Real-time prediction of higher heating value of coal in coal-fired power plants using operating parameters
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.320573Keywords:
predictive modeling, coal-fired power plant, higher heating value, real-time predictionsAbstract
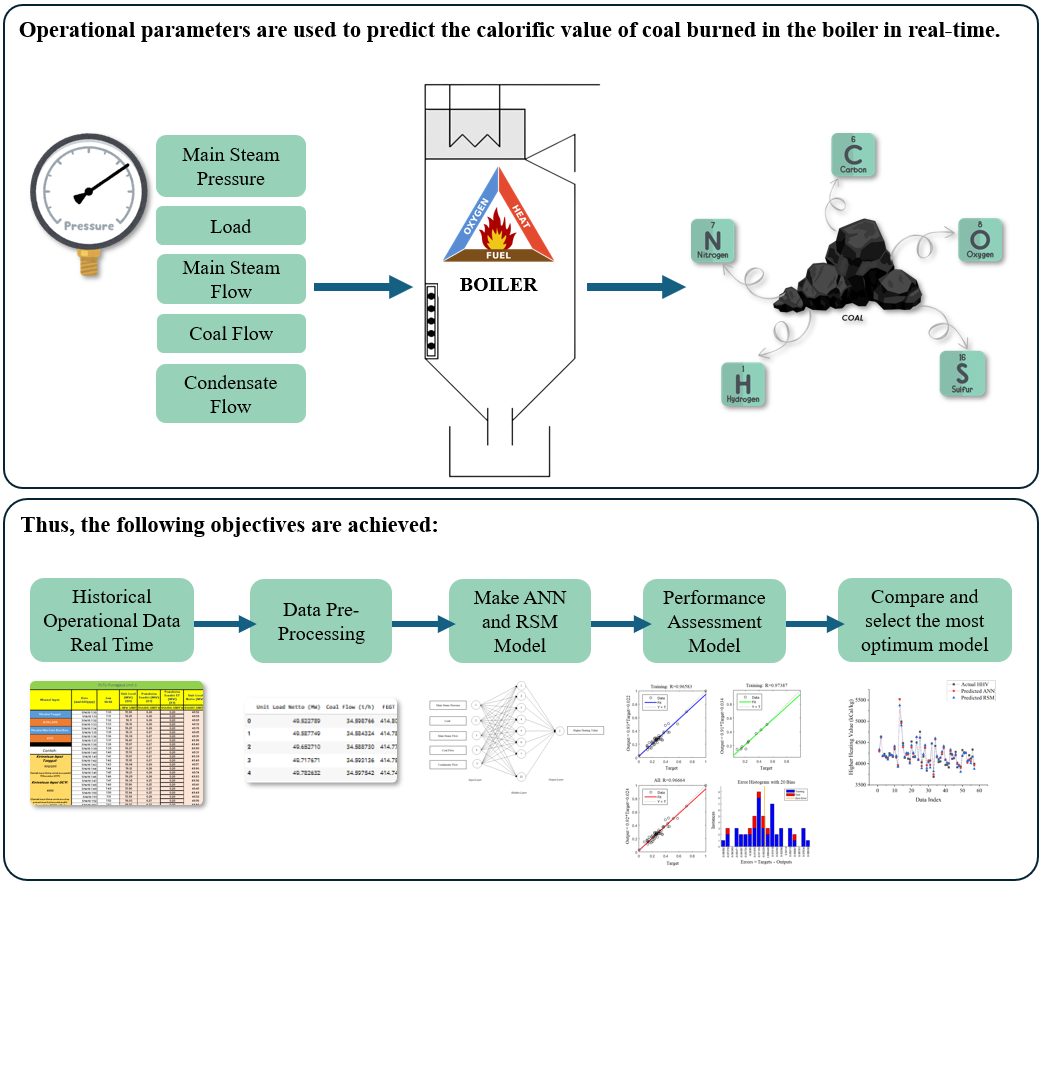
This study introduces a novel approach to estimate the higher heating value of coal using real-time operational data from coal-fired power plants, addressing a significant gap in conventional methodologies. Traditionally, coal quality assessments involve extensive laboratory testing, which is impractical for real-time applications. This research develops a practical alternative by leveraging operational parameters such as main steam pressure, temperature, load, condensate flow, and coal flow as indicators of coal’s calorific value.
