Можливості інтеграції технологій штучного інтелекту у систему обліково-аналітичного забезпечення суб’єктів державного сектору
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.319051Ключові слова:
штучний інтелект, хмарні технології, автоматизація, облік, аналіз, державний секторАнотація
Об’єкт дослідження – технології штучного інтелекту в системі обліково-аналітичного забезпечення суб’єктів державного сектору.
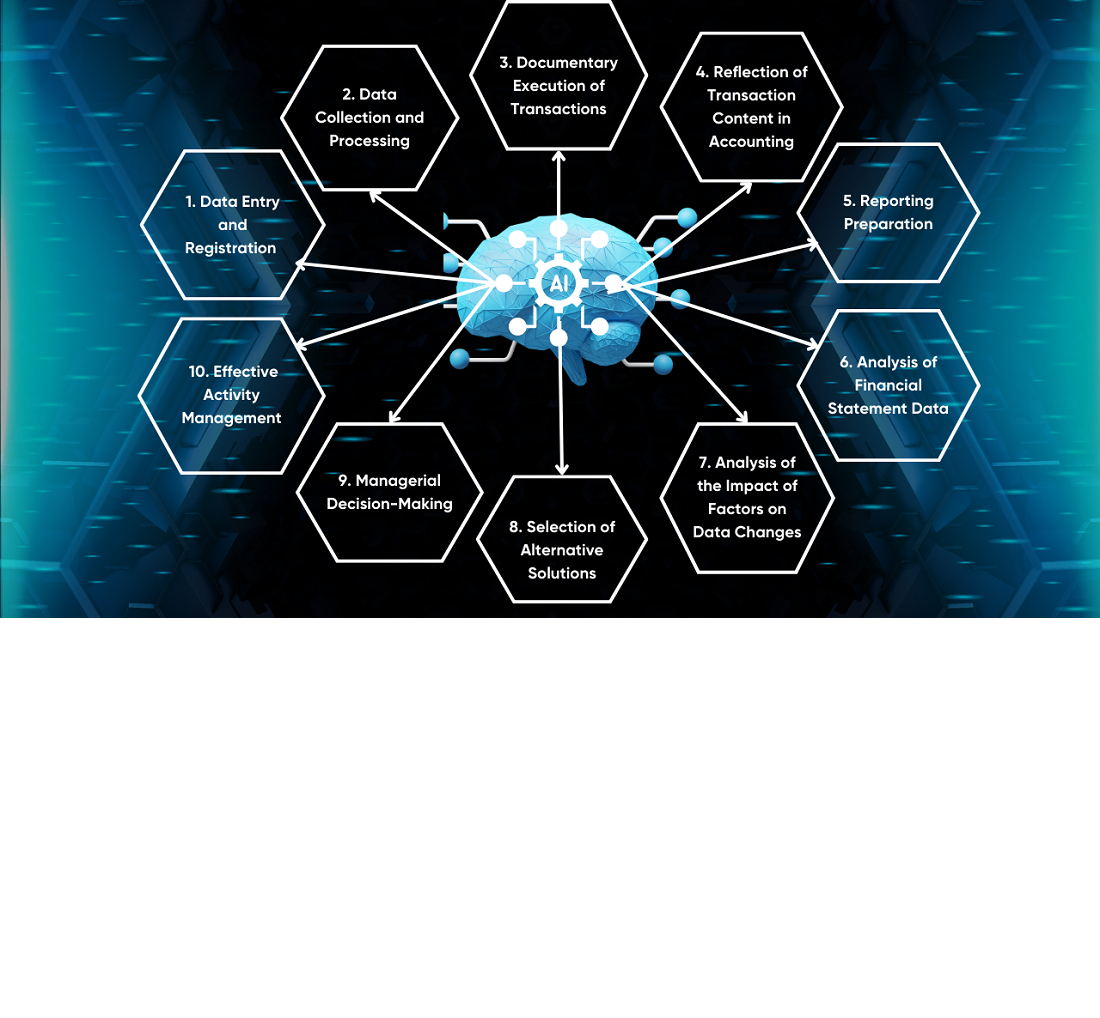
В досліджуванні вирішувались проблема щодо можливості інтеграції технологій штучного інтелекту в систему обліково-аналітичного забезпечення суб’єктів державного сектору. Визначено ключові відмінності між традиційною автоматизацією обліку та технологіями штучного інтелекту в системі обліково-аналітичного забезпечення. Проведено аналіз обсягів інвестицій на запровадження штучного інтелекту, в тому числі в систему бухгалтерського обліку. Встановлено, що за прогнозами на 2025 р. обсяги інвестиції у сферу штучного інтелекту для автоматизації обліку та звітності активно зростатимуть: США (45-50 млрд. дол), Китай (30-35 млрд. дол.), Німеччина: (15-18 млрд. дол), Японія (13-15 млрд. дол), Великобританія (12-15 млрд. дол). Проведено аналіз характеристик та вартості інтеграції сучасних технологій штучного інтелекту в систему обліково-аналітичного забезпечення. Рекомендаційним визначено хмарну технологію Zoho Books AI, яка за вартістю та властивостями найбільше підходить для інтеграції в систему обліково-аналітичного забезпечення суб’єктів державного сектору. Визначено ключові фактори впливу штучного інтелекту на автоматизацію системи обліково-аналітичного забезпечення, які призводять до економії часу на обробку документів, складання звітності та аналіз даних. За результатами розрахунків встановлено, що в результаті інтеграції технології Zoho Books AI у систему обліково-аналітичного забезпечення відбудеться зменшення часу на 2164 год/рік, що призведе до оптимізації державних коштів
Посилання
- Ubaldi, B., Fevre, E. M. L., Petrucci, E., Marchionni, P., Biancalana, C., Hiltunen, N. et al. (2019).State of the art in the use of emerging technologies in the public sector. Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development (OECD). https://doi.org/10.1787/932780bc-en
- Ulnicane, I., Eke, D. O., Knight, W., Ogoh, G., Stahl, B. C. (2021). Good governance as a response to discontents? Déjà vu, or lessons for AI from other emerging technologies. Interdisciplinary Science Reviews, 46 (1-2), 71–93. https://doi.org/10.1080/03080188.2020.1840220
- Androutsopoulou, A., Karacapilidis, N., Loukis, E., Charalabidis, Y. (2019). Transforming the communication between citizens and government through AI-guided chatbots. Government Information Quarterly, 36 (2), 358–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.giq.2018.10.001
- Fostolovych, V. (2022). Artificial intelligence in modern business: potential, current trends and prospects of integration in different spheres of economic activity and human life activity. Efektyvna ekonomika, 7. https://doi.org/10.32702/2307-2105.2022.7.4
- AI In Accounting Market Size & Share Analysis - Growth Trends & Forecasts (2024 - 2029). Available at: https://www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/artificial-intelligence-in-accounting-market
