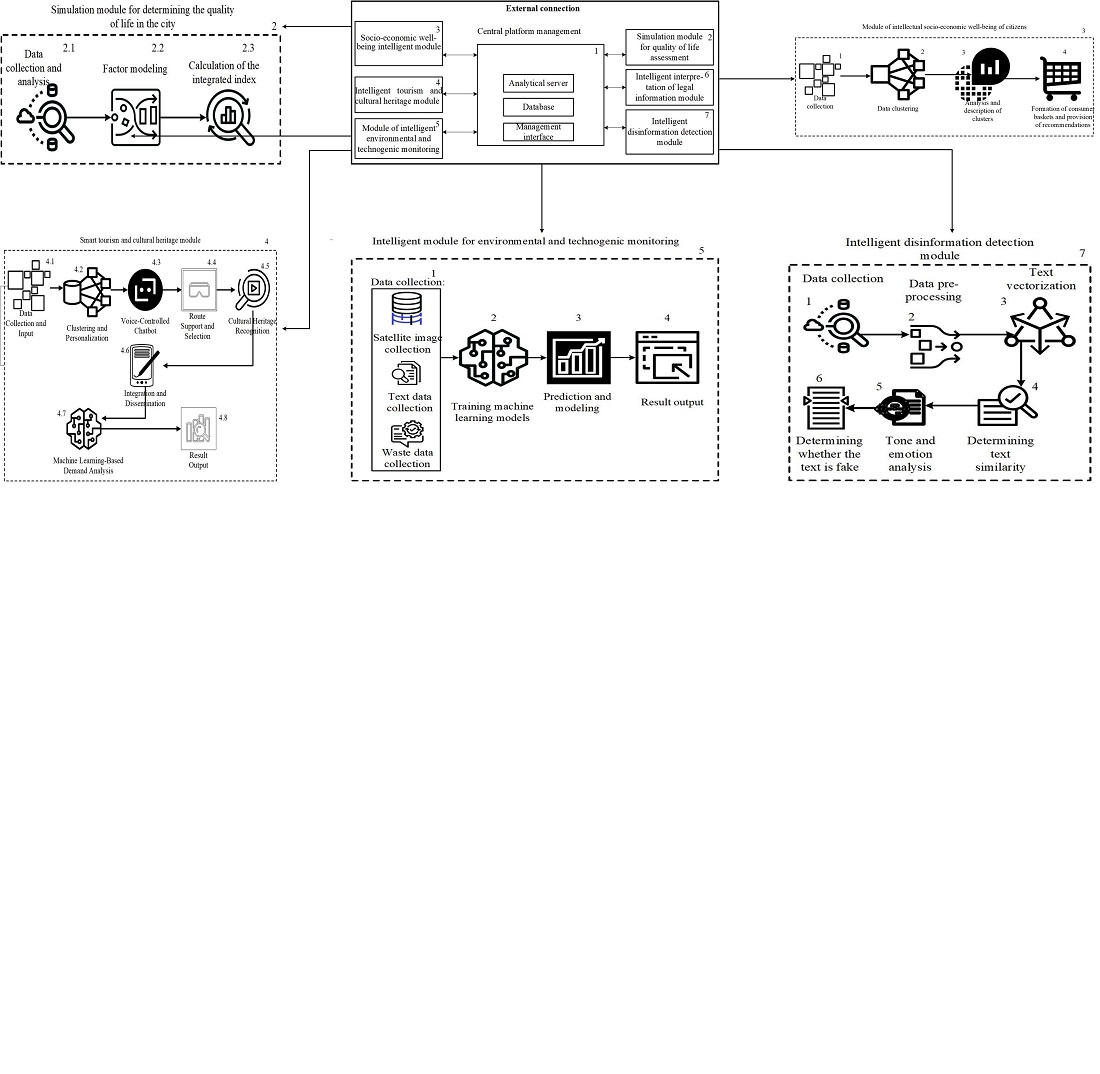
Запропонована архітектура інтелектуальної системи, інтегруючи шість модулів – моделювання якості життя, соціально-економічний аналіз, інтелектуальний туризм, моніторинг довкілля, юридичну інтерпретацію та виявлення дезінформації, продемонструвала підвищення продуктивності на 25–40 % в залежності від модуля.
Ефективність запропонованої системи пояснюється застосуванням передових алгоритмів машинного навчання та аналізу даних, що дозволяє скорочувати час вирішення критичних завдань та підвищувати адаптивність міської інфраструктури до майбутніх викликів.
Завдяки інтеграції інтелектуальних систем у міське управління, міста здобувають можливість ефективніше реагувати на поточні та прогнозовані соціальні та екологічні виклики, значно підвищуючи якість життя та екологічну стійкість.