The model developed in this study bypasses the time-consuming processes associated with traditional methods, enabling real-time estimation of coal’s higher heating value. Empirical validation shows the model’s high predictive accuracy, evidenced by an R2 value of 0.9666, indicating that it accounts for approximately 96.66 % of the variance in higher heating value. These results are supported by low mean square error and root mean square error values, underscoring superior performance compared to conventional methods.
The effective use of operational data not only addresses the challenge of real-time higher heating value estimation but also optimizes the combustion process and enhances power plant efficiency. The practical application of these findings is pivotal for real-time coal quality control and plant performance management, providing a crucial tool for optimizing energy management.
In conclusion, this research successfully develops and validates a data-driven approach for the real-time prediction of coal’s calorific value. This approach holds potential for widespread application, thereby improving energy management and operational efficiency in an industry that remains a major global energy provider
References
- References
- G. Guan, "Clean coal technologies in Japan: A review," Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, vol. 25, no. 6, pp. 689-697, 2017/06/01/ 2017, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2016.12.008.
- A. K. Majumder, R. Jain, P. Banerjee, and J. P. Barnwal, "Development of a new proximate analysis based correlation to predict calorific value of coal," Fuel, vol. 87, no. 13, pp. 3077-3081, 2008/10/01/ 2008, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2008.04.008.
- A. J. Callejón-Ferre, J. Carreño-Sánchez, F. J. Suárez-Medina, J. Pérez-Alonso, and B. Velázquez-Martí, "Prediction models for higher heating value based on the structural analysis of the biomass of plant remains from the greenhouses of Almería (Spain)," Fuel, vol. 116, pp. 377-387, 2014/01/15/ 2014, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2013.08.023.
- A. V. Akkaya, "Proximate analysis based multiple regression models for higher heating value estimation of low rank coals," Fuel Processing Technology, vol. 90, no. 2, pp. 165-170, 2009/02/01/ 2009, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2008.08.016.
- A. V. Akkaya, "Predicting Coal Heating Values Using Proximate Analysis via a Neural Network Approach," Energy Sources, Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects, vol. 35, no. 3, pp. 253-260, 2013/02/01 2013, doi: 10.1080/15567036.2010.509090.
- K. Büyükkanber, H. Haykiri-Acma, and S. Yaman, "Calorific value prediction of coal and its optimization by machine learning based on limited samples in a wide range," Energy, vol. 277, p. 127666, 2023/08/15/ 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2023.127666.
- P. J. García–Nieto, E. García–Gonzalo, and J. P. Paredes–Sánchez, "Estimation of the coal higher heating value for energy systems relied on ultimate analysis with machine learning techniques," Fuel, vol. 357, p. 130037, 2024/02/01/ 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2023.130037.
- J. Chen, Y. He, Y. Liang, W. Wang, and X. Duan, "Estimation of gross calorific value of coal based on the cubist regression model," Scientific Reports, vol. 14, no. 1, p. 23176, 2024/10/05 2024, doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74469-3.
- C. Qian, Q. Li, Z. Zhang, X. Wang, J. Hu, and W. Cao, "Prediction of higher heating values of biochar from proximate and ultimate analysis," Fuel, vol. 265, p. 116925, 2020/04/01/ 2020, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.116925.
- A. S. Noushabadi, A. Dashti, F. Ahmadijokani, J. Hu, and A. H. Mohammadi, "Estimation of higher heating values (HHVs) of biomass fuels based on ultimate analysis using machine learning techniques and improved equation," Renewable Energy, vol. 179, pp. 550-562, 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2021.07.003.
- M. Sözer, H. Haykiri-Acma, and S. Yaman, "Prediction of Calorific Value of Coal by Multilinear Regression and Analysis of Variance," Journal of Energy Resources Technology, vol. 144, no. 1, 2021, doi: 10.1115/1.4050880.
- T. A. Munshi, L. N. Jahan, M. F. Howladar, and M. Hashan, "Prediction of gross calorific value from coal analysis using decision tree-based bagging and boosting techniques," Heliyon, vol. 10, no. 1, 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23395.
- X. Gao, B. Jia, G. Li, and X. Ma, "Calorific Value Forecasting of Coal Gangue with Hybrid Kernel Function–Support Vector Regression and Genetic Algorithm," Energies, vol. 15, no. 18, doi: 10.3390/en15186718.
- M. Dzikuć, P. Kuryło, R. Dudziak, S. Szufa, M. Dzikuć, and K. Godzisz, "Selected Aspects of Combustion Optimization of Coal in Power Plants," Energies, vol. 13, no. 9, doi: 10.3390/en13092208.