- Sun, T. Q., Medaglia, R. (2019). Mapping the challenges of Artificial Intelligence in the public sector: Evidence from public healthcare. Government Information Quarterly, 36 (2), 368–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.giq.2018.09.008
- Cao, P. (2023). Research on the impact of artificial intelligence-based e-commerce personalization on traditional accounting methods. International Journal of Intelligent Networks, 4, 193–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijin.2023.07.004
- Abdullah, A. A. H., Almaqtari, F. A. (2024). The impact of artificial intelligence and Industry 4.0 on transforming accounting and auditing practices. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 10 (1), 100218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joitmc.2024.100218
- Luthfiani, A. D. (2024). The Artificial Intelligence Revolution in Accounting and Auditing: Opportunities, Challenges, and Future Research Directions. Journal of Applied Business, Taxation and Economics Research, 3 (5), 516–530. https://doi.org/10.54408/jabter.v3i5.290
- Hussin, N. A. K. M., Bukhari, N. A. N. M., Hashim, N. H. A. N., Bahari, S. N. A. S., Ali, M. M. (2024). The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on the Accounting Profession: A Concept Paper. Business Management and Strategy, 15 (1), 34. https://doi.org/10.5296/bms.v15i1.21620
- Norzelan, N. A., Mohamed, I. S., Mohamad, M. (2024). Technology acceptance of artificial intelligence (AI) among heads of finance and accounting units in the shared service industry. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 198, 123022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2023.123022
- Panda, K. (2024). Artificial Intelligence-based Analysis of Change in Public Finance between US and International Markets. 2024 IEEE International Conference on Computing, Power and Communication Technologies (IC2PCT), 1234–1238. https://doi.org/10.1109/ic2pct60090.2024.10486276
- Furmanchuk, O. (2023). The role of state finance audit in the system of accounting and analytical support of the state funds management system. Economics of Development, 22 (4), 34–42. https://doi.org/10.57111/econ/4.2023.34
- Odonkor, B., Kaggwa, S., Uwaoma, P. U., Hassan, A. O., Farayola, O. A. (2024). The impact of AI on accounting practices: A review: Exploring how artificial intelligence is transforming traditional accounting methods and financial reporting. World Journal of Advanced Research and Reviews, 21 (1), 172–188. https://doi.org/10.30574/wjarr.2024.21.1.2721
- Surya, L. (2019). Artificial intelligence in public sector. Novateur publications international journal of innovations in engineering research and technology, 6 (8), 7–12. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Lakshmisri-Surya/publication/349310325_ARTIFICIAL_INTELLIGENCE_IN_PUBLIC_SECTOR/links/602a01c992851c4ed5718576/ARTIFICIAL-INTELLIGENCE-IN-PUBLIC-SECTOR.pdf
- Mann, A. (2019). How AI is transforming the jobs of accountants, Accounting Today. Available at: https://www.accountingtoday.com/opinion/how-ai-is-transforming-the-jobs-of-accountants