Запропонована система може бути впроваджена у містах різного розміру та конфігурації, сприяючи довгостроковому соціально-економічному розвитку та екологічній стійкості. Ефективне впровадження системи зменшує витрати на управління містом до 30 %, одночасно знижуючи викиди CO2 на 10–15 %, що важливо у контексті боротьби зі змінами клімату
Посилання
- Khatibi, H., Wilkinson, S., Baghersad, M., Dianat, H., Ramli, H., Suhatril, M. et al. (2021). The resilient – smart city development: a literature review and novel frameworks exploration. Built Environment Project and Asset Management, 11 (4), 493–510. https://doi.org/10.1108/bepam-03-2020-0049
- Dey, P. K., Chowdhury, S., Abadie, A., Vann Yaroson, E., Sarkar, S. (2023). Artificial intelligence-driven supply chain resilience in Vietnamese manufacturing small- and medium-sized enterprises. International Journal of Production Research, 62 (15), 5417–5456. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2023.2179859
- Zhu, S., Li, D., Feng, H., Gu, T., Hewage, K., Sadiq, R. (2020). Smart city and resilient city: Differences and connections. WIREs Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 10 (6). https://doi.org/10.1002/widm.1388
- Arafah, Y., Winarso, H., Suroso, D. S. A. (2018). Towards Smart and Resilient City: A Conceptual Model. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 158, 012045. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/158/1/012045
- Xiong, K., Sharifi, A., He, B.-J. (2022). Resilient-Smart Cities: Theoretical Insights. Resilient Smart Cities, 93–118. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-95037-8_5
- Apostu, S. A., Vasile, V., Vasile, R., Rosak-Szyrocka, J. (2022). Do Smart Cities Represent the Key to Urban Resilience? Rethinking Urban Resilience. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19 (22), 15410. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192215410
- Sharifi, A., Khavarian-Garmsir, A. R., Kummitha, R. K. R. (2021). Contributions of Smart City Solutions and Technologies to Resilience against the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Literature Review. Sustainability, 13 (14), 8018. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13148018
- Balakrishnan, S., Elayan, S., Sykora, M., Solter, M., Feick, R., Hewitt, C. et al. (2023). Sustainable Smart Cities – Social Media Platforms and Their Role in Community Neighborhood Resilience – A Systematic Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20 (18), 6720. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20186720
- Megahed, N. A., Abdel-Kader, R. F. (2022). Smart Cities after COVID-19: Building a conceptual framework through a multidisciplinary perspective. Scientific African, 17, e01374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2022.e01374
- Petchamé, J., Iriondo, I., Korres, O., Paños-Castro, J. (2023). Digital transformation in higher education: A qualitative evaluative study of a hybrid virtual format using a smart classroom system. Heliyon, 9 (6), e16675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16675
- Rani, S., Kataria, A., Kumar, S., Tiwari, P. (2023). Federated learning for secure IoMT-applications in smart healthcare systems: A comprehensive review. Knowledge-Based Systems, 274, 110658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2023.110658
- Molnar, A. (2021). Smart cities education: An insight into existing drawbacks. Telematics and Informatics, 57, 101509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2020.101509
- Dai, Z., Xiong, J., Zhao, L., Zhu, X. (2023). Smart classroom learning environment preferences of higher education teachers and students in China: An ecological perspective. Heliyon, 9 (6), e16769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16769
- Gong, Z., Ji, J., Tong, P., Metwally, A. S. M., Dutta, A. K., Rodrigues, J. J. P. C., Mohamad, U. H. (2023). Smart urban planning: Intelligent cognitive analysis of healthcare data in cloud-based IoT. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 110, 108878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2023.108878
- Corsi, A., Florencio de Souza, F., Pagani, R. N., Kovaleski, J. L. (2022). Ultimate approach and technologies in smart healthcare: A broad systematic review focused on citizens. Smart Health, 26, 100310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smhl.2022.100310
- Garcia-Retuerta, D., Chamoso, P., Hernández, G., Guzmán, A. S. R., Yigitcanlar, T., Corchado, J. M. (2021). An Efficient Management Platform for Developing Smart Cities: Solution for Real-Time and Future Crowd Detection. Electronics, 10 (7), 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10070765
- Kaluarachchi, Y. (2022). Implementing Data-Driven Smart City Applications for Future Cities. Smart Cities, 5 (2), 455–474. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities5020025
- Chamoso, P., González-Briones, A., Rodríguez, S., Corchado, J. M. (2018). Tendencies of Technologies and Platforms in Smart Cities: A State‐of‐the‐Art Review. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2018 (1). https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/3086854
- Qi, L., Guo, J. (2019). Development of smart city community service integrated management platform. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 15 (6), 155014771985197. https://doi.org/10.1177/1550147719851975