- A. Reza, ASME PTC 6 Steam Turbine. 2020.
- M. A. Bolarinwa and F.-G. Udensi, "Operational Performance Analysis of Generating Power Plant," European Journal of Energy Research, vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 44-56, 06/23 2024, doi: 10.24018/ejenergy.2024.4.2.144.
- R. Jradi, C. Marvillet, and M. R. Jeday, "Multi-objective optimization and performance assessment of response surface methodology (RSM), artificial neural network (ANN) and adaptive neuro-fuzzy interfence system (ANFIS) for estimation of fouling in phosphoric acid/steam heat exchanger," Applied Thermal Engineering, vol. 248, p. 123255, 2024/07/01/ 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2024.123255.
- A. Jankovic, G. Chaudhary, and F. Goia, "Designing the design of experiments (DOE) – An investigation on the influence of different factorial designs on the characterization of complex systems," Energy and Buildings, vol. 250, p. 111298, 2021/11/01/ 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2021.111298.
- W. A. Jensen, "Response Surface Methodology: Process and Product Optimization Using Designed Experiments 4th edition," Journal of Quality Technology, vol. 49, no. 2, pp. 186-188, 2017/04/01 2017, doi: 10.1080/00224065.2017.11917988.
- N. Draper, Applied regression analysis. McGraw-Hill. Inc, 1998.
- R. Rizal, F. Wahyuni, J. Julian, Nasruddin, and F. Yulia, "Optimal design and modelling of sustainable bio-catalytic enzyme for wastewater treatment using response surface methodology and artificial neural network," Energy Sources, Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects, vol. 46, no. 1, pp. 5254-5273, 2024/12/31 2024, doi: 10.1080/15567036.2024.2332468.
- V. Vendittoli, W. Polini, M. S. J. Walter, and S. Geißelsöder, "Using Bayesian Regularized Artificial Neural Networks to Predict the Tensile Strength of Additively Manufactured Polylactic Acid Parts," Applied Sciences, vol. 14, no. 8, doi: 10.3390/app14083184.
- S. S. Haykin, Neural Networks and Learning Machines. Pearson, 2009.
- R. Jradi, C. Marvillet, and M. R. Jeday, "Modeling and comparative study of heat exchangers fouling in phosphoric acid concentration plant using experimental data," Heat and Mass Transfer, vol. 56, no. 9, pp. 2653-2666, 2020/09/01 2020, doi: 10.1007/s00231-020-02888-9.
- K. Yotov, E. Hadzhikolev, and S. Hadzhikoleva, "Determining the Number of Neurons in Artificial Neural Networks for Approximation, Trained with Algorithms Using the Jacobi Matrix," TEM Journal, vol. 9, pp. 1320-1329, 11/27 2020, doi: 10.18421/TEM94-02.
- A. Amato and V. Di Lecce, "Data preprocessing impact on machine learning algorithm performance," vol. 13, no. 1, 2023, doi: doi:10.1515/comp-2022-0278.
- R. Muhammad, A. Rahman, and M. Jamil, "A Linear Regression Modeling Analysis of the Energy, Water, and Chemical Consumption in the Operating Configuration at 740 MW Priok Combined Cycle Power Plant," Journal of Mechanical Design and Testing, vol. 6, p. 27, 06/30 2024, doi: 10.22146/jmdt.97748.
- B. Padmaja and V. M. Manikandan, "A Novel Prediction Error Histogram Shifting-based Reversible Data Hiding Scheme for Medical Image Transmission," in 2021 4th International Conference on Security and Privacy (ISEA-ISAP), 27-30 Oct. 2021 2021, pp. 1-6, doi: 10.1109/ISEA-ISAP54304.2021.9688572.
- K. Suphawan, R. Kardkasem, and K. Chaisee, "A Gaussian Process Regression Model for Forecasting Stock Exchange of Thailand," Trends in Sciences, vol. 19, no. 6, p. 3045, 03/03 2022, doi: 10.48048/tis.2022.3045.
- M. Gasser, A. Naguib, M. Abdelhafiz, S. Elnekhaily, and O. Mahmoud, "Artificial Neural Network Model to Predict Filtrate Invasion of Nanoparticle-Based Drilling Fluids," Trends in Sciences, vol. 20, no. 5, p. 6736, 03/08 2023, doi: 10.48048/tis.2023.6736.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Enrico Gultom, Dimas Angga Fakhri Muzhoffar, Muhammad Arif Budiyanto, Achmad Riadi, Andy Rivai

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.