- Madiega, Т., Ilnicki, R. (2024). AI investment: EU and global indicators. EPRS | European Parliamentary Research Service. Available at: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/RegData/etudes/ATAG/2024/760392/EPRS_ATA(2024)760392_EN.pdf
- Аrtificial intelligence: current and future usage within investment management (2024). Final Report from the Technology Working Group. Available at: https://www.theia.org/sites/default/files/2024-10/Technology%20Working%20Group%20AI%20Report%20Oct%202024.pdf
- Artificial intelligence in UK financial services - 2024. The Bank of England and Financial Conduct Authority conducted a third survey of artificial intelligence and machine learning in UK financial services. Available at: https://www.bankofengland.co.uk/report/2024/artificial-intelligence-in-uk-financial-services-2024
- Sharma, A.-M. (2024). Artificial Intelligence News. Available at: https://www.gtai.de/en/invest/industries/digital-economy/artificial-intelligence-news-august-2024-1812588
- AI Guidelines for Business Ver1.0 (2024). Available at: https://www.meti.go.jp/shingikai/mono_info_service/ai_shakai_jisso/pdf/20240419_9.pdf
- Madakam, S., Holmukhe, R. M., Jaiswal, D. K. (2019). The Future Digital Work Force: Robotic Process Automation (RPA). Journal of Information Systems and Technology Management, 16. https://doi.org/10.4301/s1807-1775201916001
- Liang, Y., Jiang, G., He, Y. (2024). Integrating AI with Financial Accounting Processes: Innovations and Challenges. International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology, 3 (3), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.62051/ijcsit.v3n3.01
- How Much Does it Cost to Build a Custom AI-based Accounting Software? (2024). Available at: https://appinventiv.com/blog/ai-accounting-software-development-cost/
- Nykyforak, I., Dutchak, I., Roshko, N. (2024). Innovations in accounting in Ukraine: the study of the impact of new developments. Economics. Finances. Law, 2/2024, 67–71. https://doi.org/10.37634/efp.2024.2.14
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2024 Tetiana Larikova, Pavlo Ivankov, Liudmyla Novichenko, Kydysiuk Khrystyna

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.
Ліцензійний договір – це документ, в якому автор гарантує, що володіє усіма авторськими правами на твір (рукопис, статтю, тощо).
Автори, підписуючи Ліцензійний договір з ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР», мають усі права на подальше використання свого твору за умови посилання на наше видання, в якому твір опублікований. Відповідно до умов Ліцензійного договору, Видавець ПП «ТЕХНОЛОГІЧНИЙ ЦЕНТР» не забирає ваші авторські права та отримує від авторів дозвіл на використання та розповсюдження публікації через світові наукові ресурси (власні електронні ресурси, наукометричні бази даних, репозитарії, бібліотеки тощо).
За відсутності підписаного Ліцензійного договору або за відсутністю вказаних в цьому договорі ідентифікаторів, що дають змогу ідентифікувати особу автора, редакція не має права працювати з рукописом.
Важливо пам’ятати, що існує і інший тип угоди між авторами та видавцями – коли авторські права передаються від авторів до видавця. В такому разі автори втрачають права власності на свій твір та не можуть його використовувати в будь-який спосіб.