- Samih, H. (2019). Smart cities and internet of things. Journal of Information Technology Case and Application Research, 21 (1), 3–12. https://doi.org/10.1080/15228053.2019.1587572
- Sarker, I. H. (2022). Smart City Data Science: Towards data-driven smart cities with open research issues. Internet of Things, 19, 100528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iot.2022.100528
- Ismagilova, E., Hughes, L., Dwivedi, Y. K., Raman, K. R. (2019). Smart cities: Advances in research – An information systems perspective. International Journal of Information Management, 47, 88–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2019.01.004
- Chamoso, P., González-Briones, A., De La Prieta, F., Venyagamoorthy, G. K., Corchado, J. M. (2020). Smart city as a distributed platform: Toward a system for citizen-oriented management. Computer Communications, 152, 323–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comcom.2020.01.059
- Huang, Y., Peng, H., Sofi, M., Zhou, Z., Xing, T., Ma, G., Zhong, A. (2022). The city management based on smart information system using digital technologies in China. IET Smart Cities, 4 (3), 160–174. https://doi.org/10.1049/smc2.12035
- Lipianina-Honcharenko, K., Wolff, C., Chyzhovska, Z., Sachenko, A., Lendiuk, T., Grodskyi, S. (2022). Intelligent Method for Forming the Consumer Basket. Information and Software Technologies, 221–231. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16302-9_17
- Krylov, V., Sachenko, A., Strubytskyi, P., Lendiuk, D., Lipyanina, H., Zahorodnia, D. et al. (2019). Multiple Regression Method for Analyzing the Tourist Demand Considering the Influence Factors. 2019 10th IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Data Acquisition and Advanced Computing Systems: Technology and Applications (IDAACS), 974–979. https://doi.org/10.1109/idaacs.2019.8924461
- Lipianina-Honcharenko, K., Savchyshyn, R., Sachenko, A., Chaban, A., Kit, I., Lendiuk, T. (2022). Concept of the Intelligent Guide with AR Support. International Journal of Computing, 271–277. https://doi.org/10.47839/ijc.21.2.2596
- Lipianina-Honcharenko, K., Sachenko, A., Kulyk, V., Savchyshyn, R., Provozin, O., Shchur, S., Kurpita, L. (2022). Simulation model structure of business processes for a product based on auralization technology. Computer Systems and Information Technologies, 4, 114–120. https://doi.org/10.31891/csit-2022-4-15
- Pisnyi, O., Kit, I., Lipianina-Honcharenko, K., Sieck, J., Sachenko, A., Dobrowolski, M., Sapozhnyk, G. (2023). AR Intelligent Real-time Method for Cultural Heritage Object Recognition. 2023 IEEE 5th International Conference on Advanced Information and Communication Technologies (AICT), 62–66. https://doi.org/10.1109/aict61584.2023.10452426
- Komar, M., Savchyshyn, R., Lipianina-Honcharenko, K., Osolinskyi, O. (2023). Intelligent method for counting cars from satellite images. Selected Papers of the III International Scientific Symposium “Intelligent Solutions” (IntSol-2023). Symposium Proceedings. Kyiv – Uzhhorod, 295–303. Available at: https://ceur-ws.org/Vol-3538/Short_1.pdf
- Lipianina-Honcharenko, K., Wolff, C., Sachenko, A., Kit, I., Zahorodnia, D. (2023). Intelligent Method for Classifying the Level of Anthropogenic Disasters. Big Data and Cognitive Computing, 7 (3), 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc7030157
- Schauer, S., Sieck, J., Lipianina-Honcharenko, K., Sachenko, A., Kit, I. (2023). Use of Digital Auralised 3D Models of Cultural Heritage Sites for Long-term Preservation. 2023 IEEE 12th International Conference on Intelligent Data Acquisition and Advanced Computing Systems: Technology and Applications (IDAACS), 708–712. https://doi.org/10.1109/idaacs58523.2023.10348637
- Lipianina-Honcharenko, K., Komar, M., Osolinskyi, O., Shymanskyi, V., Havryliuk, M., Semaniuk, V. (2023). Intelligent Waste-Volume Management Method in the Smart City Concept. Smart Cities, 7 (1), 78–98. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities7010004
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2024 Khrystyna Lipianina-Honcharenko, Myroslav Komar, Roman Madarash, Stanislav Novosad, Volodymyr Zhabiuk, Nazar Mykhalchuk, Kostiantyn Koshytskii, Dmytro Lendiuk, Nazar Melnyk, Oles Telikhovskyi

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.
Ліцензійний договір – це документ, в якому автор гарантує, що володіє усіма авторськими правами на твір (рукопис, статтю, тощо).
Автори, підписуючи Ліцензійний договір з ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР», мають усі права на подальше використання свого твору за умови посилання на наше видання, в якому твір опублікований. Відповідно до умов Ліцензійного договору, Видавець ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР» не забирає ваші авторські права та отримує від авторів дозвіл на використання та розповсюдження публікації через світові наукові ресурси (власні електронні ресурси, наукометричні бази даних, репозитарії, бібліотеки тощо).
За відсутності підписаного Ліцензійного договору або за відсутністю вказаних в цьому договорі ідентифікаторів, що дають змогу ідентифікувати особу автора, редакція не має права працювати з рукописом.
Важливо пам’ятати, що існує і інший тип угоди між авторами та видавцями – коли авторські права передаються від авторів до видавця. В такому разі автори втрачають права власності на свій твір та не можуть його використовувати в будь-який спосіб.









